Respiration in Plants Class 11 important questions with answers PDF download
Free PDF download of Important Questions with Answers for CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 - Respiration in Plants prepared by expert Biology teachers from latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. Register online for Biology tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in your examination.
Study Important Questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12– Respiration in Plants
Very Short Answer Questions. (1 Mark)
1. Define fermentation and aerobic respiration.
Ans: Fermentation is the process in which partial breakdown of glucose occurs.
Aerobic respiration glucose is completely degraded into CO2 and H2O.
2. What are the different types of respiration occur in plants?
Ans: The different types of respiration that occur in plants are -aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
3. Name the energy currency of the cells.
Ans: ATP is the energy currency of the cells.
4. What are the other two names for Kreb’s cycle?
Ans: Citric acid cycle (CAC), Tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) are the other two names for Kreb’s cycle.
5. In which organelle does Kreb’s cycle occur in living cells?
Ans: Kreb’s cycle occurs in the mitochondria in living cells.
6. Mention the conditions under which
(i) RQ is 1 (ii) R.Q is less than 1
Ans: The conditions for the above-mentioned points are:
(i) If carbohydrates are used as substrate and are fully oxidized the R.Q will be 1.
(ii) If fats are used in respiration, the R.Q will be less than 1.
7. What is respiration?
Ans: Respiration is a process of physiochemical change by which environmental oxygen is taken into, to oxidize stored food, for releasing CO2, water, and energy. The energy released is used for various activities, whereas CO2 is used by plants.
8. Give two types of cellular respiration.
Ans: The two types of cellular respiration are
Aerobic
Anaerobic
9. How many carbon atoms are present in the molecule of each of:
Ans: The number of carbon atoms is-
(i) 6 carbon in glucose (ii) 3 carbon in pyruvate.
10. Name the molecule which is the terminal acceptor of the electron.
Ans: Oxygen is the molecule that is the terminal acceptor of electrons.
11. How many ATP molecules are produced from a molecule of glucose on complete oxidation in eukaryotes?
Ans: 36 ATP are produced from a molecule of glucose on complete oxidation in eukaryotes.
12. Where does ETC found in eukaryotic cells?
Ans: ETC is found in the eukaryotic cell of the mitochondrial membrane.
13. Name the enzyme which converts sugar into glucose and fructose.
Ans: Invertase is the enzyme that converts sugar into glucose and fructose.
14. How many molecules of ATP are produced by the oxidation of one molecule of FADH2?
Ans: 2 ATP molecules are produced by the oxidation of one molecule of FADH2.
15. Why does the person with sufficient while fibers get fatigued in a short period?
Ans: Due to the formation of lactic acid, a person feels fatigued in a short period.
16. Write the name of the end product of glycolysis.
Ans: Pyruvic acid is the end product of glycolysis.
17. Name the first product formed in Kerb’s cycle.
Ans: Citric acid is the first product formed in Kerb’s cycle.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. Define RQ. What is its value for fats?
Ans: Respiratory Quotient (RQ): The ratio of the volume of CO2 evolved to the volume of O2 consumed in respiration is termed the respiratory quotient or respiratory ratio.
Its value for fats is less than one.
2. What is the importance of F0 -F1 particles in ATP production during aerobic respiration?
Ans: F1 headpiece contains the site for ATP synthesis from ADP and phosphate.
F0 forms the channel through which protons across the inner membrane.
3. What is oxidative decarboxylation? What happens to pyruvate immediately after this reaction?
Ans: Oxidative decarboxylation– It is the process in which carbon is removed from a compound as carbon dioxide and the compound is oxidized.
Pyruvate is oxidatively decarboxylated into a 2C acetate unit, which joins coenzyme A (COA) to form acetyl CO– A.
4. What is respiration?
Ans: A process of physicochemical change by which environmental oxygen is taken into, to oxidize the stored food, for the release of CO2, water, and energy. The energy released is used for doing various life activities, whereas CO2 is used by plants.
5. Why less energy is produced during anaerobic respiration?
Ans: Less energy is produced during anaerobic respiration because-
Incomplete breakdown of the respiratory substrate takes place.
