
A beam of light strikes one mirror of a right-angle mirror assembly at an angle of incidence $45^{0}$ as shown in the figure. The right-angle mirror assembly is rotated such that the angle of incidence becomes $60^{0} .$ Which of the following statements is correct about the emerging light beam?
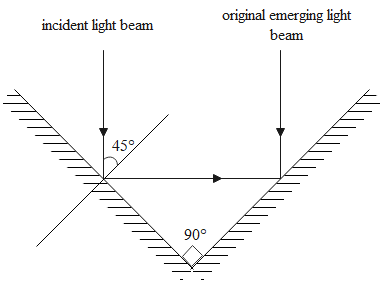
(A) It will move through an angle of ${{15}^{{}^\circ }}$with respect to the original emerging beam.
(B) It will move through an angle of ${{30}^{{}^\circ }}$with respect to the original emerging beam.
(C) It will move through an angle of ${{45}^{{}^\circ }}$with respect to the original beam.
(D) It will emerge parallel to the original emerging beam.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We should know that an incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The angle between this ray and the perpendicular or normal to the surface is the angle of incidence. The reflected ray corresponding to a given incident ray, is the ray that represents the light reflected by the surface. When a line is drawn perpendicular to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, this line is known as normal. It is the imaginary line which is perpendicular to the reflecting surface. The normal ray is incident at 90 degrees to the reflecting surface. Based on this concept we have to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer:
We should know that reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. And refraction is the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another or from a gradual change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomenon, but other waves such as sound waves and water waves also experience refraction.
The diagram for this question is given below:
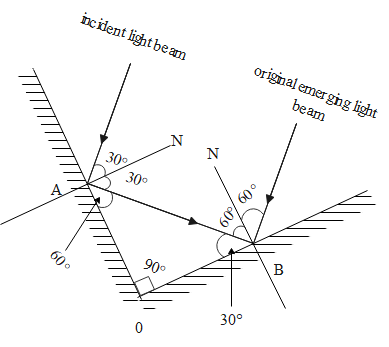
The ray of light strikes the mirror at an angle of, it means it will make an angle of and also from the laws of reflection from the mirror, we know that the angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence.
Therefore, the angle of reflection is equal to 45 degrees.
So, we can say that an emerging light beam will move through an angle of ${{45}^{{}^\circ }}$with respect to the original beam.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note: We should know that Snell's law, in optics, the relationship between the path taken by a ray of light in crossing the boundary or surface of separation between two contacting substances and the refractive index of each. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflection surface at the point of the incidence lie in the same plane. The angle which the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle which the reflected ray makes to the same normal. Refraction is an effect that occurs when a light wave, incident at an angle away from the normal, passes a boundary from one medium into another in which there is a change in velocity of the light. The wavelength decreases as the light enters the medium and the light wave changes direction.
Complete step by step answer:
We should know that reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. And refraction is the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another or from a gradual change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomenon, but other waves such as sound waves and water waves also experience refraction.
The diagram for this question is given below:

The ray of light strikes the mirror at an angle of, it means it will make an angle of and also from the laws of reflection from the mirror, we know that the angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence.
Therefore, the angle of reflection is equal to 45 degrees.
So, we can say that an emerging light beam will move through an angle of ${{45}^{{}^\circ }}$with respect to the original beam.
Hence, option C is the correct answer.
Note: We should know that Snell's law, in optics, the relationship between the path taken by a ray of light in crossing the boundary or surface of separation between two contacting substances and the refractive index of each. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflection surface at the point of the incidence lie in the same plane. The angle which the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle which the reflected ray makes to the same normal. Refraction is an effect that occurs when a light wave, incident at an angle away from the normal, passes a boundary from one medium into another in which there is a change in velocity of the light. The wavelength decreases as the light enters the medium and the light wave changes direction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




