
A charge $q_1$ is revolving around a circle with charge $q_2$ at its centre. Find the speed of charge $q_1$.
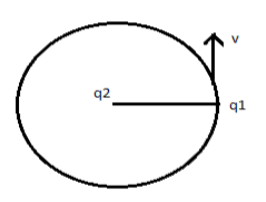
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When the motion is circular then the centripetal force comes into play and it is a charge then electrostatic force also being generated.
Centripetal force is given as:
$\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}$(m is the mass of the body, R is the radius of the circular region, v is the velocity)
Electrostatic force is given by:
$\dfrac{{qQ}}{{4\pi {R^2}}}$(q and Q are the charges R is the radius)
Using the above two forces we will solve this problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us discuss the centripetal force and electrostatic force in detail.
Centripetal force is defined as the force that is necessary to keep an object moving in a curved path and that is directed inward towards the centre of rotation. It is always directed orthogonally to the motion of the body and towards the fixed point of the instantaneous centre of curvature of the path.
Electrostatic force: Electrostatic force is the attractive or repulsive forces between the charged particles. When the charges are both of same polarity they repel each other and when the charges are of opposite polarity they attract each other.
Now we come to the calculation part.
We assume the charges like polarity and thus the electrostatic force will be repulsive in nature.
The force which is generated between the two charges is electrostatic and it is given by:
${F_e} = \dfrac{{KQq}}{{{R^2}}}$
Charge is revolving around the circular path, then centripetal force also comes into play which is given as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}$
Both the forces are balancing each other because one is acting outwards and the other is acting inwards, thus we can equate the two forces.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{KQq}}{{{R^2}}} = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}$................(1)
We will cancel the common terms from equation 1
$ \Rightarrow {v^2} = \dfrac{{KQq}}{{Rm}}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{K{q_1}{q_2}}}{{Rm}}} $ velocity of charge $q_1$ .
Note: We have many applications of centripetal force such as the turn we take while driving a car, scooter or bicycle, planets revolving around the sun, bucket tied to a string. Electrostatic force has application in Van de Graff generators, photocopiers, laser printers and inkjet printers.
Centripetal force is given as:
$\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}$(m is the mass of the body, R is the radius of the circular region, v is the velocity)
Electrostatic force is given by:
$\dfrac{{qQ}}{{4\pi {R^2}}}$(q and Q are the charges R is the radius)
Using the above two forces we will solve this problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us discuss the centripetal force and electrostatic force in detail.
Centripetal force is defined as the force that is necessary to keep an object moving in a curved path and that is directed inward towards the centre of rotation. It is always directed orthogonally to the motion of the body and towards the fixed point of the instantaneous centre of curvature of the path.
Electrostatic force: Electrostatic force is the attractive or repulsive forces between the charged particles. When the charges are both of same polarity they repel each other and when the charges are of opposite polarity they attract each other.
Now we come to the calculation part.
We assume the charges like polarity and thus the electrostatic force will be repulsive in nature.
The force which is generated between the two charges is electrostatic and it is given by:
${F_e} = \dfrac{{KQq}}{{{R^2}}}$
Charge is revolving around the circular path, then centripetal force also comes into play which is given as:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}$
Both the forces are balancing each other because one is acting outwards and the other is acting inwards, thus we can equate the two forces.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{KQq}}{{{R^2}}} = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R}$................(1)
We will cancel the common terms from equation 1
$ \Rightarrow {v^2} = \dfrac{{KQq}}{{Rm}}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{K{q_1}{q_2}}}{{Rm}}} $ velocity of charge $q_1$ .
Note: We have many applications of centripetal force such as the turn we take while driving a car, scooter or bicycle, planets revolving around the sun, bucket tied to a string. Electrostatic force has application in Van de Graff generators, photocopiers, laser printers and inkjet printers.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




