
A nitrogen-containing organic compound gave an oily liquid on heating with bromine and potassium hydroxide solution. On shaking the product with acetic anhydride, an antipyretic drug was obtained. The reactions indicate that the starting compound is:
A. Aniline
B. Benzamide
C. Acetamide
D. Nitrobenzene
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: All the options are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. Aniline, benzamide, acetamide, and nitrobenzene have amine, amide, amide, and nitro functional groups respectively.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
On heating with bromine and potassium hydroxide, the Hoffmann bromamide reaction takes place. In this reaction, primary amide gets degraded and forms primary amine. So first, find the compounds with amide functional groups from the given options.
Here, in the options, the first options B and C contain an amide functional group. In the question, it is mentioned that an oily compound is formed meaning it is non-volatile and aromatic compounds are non-volatile. Of the B and C options, only the B option i.e., benzamide is aromatic. And also, acetamide is solid, not an oily compound. So, the starting compound is benzamide.
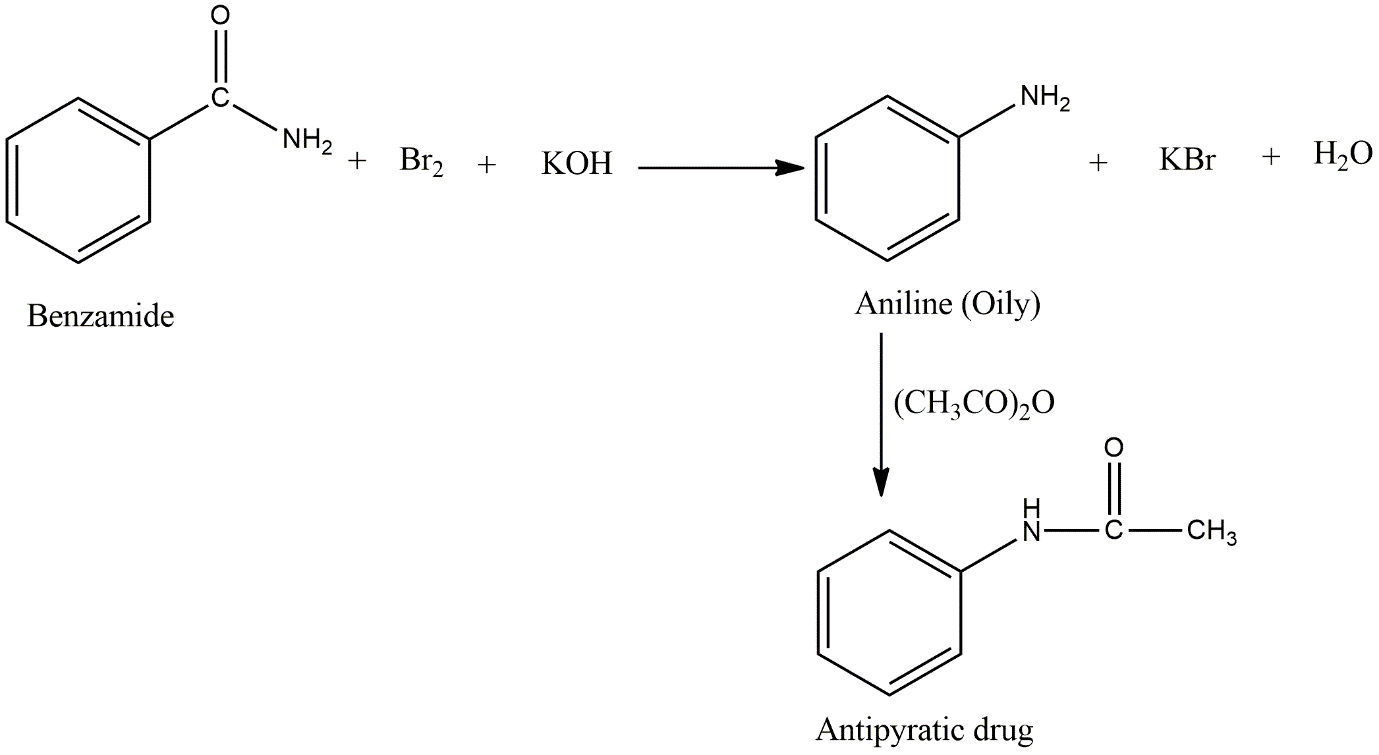
Image:Hofmann bromamide reaction of benzamide and formation of antipyretic drug.
In this reaction product without a carbonyl functional group and hence benzamide forms aniline which is aromatic in nature and oily. Aniline then further reacted with acetic anhydride to give acetanilide which is an antipyretic drug.
So, the option B is correct.
Note: Antipyretic drugs are used in fever. Some examples are acetanilide, ibuprofen, and acetaminophen. Physical properties of compounds are equally important to understanding the chemistry of reactions. Here, aromatic compounds are non-volatile compounds because of the conjugation present in the system making the system stable.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
On heating with bromine and potassium hydroxide, the Hoffmann bromamide reaction takes place. In this reaction, primary amide gets degraded and forms primary amine. So first, find the compounds with amide functional groups from the given options.
Here, in the options, the first options B and C contain an amide functional group. In the question, it is mentioned that an oily compound is formed meaning it is non-volatile and aromatic compounds are non-volatile. Of the B and C options, only the B option i.e., benzamide is aromatic. And also, acetamide is solid, not an oily compound. So, the starting compound is benzamide.

Image:Hofmann bromamide reaction of benzamide and formation of antipyretic drug.
In this reaction product without a carbonyl functional group and hence benzamide forms aniline which is aromatic in nature and oily. Aniline then further reacted with acetic anhydride to give acetanilide which is an antipyretic drug.
So, the option B is correct.
Note: Antipyretic drugs are used in fever. Some examples are acetanilide, ibuprofen, and acetaminophen. Physical properties of compounds are equally important to understanding the chemistry of reactions. Here, aromatic compounds are non-volatile compounds because of the conjugation present in the system making the system stable.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




