
A force of \[20{\rm{ }}N\] is applied on a body of mass \[5{\rm{ }}kg\] resting on a horizontal plane. The body gains kinetic energy of \[10{\rm{ }}joules\] after it moves a distance of \[2{\rm{ }}m\]. The frictional force is:
1. \[10N\]
2. \[15N\]
3. \[20N\]
4. \[30N\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we should first start with the free body diagram so that will understand all kinds of forces acting on it. In this question, we will use the concept of kinetic energy to find the velocity of the block.
Formula Used:
\[K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\]
\[{v^2} = {u^2} + 2as\]
\[f = F - ma\]
Complete answer:
Given Data:
Force \[ = 20N\]
Mass of the body \[ = 5kg\]
Kinetic energy gained by the body on the horizontal surface after moving \[2{\rm{ }}m\] \[ = 10J\]
Now, let us draw a free body diagram for a better understanding of the concept,
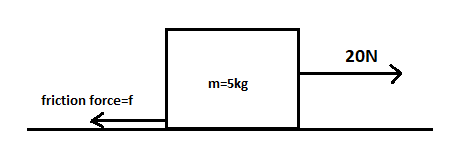
So, from the above figure, we can see that both forces applied and the force of friction are opposite to each other in direction as shown in the above figure.
Now, we have to calculate frictional force from the above-given data:
Using the formula for K.E. we get
\[K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 10J = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 5kg \times {v^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v^2} = 4\]
\[\therefore v = 2m/s\]
For finding out frictional force we need the velocity of the box, now for finding acceleration we have to use a kinematic equation and that is given by:
\[{v^2} = {u^2} + 2as\]
\[u\] is the initial velocity and it is zero since the box was at rest, \[s\] is the distance the box is pushed i.e., \[2{\rm{ }}m\]
Therefore, after putting all the values in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 4 = 0 + 2a(2)\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 1m/{s^2}\]
Now, we have a formula for the frictional force
\[f = F - ma\]
\[ \Rightarrow f = 20N - 5kg \times 1m/{s^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f = 20N - 5N\]
\[\therefore f = 15N\]
Thus, the frictional force acting on the box is \[15N\]
Therefore, the right answer is option 2.
Note: We should remember that we can not always use the kinetic energy formula to find the velocity of the block. In this problem we had given the value of the kinetic energy thus we can use the formula to attain the required value of velocity.
Formula Used:
\[K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\]
\[{v^2} = {u^2} + 2as\]
\[f = F - ma\]
Complete answer:
Given Data:
Force \[ = 20N\]
Mass of the body \[ = 5kg\]
Kinetic energy gained by the body on the horizontal surface after moving \[2{\rm{ }}m\] \[ = 10J\]
Now, let us draw a free body diagram for a better understanding of the concept,

So, from the above figure, we can see that both forces applied and the force of friction are opposite to each other in direction as shown in the above figure.
Now, we have to calculate frictional force from the above-given data:
Using the formula for K.E. we get
\[K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 10J = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 5kg \times {v^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v^2} = 4\]
\[\therefore v = 2m/s\]
For finding out frictional force we need the velocity of the box, now for finding acceleration we have to use a kinematic equation and that is given by:
\[{v^2} = {u^2} + 2as\]
\[u\] is the initial velocity and it is zero since the box was at rest, \[s\] is the distance the box is pushed i.e., \[2{\rm{ }}m\]
Therefore, after putting all the values in the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 4 = 0 + 2a(2)\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 1m/{s^2}\]
Now, we have a formula for the frictional force
\[f = F - ma\]
\[ \Rightarrow f = 20N - 5kg \times 1m/{s^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow f = 20N - 5N\]
\[\therefore f = 15N\]
Thus, the frictional force acting on the box is \[15N\]
Therefore, the right answer is option 2.
Note: We should remember that we can not always use the kinetic energy formula to find the velocity of the block. In this problem we had given the value of the kinetic energy thus we can use the formula to attain the required value of velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)




