
A pipe of length $85cm$ is closed from one end. Find the number of possible natural oscillations of the air column in the pipe whose frequencies lie below $1250Hz$. The velocity of sound in air is $340m/s$.
(A) $6$
(B) $4$
(C) $12$
(D) $8$
Answer
240k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to use the formula for the frequency of the sound in a pipe which is closed at one end. From there we can find out the values of the possible frequencies.
Formula used: The formula used to solve this question is given by
$\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$, here $\lambda $ is the wavelength, $v$ is the velocity, and $f$ is the frequency of a wave.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that at the open end of a pipe, an antinode is formed. Also, at the closed end, a node is formed. So for the fundamental frequency, there will be one node and one antinode along the length of the pipe. We know that the distance between the node and the anti node is equal to one fourth of the wavelength. So the length of the pipe is
\[L = \dfrac{\lambda }{4}\]
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 4L$
We know that $\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$. So we have
$\dfrac{v}{{{f_0}}} = 4L$
\[ \Rightarrow {f_0} = \dfrac{v}{{4L}}\] (1)
According to the question, $v = 340m/s$ and $L = 85cm = 0.85m$. Putting these above, we get
${f_0} = \dfrac{{340}}{{4 \times 0.85}}$
On solving we get
${f_0} = 100Hz$ (2)
So the fundamental frequency is equal to $100Hz$.
Now, for the first overtone frequency, there will be two nodes and two antinodes, as shown below.
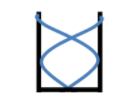
So the length of the pipe in this case is
\[L = \dfrac{{3\lambda }}{4}\]
Substituting $\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$, we get
$L = \dfrac{{3v}}{{4{f_1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {f_1} = \dfrac{{3v}}{{4L}}$
From (1)
${f_1} = 3{f_0}$
Similarly, we can prove that the frequency of the nth overtone is given by
${f_n} = \left( {2n + 1} \right){f_0}$
From (2)
${f_n} = \left( {2n + 1} \right)100Hz$
According to the question, we have to determine the number of oscillations of air below the frequency of $1250Hz$. Therefore, we substitute ${f_n} = 1250Hz$ above to get
$1250 = \left( {2n + 1} \right)100$
$ \Rightarrow 2n + 1 = 12.5$
On solving we get
$n = 5.75$
So the greatest number of overtone frequencies of oscillations of the air is equal to $5$. But there is also natural frequency which is not included in this calculation. So on adding it we get a total of $6$ possible oscillations of the air below the given frequency of $1250Hz$.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: We should not forget to include the natural frequency in your final count of the oscillations. This is because the fundamental mode of oscillation is also a valid oscillation of the air column inside the pipe.
Formula used: The formula used to solve this question is given by
$\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$, here $\lambda $ is the wavelength, $v$ is the velocity, and $f$ is the frequency of a wave.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that at the open end of a pipe, an antinode is formed. Also, at the closed end, a node is formed. So for the fundamental frequency, there will be one node and one antinode along the length of the pipe. We know that the distance between the node and the anti node is equal to one fourth of the wavelength. So the length of the pipe is
\[L = \dfrac{\lambda }{4}\]
$ \Rightarrow \lambda = 4L$
We know that $\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$. So we have
$\dfrac{v}{{{f_0}}} = 4L$
\[ \Rightarrow {f_0} = \dfrac{v}{{4L}}\] (1)
According to the question, $v = 340m/s$ and $L = 85cm = 0.85m$. Putting these above, we get
${f_0} = \dfrac{{340}}{{4 \times 0.85}}$
On solving we get
${f_0} = 100Hz$ (2)
So the fundamental frequency is equal to $100Hz$.
Now, for the first overtone frequency, there will be two nodes and two antinodes, as shown below.

So the length of the pipe in this case is
\[L = \dfrac{{3\lambda }}{4}\]
Substituting $\lambda = \dfrac{v}{f}$, we get
$L = \dfrac{{3v}}{{4{f_1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow {f_1} = \dfrac{{3v}}{{4L}}$
From (1)
${f_1} = 3{f_0}$
Similarly, we can prove that the frequency of the nth overtone is given by
${f_n} = \left( {2n + 1} \right){f_0}$
From (2)
${f_n} = \left( {2n + 1} \right)100Hz$
According to the question, we have to determine the number of oscillations of air below the frequency of $1250Hz$. Therefore, we substitute ${f_n} = 1250Hz$ above to get
$1250 = \left( {2n + 1} \right)100$
$ \Rightarrow 2n + 1 = 12.5$
On solving we get
$n = 5.75$
So the greatest number of overtone frequencies of oscillations of the air is equal to $5$. But there is also natural frequency which is not included in this calculation. So on adding it we get a total of $6$ possible oscillations of the air below the given frequency of $1250Hz$.
Hence, the correct answer is option A.
Note: We should not forget to include the natural frequency in your final count of the oscillations. This is because the fundamental mode of oscillation is also a valid oscillation of the air column inside the pipe.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26




