




An Introduction to Keynesian Economics
John Maynard Keynes developed Keynesian Economics in the 1930s. This economics is additionally known as demand-side economics. Keynes developed this theory to elucidate the world's understanding and recovery from the Great Depression. According to Keynesians, demand plays a crucial role in the economy. This theory relates to how aggregate demand impacts output and inflation. Keynes also explained various theoretical principles regarding this in his book The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money.

An Introduction
Meaning of Keynesian Economics
Keynesian economic theory is a macroeconomic theory that is related to total spending in the economy and its effects on output, employment, and inflation. This theory focuses on the changes within the economy over the short run. According to this theory, government intervention can strengthen the economy.
Features of Keynesian Theory
The basic features of Keynes’s theory are:
Effective demand is controlled by aggregate demand and supply.
Employment and income depend on effective demand.
As aggregate supply remains constant in the short run, Keynes focused on aggregate demand.
Aggregate demand in a two-sector economy is determined by: i) consumption expenditure and ii) investment expenditure.
Consumption expenditure is determined by the size of income and propensity to consume.
Propensity to consume is of two types - average propensity to consume and marginal propensity to consume.
Difference Between Keynesian Economics and Monetarist Economics
Keynesian economic theory states that the government should increase the demand to boost the economy.
On the other hand, monetarist economics states that the government can encourage economic stability by controlling the amount of money in an economy.
Keynesian Economics VS Monetarist Economics
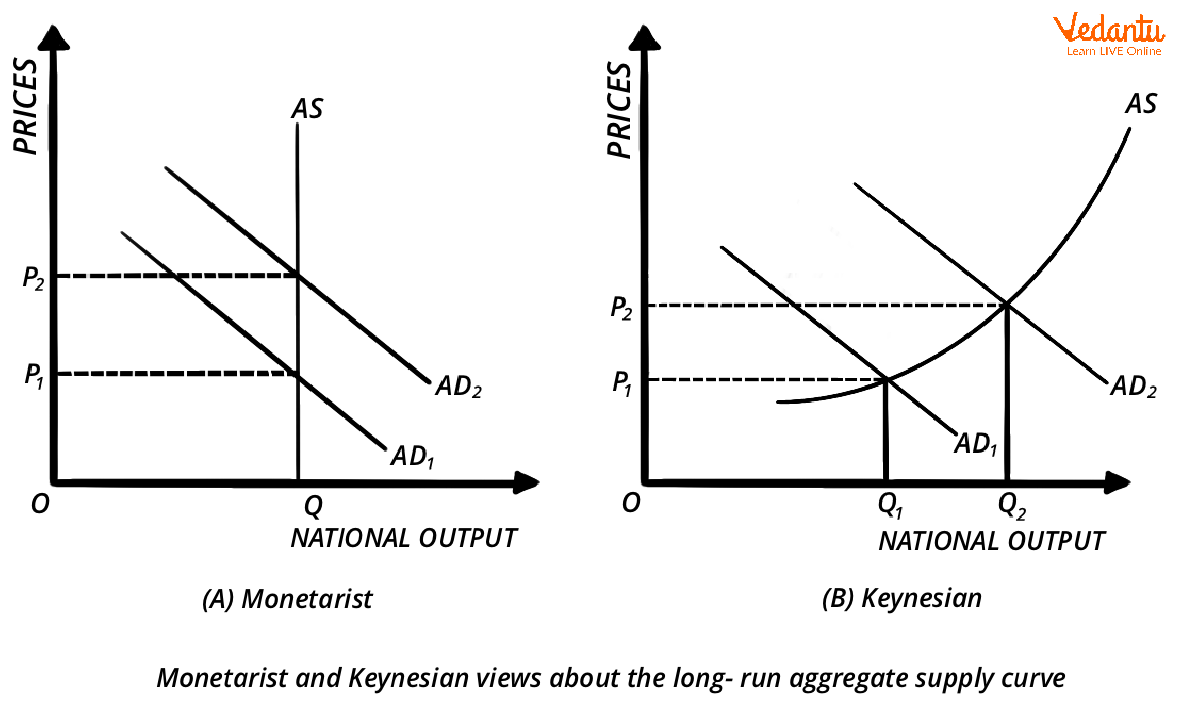
Difference between Keynesian Economics and Monetarist Economics
Difference Between Classical and Keynesian Economics
Keynesian economics believes that government spending is the most important economic activity. On the other hand, classical economics believes that a self-regulating economy is efficient and there is no need for government intervention.