Some of the products of anaerobic respiration can be oxidized further to release energy which shows that anaerobic respiration does not liberate the whole of energy contained on the respiratory substrate.
O2 is not utilized for securing electrons and protons.
NADH2 does not produce ATP as electron transport is absent.
6. What is the function of phosphofructokinase in glycolysis?
Ans: phosphofructokinase in glycolysis catalyzes the formation of fructose-1,6-biphosphate from fructose-6- phosphate and adenosine–triphosphatetri- phosphate (ATP) Fructose-1,6-biophosphate is split into 2 molecules of triose phosphate–3 phosphoglyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
7. Give the difference between Breathing and Respiration?
Ans: The difference between breathing and respiration are:
Breathing | Respiration |
It is a biophysical process | It is a biochemical process |
Oxygen is taken in and CO2 is given out | Water, carbon dioxide, and energy is released by the oxidation of carbohydrates |
8. Define aerobic respiration?
Ans: The process of release of energy through intake of molecular oxygen and release of CO2 is known as aerobic respiration.
9. What is the compensation point?
Ans. At low concentrations of CO2 and non-limiting light intensity, the photosynthetic rate of a given plant will be equal to the total amount of respiration. The atmospheric concentration of CO2 at which photosynthesis just compensates for respiration is referred to as the CO2 compensation point.
