Solutions Class 12 extra questions and answers Free PDF Download
FAQs on Important Questions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26
1. What are the most important topics in CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1, Solutions, for the 2025-26 board exam?
For the CBSE 2025-26 board exams, the high-weightage topics from the Solutions chapter that students must focus on are:
- Colligative Properties: Relative lowering of vapour pressure, elevation in boiling point, depression in freezing point, and osmotic pressure. Numerical problems from this section are very common.
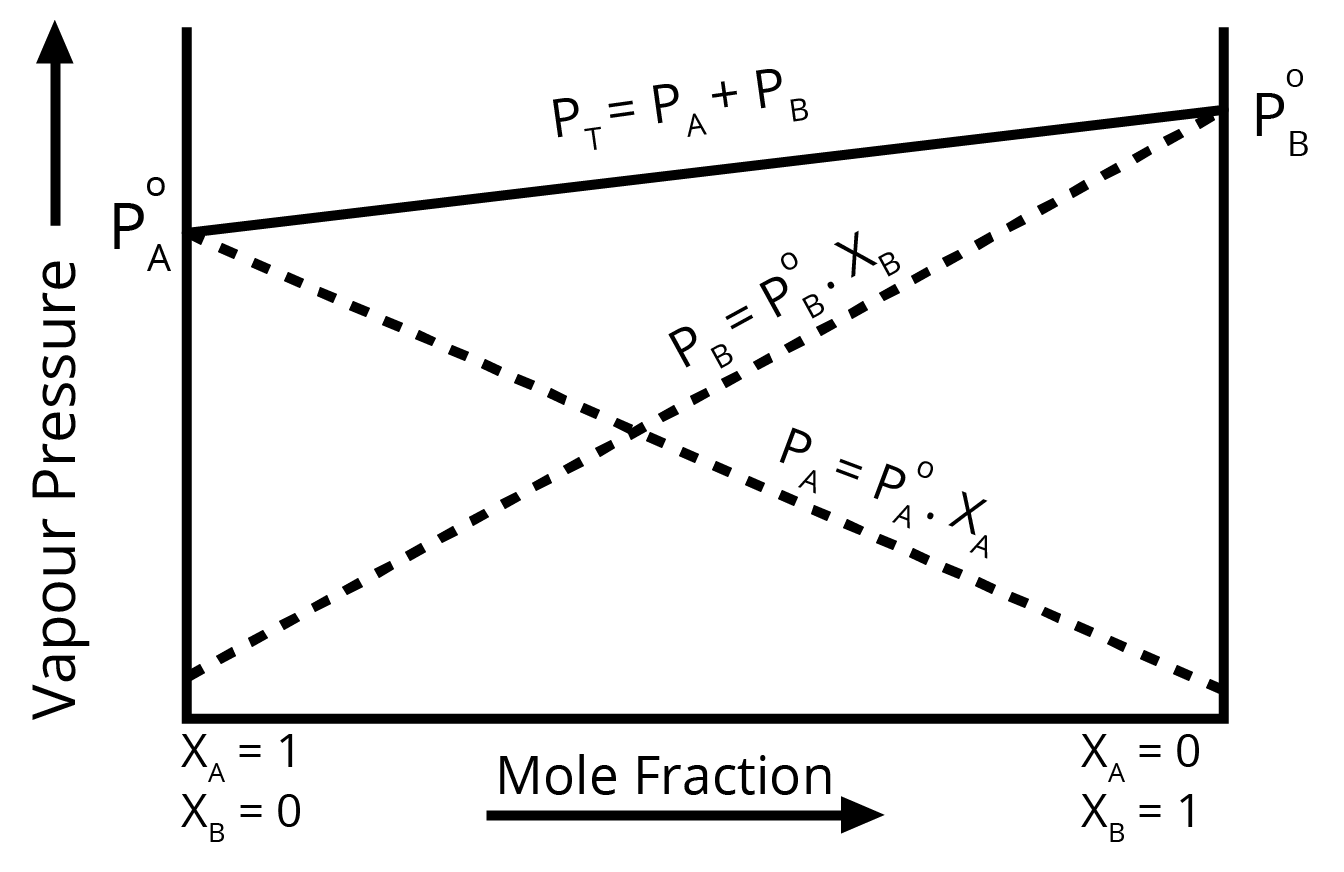
- Raoult's Law: Its statement, mathematical expression, and the distinction between ideal and non-ideal solutions (positive and negative deviations).
- Van't Hoff Factor (i): Understanding its significance in calculating abnormal molecular masses due to association or dissociation of solutes.
- Henry's Law: Its statement, applications (like in scuba diving and carbonated drinks), and related numericals.
- Concentration Terms: Molarity, molality, and mole fraction, including problems involving their calculation and conversion.
2. Why is practising important questions for the Solutions chapter more effective than just reading the NCERT textbook?
While the NCERT textbook builds your conceptual foundation, practising important questions is crucial for exam success for several reasons:
- Pattern Recognition: It helps you understand the types of questions that are frequently asked in board exams, including direct definitions, reasoning-based questions (HOTS), and numericals.
