
A plano-convex then lens of focal length \[10{\rm{ }}cm\] is silvered at its plane surface. The distance \[d\;\] are which an object must be kept in order to get its image on itself is:
1. \[5{\rm{ }}cm\]
2. \[20{\rm{ }}cm\]
3. \[10{\rm{ }}cm\]
4. \[2.5{\rm{ }}cm\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: First of all to solve this question you need to understand that this is the question of optical physics where we study mirrors and images from those. In this question, it has been asked that if we want images exactly on the place where the object is kept then where should we put them or at what distance the object should be placed. We have to draw ray diagram for obtaining answer to this question. For that you must know all the concepts that are used in Ray optics while drawing Ray diagrams.
Complete answer:
We know the rules of drawing a Ray diagram, by using those rules we are going to draw a diagram below:
1. Plano-concave mirror
2. An object should be placed at some distance, let us consider at the focus because the focus is always the first priority to use while drawing the Ray diagram.
3. Here, the plane side of the plano-concave lens is silvered so that the ray must get reflected from that surface.
Now, let AB be the principle axis and also the plane of the given lens, Let FF’ be the object kept on the focus at \[10{\rm{ }}cm\]as mentioned in point 2. Now let us draw a ray diagram as shown in fig below:
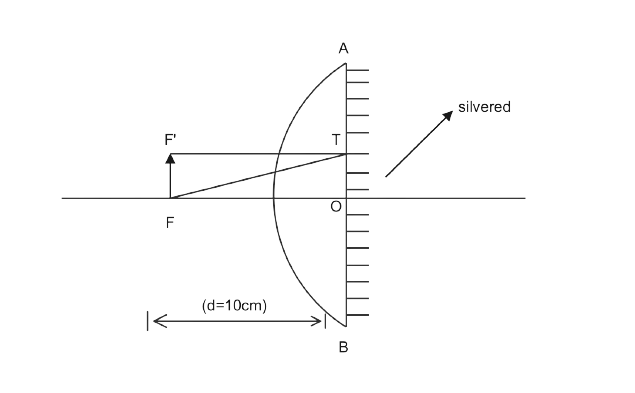
Here, in the above diagram, we have taken rays from F to T and get reflected towards TF’ also from F’T also gets reflected on the same line from the plane. Because, when the rays are drawn on the plane mirror that ray will get reflected into a straight line and becomes right-angled to the principle axis. Hence, the image that we want can only be in the same place as that of the object if the object is placed on focus otherwise not. Focus is at \[10{\rm{ }}cm\].
Therefore, at a of distance 10 cm an object must be kept in order to get its image on itself. Thus, option 3 is the right answer.
Note: It is very important to know about all the concepts of ray diagram to draw one properly, Ray optics is very interesting and is a different kind of world. Just remember that concept should be concrete to solve this type of questions.
Complete answer:
We know the rules of drawing a Ray diagram, by using those rules we are going to draw a diagram below:
1. Plano-concave mirror
2. An object should be placed at some distance, let us consider at the focus because the focus is always the first priority to use while drawing the Ray diagram.
3. Here, the plane side of the plano-concave lens is silvered so that the ray must get reflected from that surface.
Now, let AB be the principle axis and also the plane of the given lens, Let FF’ be the object kept on the focus at \[10{\rm{ }}cm\]as mentioned in point 2. Now let us draw a ray diagram as shown in fig below:

Here, in the above diagram, we have taken rays from F to T and get reflected towards TF’ also from F’T also gets reflected on the same line from the plane. Because, when the rays are drawn on the plane mirror that ray will get reflected into a straight line and becomes right-angled to the principle axis. Hence, the image that we want can only be in the same place as that of the object if the object is placed on focus otherwise not. Focus is at \[10{\rm{ }}cm\].
Therefore, at a of distance 10 cm an object must be kept in order to get its image on itself. Thus, option 3 is the right answer.
Note: It is very important to know about all the concepts of ray diagram to draw one properly, Ray optics is very interesting and is a different kind of world. Just remember that concept should be concrete to solve this type of questions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