Classical Economics VS Keynesian Economics
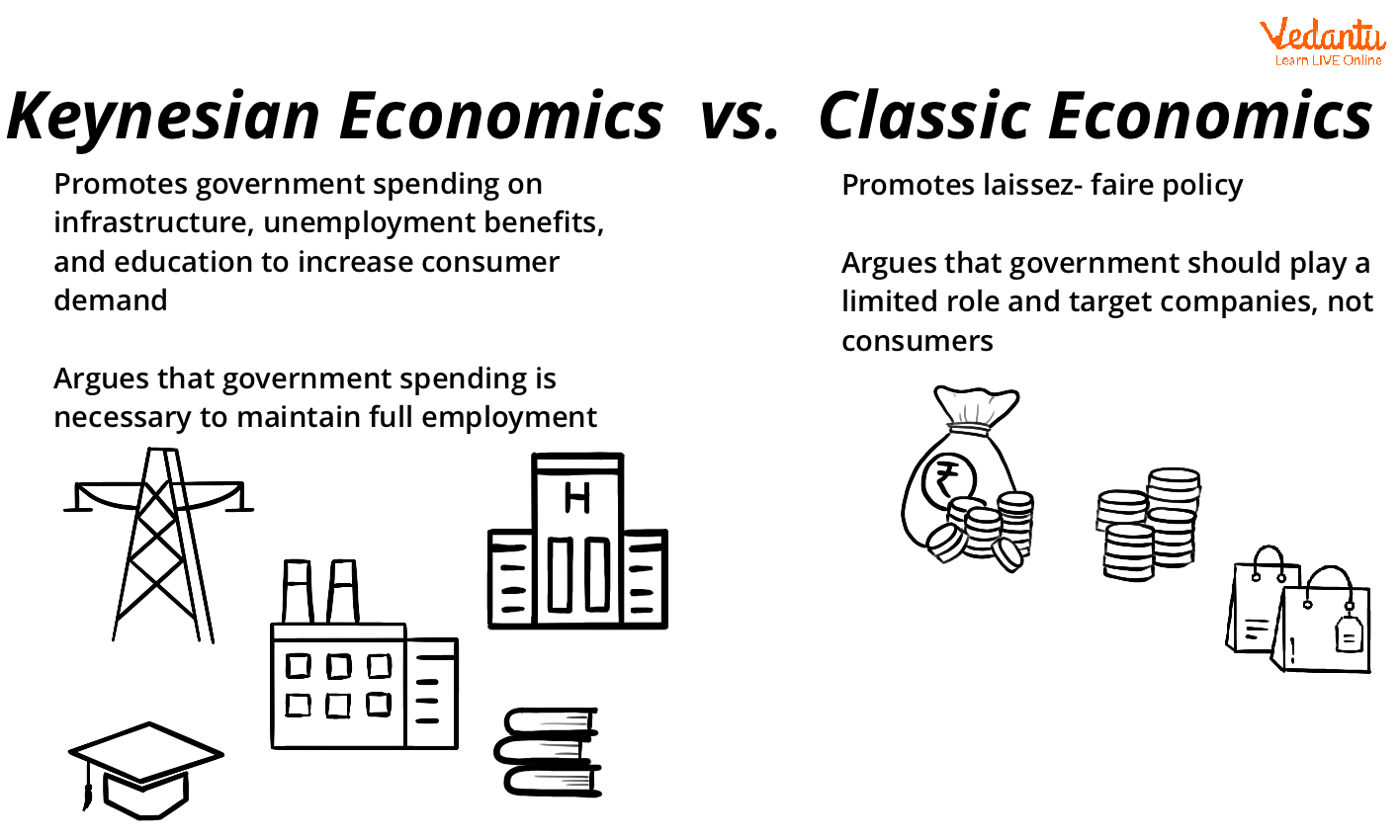
Difference between Classical Economics and Keynesian Economics
Keynes VS Hayek
John Maynard Keynes and Freidrich August Hayek were the two economists of the early twentieth century. Both of them have different opinions regarding the same matter. According to Keynes, the government must play an important role in controlling unemployment. Deficit spending was considered the only way to bring an economy out of the depression.
But Hayek criticised Keynes’s belief in monetary policy that low-interest rates through increased money supply. According to him, this will increase inflation, leading to malinvestment as interest rates are quite low.
