
A light disc made of aluminium (a nonmagnetic material) is kept horizontally and is free to rotate about its axis as shown in the figure. A strong magnet is held vertically at a point above the disc away from its axis. On revolving the magnet about the axis of the disc, what happens to the disc? (The figure is schematic and not drawn to scale).
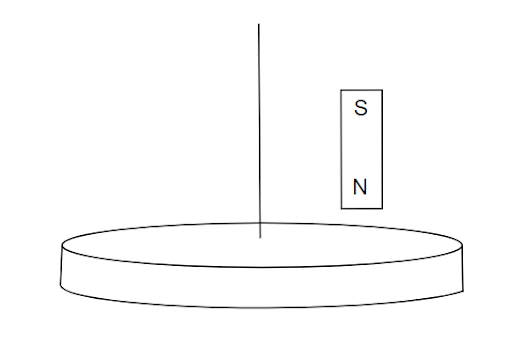
A. Rotate in the direction opposite to the direction of the magnet’s motion
B. Rotate in the same direction as the direction of the magnet’s motion
C. Not rotate and its temperature will remain unchanged
D. Not rotate but its temperature will slowly rise
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:Before we proceed with the problem, it is important to know about the Lenz law. The emf will be induced Whenever there is a magnetic flux linked with the coil and the direction of induced emf opposes the change in magnetic flux known as Lenz law.
Complete step by step solution:
Now we can solve the problem step by step as follows.
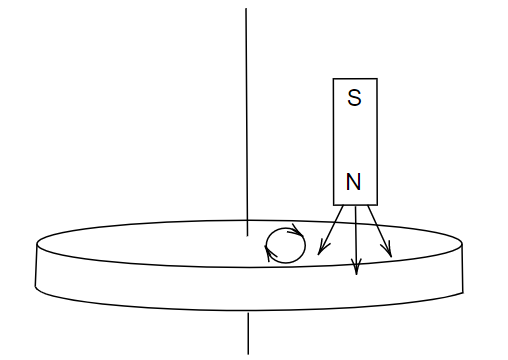
Image: An aluminium disc with the magnet held above it.
The aluminium disc and the magnet area as shown in the figure. Now, if we start moving the magnet about the axis of the disc, the number of magnetic field lines changes, that is the magnetic field line decreases. Here considering a small area of the disc where the magnetic field line passes. The magnetic flux is defined as the number of field lines passing per unit area, whereas flux and magnetic field are directly proportional to each other, the magnetic field decreases, and the flux also decreases.
Based on Lenz’s law, the disc also tries to move in the same direction as the magnet. On the underside of the disc, due to the movement of the magnet, there is a reduction in flux. This flux change causes the production of eddy currents which leads to the generation of heat. These currents are such that they oppose the relative motion of the disc. So, the disc will rotate in the direction of the rotation of the magnet.
Hence, Option B is the correct answer
Note:Lenz's law will be helpful to understand the concept of stored magnetic energy in an inductor. It is also used in microphones, AC generators, etc.
Complete step by step solution:
Now we can solve the problem step by step as follows.

Image: An aluminium disc with the magnet held above it.
The aluminium disc and the magnet area as shown in the figure. Now, if we start moving the magnet about the axis of the disc, the number of magnetic field lines changes, that is the magnetic field line decreases. Here considering a small area of the disc where the magnetic field line passes. The magnetic flux is defined as the number of field lines passing per unit area, whereas flux and magnetic field are directly proportional to each other, the magnetic field decreases, and the flux also decreases.
Based on Lenz’s law, the disc also tries to move in the same direction as the magnet. On the underside of the disc, due to the movement of the magnet, there is a reduction in flux. This flux change causes the production of eddy currents which leads to the generation of heat. These currents are such that they oppose the relative motion of the disc. So, the disc will rotate in the direction of the rotation of the magnet.
Hence, Option B is the correct answer
Note:Lenz's law will be helpful to understand the concept of stored magnetic energy in an inductor. It is also used in microphones, AC generators, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




