
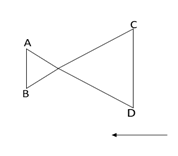
A conducting wire frame is placed in a magnetic field which is directed into the plane of the paper (figure). The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate. The directions of induced currents in wires AB and CD are:
$\left( A \right)$ B to A and D to C
$\left( B \right)$ A to B and C to D
$\left( C \right)$ A to B and D to C
$\left( D \right)$ B to A and C to D
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Ampere’s circuital law states the relationship between the magnetic and the electric field. A magnetic field is generated, whenever a current travels through a conductor. Right-Hand Thumb Rule determines the direction of magnetic field lines. Then apply Lenz's law to determine the direction of the induced current in the system.
Complete solution:
A magnetic field is generated, whenever a current travels through a conductor. Right-Hand Thumb Rule determines the direction of magnetic field lines.
Electric fields are caused by stationary charges and magnetic fields are caused by moving electric charges. Stationary charges cause electric fields.
Since a non-relativistic proton beam passes without deviation through a region of space, we can say that force due to magnetic field equals force due to electric field.
The relationship between the magnetic and the electric field is given by Ampere circuit law.
We can say that from the Lenz law that the induced emf induces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in magnetic flux.
Now let us consider the surface having points A, B, C and D facing upwards in anticlockwise direction when viewing towards the surface.
From Lenz's law we can say that when the flux increases, the induced current will be in the direction CBABC, so it can oppose the increase in flux.
Then the direction of induced current in wires AB and CD is anticlockwise
$B \to A$ and $D \to C$
Then option A is the right option.
Note: A magnetic field is generated, whenever a current travels through a conductor. Right-Hand Thumb Rule determines the direction of magnetic field lines. We can say that from the Lenz law that the induced emf induces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in magnetic flux.
Complete solution:
A magnetic field is generated, whenever a current travels through a conductor. Right-Hand Thumb Rule determines the direction of magnetic field lines.
Electric fields are caused by stationary charges and magnetic fields are caused by moving electric charges. Stationary charges cause electric fields.
Since a non-relativistic proton beam passes without deviation through a region of space, we can say that force due to magnetic field equals force due to electric field.
The relationship between the magnetic and the electric field is given by Ampere circuit law.
We can say that from the Lenz law that the induced emf induces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in magnetic flux.
Now let us consider the surface having points A, B, C and D facing upwards in anticlockwise direction when viewing towards the surface.
From Lenz's law we can say that when the flux increases, the induced current will be in the direction CBABC, so it can oppose the increase in flux.
Then the direction of induced current in wires AB and CD is anticlockwise
$B \to A$ and $D \to C$
Then option A is the right option.
Note: A magnetic field is generated, whenever a current travels through a conductor. Right-Hand Thumb Rule determines the direction of magnetic field lines. We can say that from the Lenz law that the induced emf induces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in magnetic flux.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




