
When 2-bromobutane reacts with alcoholic KOH, the reaction is called
A. Halogenation
B. Hydrogenation
C. Chlorination
D. Dehydrohalogenation
Answer
240.9k+ views
Hint: When a haloalkane reacts with an alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) solution, an alkene is created as the product. A halogen atom and a hydrogen atom from the haloalkane get removed in the form of hydrogen halide.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When hydrogen in an alkane is replaced by a halogen atom, haloalkane is formed.
Alcoholic KOH is a concentrated alcoholic
solution of potassium hydroxide.
Alcoholic KOH disintegrates in water forming\[R{O^ - }\]ions which is a strong base.
It takes hydrogen from the haloalkane.
The carbon atom which carries the halogen atom is\[\alpha \]-carbon.
The carbon atom which holds the hydrogen atom is the\[\beta \]-carbon.
The hydrogen atom is eliminated from \[\beta \]carbon, this reaction is similarly called the \[\beta \]-elimination reaction.
In this reaction, a halogen atom and a hydrogen atom from the haloalkane are withdrawn in the form of hydrogen halide.
So, it is called a dehydrohalogenation reaction.
It is an elimination reaction.
For instance - dehydrobromination of bromoethane
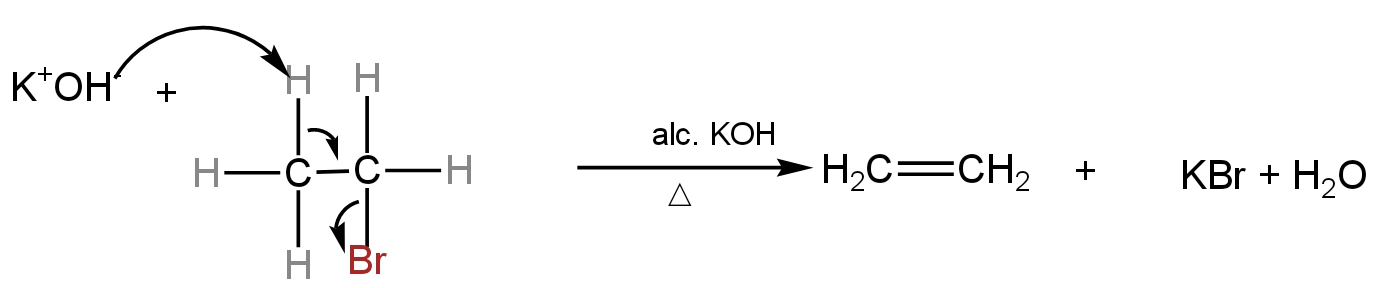
Image: Dehydrobromination of bromoethane forming ethene.
In the given reaction, the α-carbon loses the bromine atom and the\[\beta \]-carbon loses the hydrogen atom.
The resulting product is an alkene.
Here in this question, we are given 2-bromobutane which is treated with alcoholic KOH.
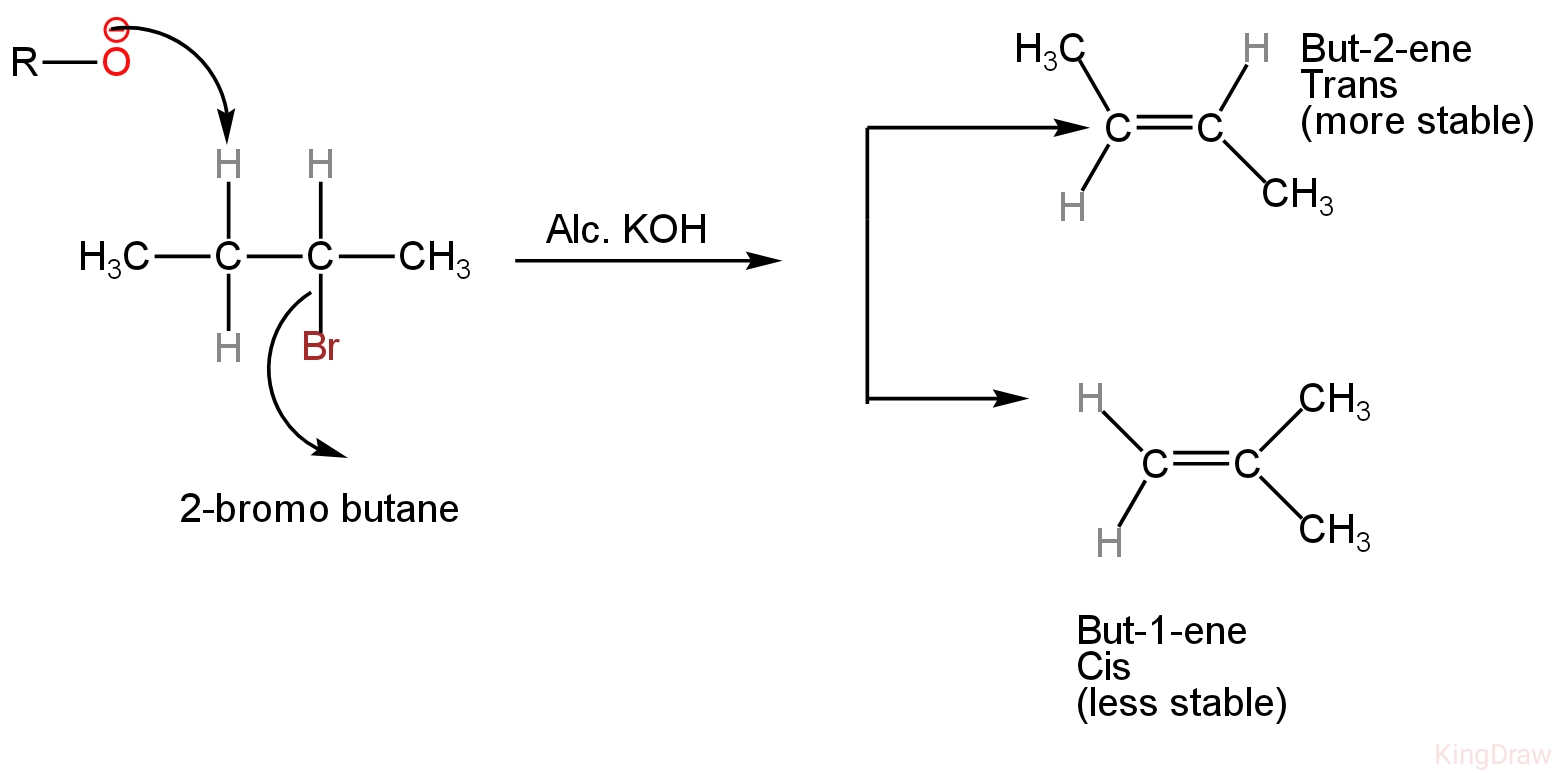
Image: Dehydrobromination of 2-bromobutane.
So, when 2-bromobutane reacts with alcoholic KOH, the reaction is called dehydrohalogenation.
So, option D is correct.
Note: Formation of but-2-ene as the main product according to Saytzeff’s rule.