Differentiate Between Classical and Keynesian Theory of Employment
Conclusion
In conclusion, we may conclude that Keynesian economics is based on the fact that the government should manage demand in an economy. This theory supported higher employment levels in the economy. When the government invests in various public projects, this increases employment directly. But the major drawback of this theory is that overdoing it can result in inflation.
FAQs on Keynesian Economics vs. Monetarist Economics
1. What is the main idea of Keynesian economics?
Keynesian economics, also known as demand-side economics, posits that aggregate demand (total spending in an economy) is the most important driving force for economic growth, especially in the short run. It argues that government intervention, through fiscal policy like increased spending on public works, is necessary to manage the economy, stimulate demand, and reduce unemployment during a recession.
2. What is the core principle of Monetarist economics?
Monetarist economics, most famously associated with Milton Friedman, argues that the most significant factor influencing economic activity is the money supply. Monetarists believe that governments should aim for stable and predictable growth in the money supply rather than engaging in active fiscal intervention. They contend that controlling the money supply is the key to controlling inflation and fostering long-term economic stability.
3. What is the primary difference between Keynesian and Monetarist economics on government intervention?
The primary difference lies in the preferred tool for economic management. Keynesians advocate for active fiscal policy (government spending and taxation) to manage aggregate demand. In contrast, Monetarists argue for a more passive role for government, focusing strictly on controlling the money supply through monetary policy and allowing free markets to function with minimal interference.
4. How does the Classical view of the economy differ from the Keynesian perspective?
The main difference is on the flexibility of the economy and the role of government.
- Classical economics believes in self-regulating markets where wages and prices are flexible, ensuring that the economy naturally returns to full employment without government help.
- Keynesian economics, developed during the Great Depression, argues that prices and wages can be 'sticky' downwards, leading to prolonged periods of unemployment. Therefore, government intervention is essential to restore full employment.
5. What are the main criticisms of Keynesian economic theory?
While influential, Keynesian theory faces several criticisms, including:
- Inflationary Risk: Over-stimulating the economy with government spending can lead to high inflation.
- Crowding Out: Increased government borrowing to fund spending can raise interest rates, which discourages, or 'crowds out', private investment.
- Time Lags: It takes time to recognise an economic problem, implement a fiscal policy response, and for that response to have an effect, by which time the economic conditions may have changed.
- Focus on Short-Run: Critics argue it offers solutions for short-term crises but neglects long-term economic stability and growth.
6. Why did Monetarism emerge as a significant challenge to Keynesian economics?
Monetarism gained prominence in the 1970s primarily because traditional Keynesian policies seemed unable to solve the problem of 'stagflation' — a period of high unemployment and high inflation occurring simultaneously. Keynesian theory struggled to explain this phenomenon, as it typically saw a trade-off between inflation and unemployment. Monetarists offered an alternative explanation, blaming excessive growth in the money supply for the inflation, which strengthened their case for focusing on monetary policy over fiscal stimulus.
7. In a recession, how would the policy advice of a Keynesian and a Monetarist differ in practice?
In a real-world recession, their advice would be starkly different:
- A Keynesian economist would recommend expansionary fiscal policy. This means the government should increase its spending (e.g., on infrastructure projects) or cut taxes to boost consumer spending and aggregate demand, even if it means running a budget deficit.
- A Monetarist economist would advise against large-scale fiscal intervention. Instead, they would recommend that the central bank ensure the money supply continues to grow at a slow, steady, and predictable rate. They would argue that this provides a stable environment for the economy to recover on its own.
8. How does inflation arise according to Keynesian theory?
According to Keynesian theory, inflation is typically 'demand-pull' inflation. It occurs when aggregate demand in an economy outpaces aggregate supply. This can be caused by several factors, such as:
- High Consumer Spending: When consumers are confident and spending heavily, often on credit.
- Excessive Government Spending: When the government injects too much money into the economy through its expenditures.
- Strong Export Demand: A sudden surge in demand for a country's exports can also pull prices up.
9. How do Keynesians and Monetarists fundamentally disagree on the velocity of money?
The disagreement on the velocity of money—the rate at which money changes hands—is a core technical difference.
- Keynesians believe the velocity of money is unstable and unpredictable. They argue that during a downturn, people might hoard cash (reducing velocity), making an increase in the money supply ineffective. This is why they favour direct government spending.
- Monetarists believe the velocity of money is stable and predictable in the long run. This belief underpins their entire theory; if velocity is stable, then changes in the money supply will have a direct and predictable effect on the nominal GDP (Price x Quantity), making monetary policy a powerful tool.