10. Mention two steps of glycolysis in which ATP is utilized.
Ans: The two steps of glycolysis in which ATP is utilized are-
(i) ATP molecules are formed by the direct transfer of Pi to ADP.
(ii) By oxidation of NADH.
Short Answer Question (3 Marks)
1. Describe the mechanism of Respiration.
Ans: Mechanism of respiration – Glucose molecule is broken down into an intermediate molecule, Pyruvic acid.
Breakdown of Pyruvic Acid in Anaerobic Respiration – In this process in absence of oxygen, the pyruvic acid is incompletely reduced to ethyl alcohol.
${\text{Glucose }} \to {\text{ Ethyl alcohol}}\,{\text{ + }}\,{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2} + 2{\text{ ATP}}$Breakdown of Pyruvic Acid in Aerobic Respiration – In this process, the pyruvic acid is completely oxidized into CO2 and H2O is the presence of oxygen. This process occurs in the mitochondria of the cell and is known as Kreb’s cycle.
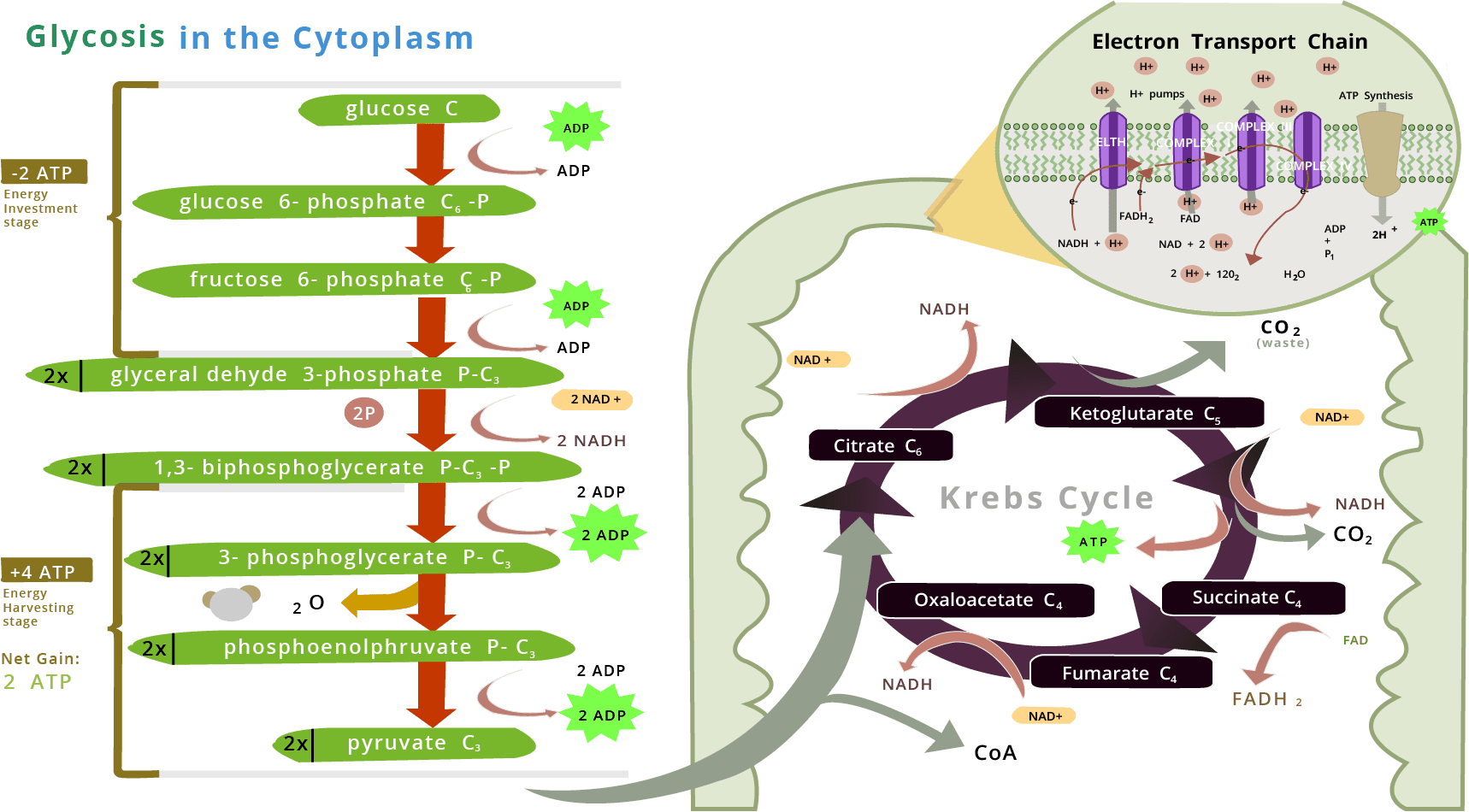
Glycolysis
2. What are the various steps involved in glycolysis?
Ans: Steps of Glycolysis –
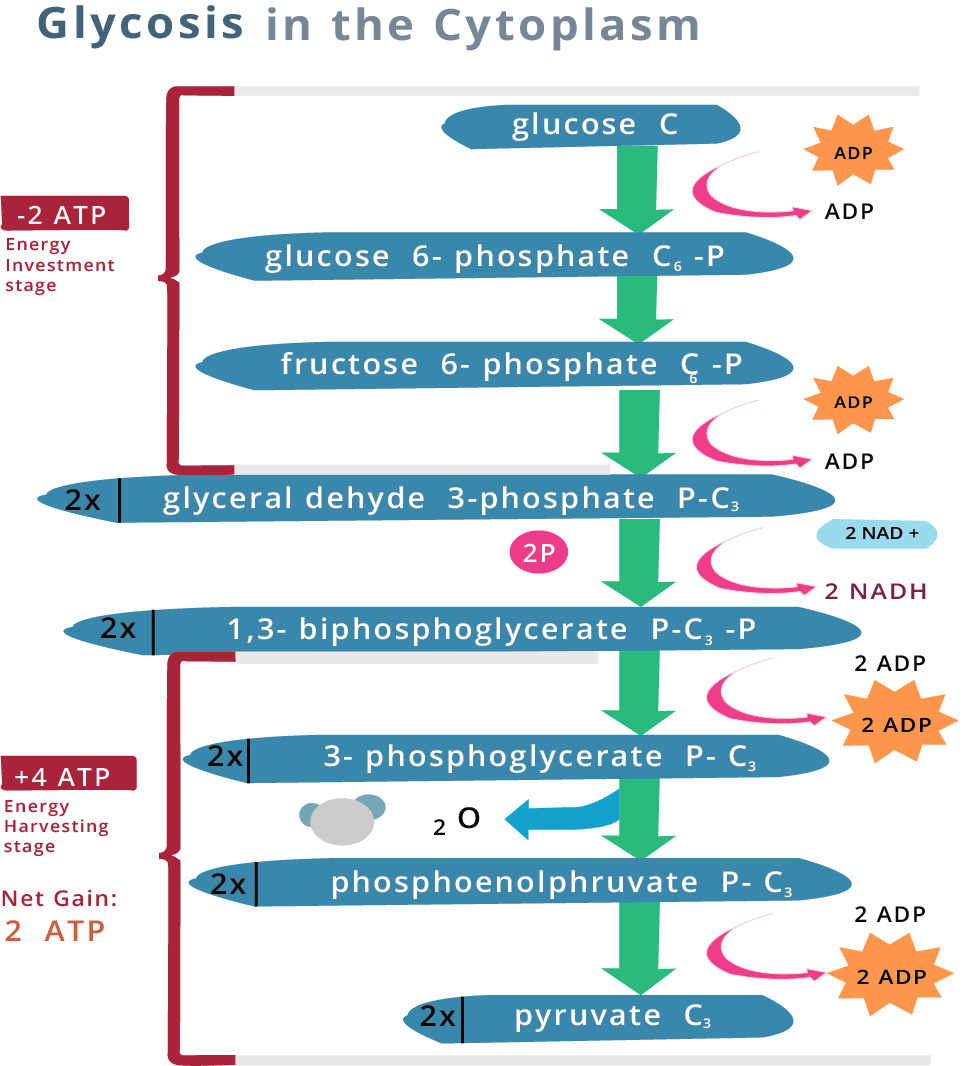
Glycolysis in the Cytoplasm
3. Explain the Respiratory Balance sheet.
Ans:
As sequential, orderly pathway functioning, with one substrate forming next one with glycolysis, TCA cycle, and ETS pathway following one after another.
NADH synthesized in glycolysis. It is transferred into mitochondria and undergoes oxidative phosphorylation.
None of the intermediates in the pathway are used to form any other compound.
Only glucose is being respired; no other alternative substrates enter in the pathway at any of the intermediary stages.
4. What is the significance of the stepwise release of energy in respiration?
Ans: Advantages of step wise oxidation during respirations
It facilitates the utilization of a relatively higher proportion of energy in ATP synthesis.
Activities of enzymes for different steps may be enhanced or inhibited by specific compounds. This provides a means of controlling the rate of the pathway and energy output according to the need of the cell.
The same pathway may be utilized for forming intermediates used in the synthesis of other bimolecular-like amino acids.
5. Write the significance of the citric acid cycle.
Ans: i) It explains the process of breaking pyruvate into CO2 and water. It is a major pathway to the generation of ATP.
(ii) More energy is released (30 ATP) in this process as compared to glycolysis.
(iii) Many intermediates compounds are formed. They are used in the synthesis of biomolecules like amino acids, nucleotides, chlorophyll, cytochromes, and fats.
6. Explain Fermentation.
Ans: It occurs in some organisms like some bacteria that produce lactic acid from pyruvic acid. In animal cells, such as muscles during exercise, when O2 is inadequate for cellular exercise, the pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid by lactate dehydrogenase. The reducing agent is NADH+H+ that is reoxidized to NAD+ in both processes.