- Application of Concepts: Solving problems forces you to apply theoretical knowledge, such as using Raoult's law to explain why a solution's boiling point elevates, a skill not fully developed by passive reading.
- Time Management: It trains you to answer questions within the stipulated time, especially complex 3-mark and 5-mark numericals on colligative properties.
- Identifying Weaknesses: You can pinpoint specific topics, like calculating the Van't Hoff factor for association, where you need more practice.
3. What type of numerical problems from the Solutions chapter are expected in the Class 12 Chemistry board exam?
You can expect numerical problems, typically for 3 or 5 marks, based on the following concepts:
- Calculating Molar Mass: Using any of the four colligative properties. The most common formulas are depression in freezing point (ΔTf = i · Kf · m) and elevation in boiling point (ΔTb = i · Kb · m).
- Van't Hoff Factor: Calculating the degree of dissociation or association of a solute using the observed colligative property.
- Osmotic Pressure: Problems using the formula π = iCRT, often to find the molar mass of macromolecules like polymers or proteins.
- Henry's Law: Calculating the solubility of a gas in a liquid using the formula P = KH · x.
- Raoult's Law: Calculating the vapour pressure of a solution containing two volatile components (PTotal = P°AxA + P°BxB).
Always remember to write the formula, show the substitution of values, and state the final answer with correct units for full marks.
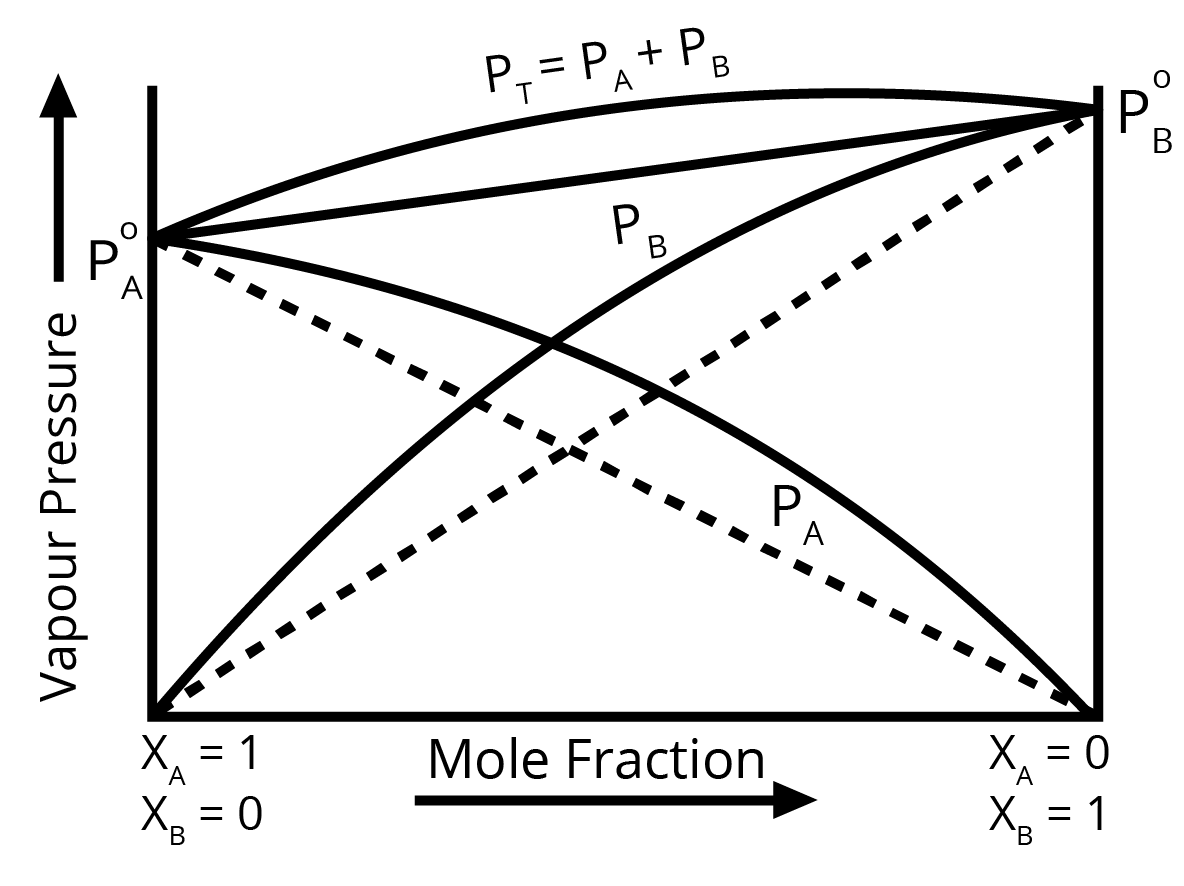
4. How should one answer a question on the deviations from Raoult's Law for full marks?
To score full marks on a question about deviations from Raoult's Law, your answer should be structured and include these key points:
- Positive Deviation: Mention that the observed vapour pressure is higher than expected. Explain that this occurs when the intermolecular forces between solute-solvent (A-B) molecules are weaker than those between solute-solute (A-A) and solvent-solvent (B-B) molecules. Also, state that ΔHmix > 0 (endothermic) and ΔVmix > 0. Provide an example like ethanol and acetone.
