
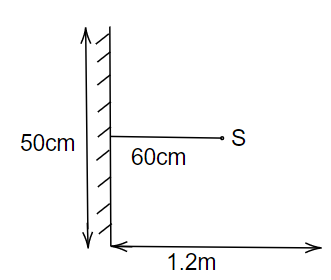
A point source of light S, placed at a distance of 60 cm in front of the center of the plane mirror of width 50 cm, hangs vertically on a wall. A man walks in front of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror at a distance of 1.2 m from it (see in the figure). Find the distance between the extreme points where he can see the image of the light source in the mirror.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The mirrors are polished surfaces, which are coated on one side with Mercury so that they can reflect most of the light that falls on them. A plane mirror always forms a virtual image and the virtual image is produced when the light rays from a source don’t cross or meet at a point to form an image.
Complete step by step solution:
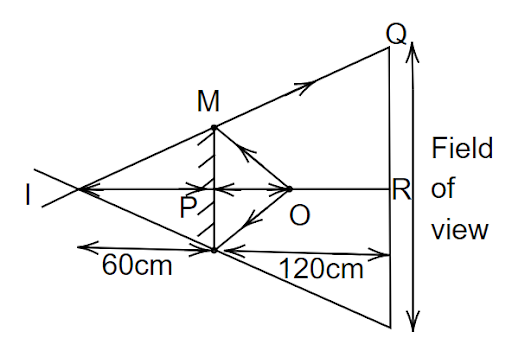
Image: A mirror placed at a distance of 60 cm from the source.
Consider a line parallel to the mirror, where a man is moving on it and a light source is placed at a distance of 60 cm and the length of the mirror is 50 cm. we need to find the distance between the extreme points where he can see the image of the light source in the mirror. From the figure, consider the triangle IMP and IQR which are similar to each other. Therefore, we can write as,
\[\dfrac{{QR}}{{MP}} = \dfrac{{IR}}{{IP}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{QR}}{{25}} = \dfrac{{180}}{{60}}\]
\[\Rightarrow QR = 75\,cm\]
Then in order to obtain the field of view that is, the distance between the extreme points where he can see the image of the light source in the mirror is,
The field of view \[ = 2 \times QR\]
The field of view \[ = 2 \times 75\]
The field of view \[ = 150\,cm\]
Therefore, the distance between the extreme points where he can see the image of the light source in the mirror is 150 cm.
Note:Suppose when a light ray falls on a surface, it can undergo one of the three phenomena, namely, reflection, refraction, and absorption. Most of the light gets absorbed when a ray of light falls on a normal surface. Based on the reflecting surface, we can classify mirrors as convex mirrors, concave mirrors, or plane mirrors.
Complete step by step solution:

Image: A mirror placed at a distance of 60 cm from the source.
Consider a line parallel to the mirror, where a man is moving on it and a light source is placed at a distance of 60 cm and the length of the mirror is 50 cm. we need to find the distance between the extreme points where he can see the image of the light source in the mirror. From the figure, consider the triangle IMP and IQR which are similar to each other. Therefore, we can write as,
\[\dfrac{{QR}}{{MP}} = \dfrac{{IR}}{{IP}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{QR}}{{25}} = \dfrac{{180}}{{60}}\]
\[\Rightarrow QR = 75\,cm\]
Then in order to obtain the field of view that is, the distance between the extreme points where he can see the image of the light source in the mirror is,
The field of view \[ = 2 \times QR\]
The field of view \[ = 2 \times 75\]
The field of view \[ = 150\,cm\]
Therefore, the distance between the extreme points where he can see the image of the light source in the mirror is 150 cm.
Note:Suppose when a light ray falls on a surface, it can undergo one of the three phenomena, namely, reflection, refraction, and absorption. Most of the light gets absorbed when a ray of light falls on a normal surface. Based on the reflecting surface, we can classify mirrors as convex mirrors, concave mirrors, or plane mirrors.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