It states that if an alkyl halide can undergo elimination in two distinct ways, then the more highly substituted alkene or the alkene possessing a deficient number of hydrogens on the doubly bonded carbon atoms is the major product of dehydrohalogenation reaction.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When hydrogen in an alkane is replaced by a halogen atom, haloalkane is formed.
Alcoholic KOH is a concentrated alcoholic
solution of potassium hydroxide.
Alcoholic KOH disintegrates in water forming\[R{O^ - }\]ions which is a strong base.
It takes hydrogen from the haloalkane.
The carbon atom which carries the halogen atom is\[\alpha \]-carbon.
The carbon atom which holds the hydrogen atom is the\[\beta \]-carbon.
The hydrogen atom is eliminated from \[\beta \]carbon, this reaction is similarly called the \[\beta \]-elimination reaction.
In this reaction, a halogen atom and a hydrogen atom from the haloalkane are withdrawn in the form of hydrogen halide.
So, it is called a dehydrohalogenation reaction.
It is an elimination reaction.
For instance - dehydrobromination of bromoethane

Image: Dehydrobromination of bromoethane forming ethene.
In the given reaction, the α-carbon loses the bromine atom and the\[\beta \]-carbon loses the hydrogen atom.
The resulting product is an alkene.
Here in this question, we are given 2-bromobutane which is treated with alcoholic KOH.

Image: Dehydrobromination of 2-bromobutane.
So, when 2-bromobutane reacts with alcoholic KOH, the reaction is called dehydrohalogenation.
So, option D is correct.
Note: Formation of but-2-ene as the main product according to Saytzeff’s rule.
It states that if an alkyl halide can undergo elimination in two distinct ways, then the more highly substituted alkene or the alkene possessing a deficient number of hydrogens on the doubly bonded carbon atoms is the major product of dehydrohalogenation reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