- Negative Deviation: Mention that the observed vapour pressure is lower than expected. Explain that this is due to stronger intermolecular forces between solute-solvent (A-B) molecules. Also, state that ΔHmix < 0 (exothermic) and ΔVmix < 0. Provide an example like chloroform and acetone.
For a question with higher marks, drawing and labelling the respective vapour pressure vs. mole fraction graphs is highly recommended.
5. Why is osmotic pressure measurement the preferred method for determining the molar masses of macromolecules?
The osmotic pressure method is preferred over other colligative properties like depression in freezing point or elevation in boiling point for determining the molar masses of macromolecules (e.g., proteins, polymers) for these reasons:
- Magnitude of Value: For dilute solutions, the magnitude of osmotic pressure (π) is significantly larger and therefore more easily and accurately measurable than the very small values of ΔTb or ΔTf.
- Room Temperature Measurement: Osmosis can be measured at room temperature, which prevents the denaturation or degradation of temperature-sensitive macromolecules like proteins. Other methods require heating or cooling, which can damage the sample.
- Use of Molarity: The formula for osmotic pressure uses Molarity (M) instead of Molality (m), making it more convenient for preparing solutions, as measuring volume is often easier than measuring the mass of the solvent.
6. What are azeotropes, and why can't they be separated by fractional distillation?
Azeotropes are binary mixtures of liquids that have the same composition in both liquid and vapour phases and boil at a constant temperature. They cannot be separated by fractional distillation because this technique works by exploiting the difference in boiling points of the components. Since an azeotrope boils at a single, constant temperature without any change in its composition, both components vaporize together, preventing separation. There are two types:
- Minimum boiling azeotropes: Formed by solutions showing large positive deviations from Raoult's law (e.g., ethanol-water).
- Maximum boiling azeotropes: Formed by solutions showing large negative deviations from Raoult's law (e.g., nitric acid-water).
7. What is the significance of the Van't Hoff factor (i) in the chapter Solutions?
The Van't Hoff factor (i) is a crucial correction factor that accounts for the behaviour of solutes in a solution. Its significance lies in relating the observed colligative property to the calculated one. It is defined as the ratio of the actual number of particles in a solution after association or dissociation to the number of formula units initially dissolved. Its value indicates:
- i = 1: For non-electrolytes that do not associate or dissociate (e.g., urea, glucose, sucrose).
- i > 1: For solutes that undergo dissociation (e.g., NaCl, MgCl2). For NaCl, i → 2.
- i < 1: For solutes that undergo association (e.g., ethanoic acid in benzene forms a dimer), so i → 0.5.
Ignoring 'i' for electrolytes leads to an incorrect calculation of both colligative properties and molar masses, making it an essential parameter in exam questions.
8. What types of 1-mark questions are commonly asked from the Solutions chapter in CBSE exams?
For 1-mark questions, expect direct definitions, examples, or simple reasoning. Common types include:
- Definitions: Define terms like ebullioscopic constant, cryoscopic constant, molality, or azeotrope.
- Examples: Provide an example of a specific type of solution (e.g., 'gas in solid') or a solution showing positive/negative deviation.
- Henry's Law Application: Reasoning questions like "Why do aquatic species feel more comfortable in cold water?"
- Van't Hoff Factor: What is the value of 'i' for the complete dissociation of K2SO4? (Answer: 3).
- Simple Comparison: Which of two solutions will have a higher boiling point or lower freezing point? (e.g., 0.1 M NaCl vs 0.1 M glucose).
9. What is a common mistake students make when solving numericals on colligative properties, and how can it be avoided?
A very common and critical mistake is forgetting to include the Van't Hoff factor (i) for solutes that are electrolytes (like NaCl, CaCl2, K2SO4). Students often use the basic formulas like ΔTf = Kf · m for all solutes, which is only correct for non-electrolytes (like urea or glucose).
How to avoid this mistake:
- Before solving any numerical, first identify the solute.
- Ask yourself: Is it an electrolyte (acid, base, salt) that will dissociate, or a non-electrolyte (like sugar, urea)?
- If it is an electrolyte, you must use the modified formula with 'i' (e.g., π = iCRT).
- Always check if the question mentions complete dissociation or provides a degree of dissociation (α) to calculate the exact value of 'i'.
10. How can Henry's Law be applied to explain why carbonated drinks are sealed under high pressure?
This is a classic application-based question. Henry's Law states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid's surface (P = KH · x). To increase the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) dissolved in a soft drink, manufacturers apply a very high pressure of CO2 gas above the liquid and then seal the bottle. This high pressure forces more CO2 molecules to dissolve and remain in the solution. When the bottle is opened, the pressure above the liquid drops to atmospheric pressure, reducing the solubility of CO2 and causing it to escape from the solution as bubbles or fizz.