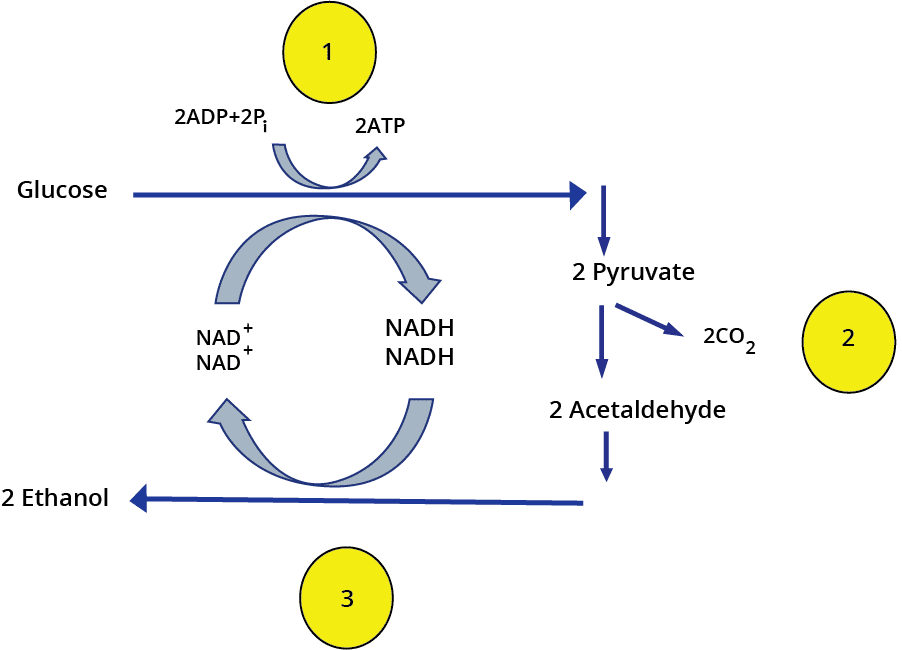
Fermentation
In both lactic acid and alcohol fermentation not much energy is released; less than seven percent of the energy in glucose is released and not all it is trapped as high energy bonds of ATP. The processes are hazardous, either acid or alcohol is produced. Yeasts poison themselves to death when the concentration of alcohol reaches approximately 13%.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. Describe the process and role of the citric acid cycle in living organisms.
Ans: It is called the “tricarboxylic acid cycle” (TCA).
Following steps are present for completing this cycle-
(i) In this step, CO2 is removed from pyruvic acid and resulting 2- carbon unit with the sulfur-containing compound coenzyme A forming Acetyl CoA. During this, hydrogen released is accepted by NAD, and NADH2 is produced.
$\text { Pyruvic acid }_{-} \mathrm{CoA}+\mathrm{NAD} \rightarrow \text { Acetyl } \mathrm{CoA}+\mathrm{NADH}_{2}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}$
(ii) Acetyl coenzyme A reacts with a 4 – carbon compound oxaloacetic acid to form citric
acid.
(iii) The citrate remains in equilibrium with cis-aconitic acid and iso-citric acid in the presence of enzyme aconitase.
Citric acid → Isocitric acid
(iv) Isocitrate is dehydrogenated in the presence of isocitrate dehydrogenase enzyme to form oxalosuccinate. The hydrogen released is accepted by NAD to form NADH2.
$\text { Isocitric acid }+\mathrm{NAD} \rightarrow \mathrm{Oxalosuccinate}+\mathrm{NADH}_{2}$
(v) A molecule of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}$ is lost from oxalosuccinate and a 5 - carbon compound $\alpha - $ ketoglutaric acid is formed in the presence of decarboxylate enzyme.
(vi) $\alpha $ - ketoglutarate loses a molecule of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}$ and 4 - carbon compound succinyl CoA is formed.
$\alpha - $ keloglutarate $ + {\text{COA}} + {\text{NAD}} \to $ succinyl $ + {\text{CoA}} + {\text{NAD}}{{\text{H}}_2} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}$
(vii) Succinyl CoA forms succinate, and ATP is found by linking ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) Succinate CoA + ADP + Pi → Succinylate + CoA + ATP b Succinate is oxidized into fumarate in the presence of succinate dehydrogenase enzyme. The hydrogen liberated is accepted by FAD and FADH2 is formed. Succinate+FAD → Fumerate+FADH2
(ix) In this step the fumarate is converted into malate in the presence of enzyme fumarate hydrase (fumarase) Fumarate→Malate.
(x) Malate is changed into oxaloacetate in the presence of the enzyme malate dehydrogenase. NAD is reduced to NADH2 by the liberated hydrogen. Thus, oxaloacetic acid produced is ready to combine with the fresh acetyl CoA obtained from pyruvic acid for completing one cycle.
Net yield Kreb’s cycle:
1 Pyruvic acid + 1ADP +4NAD+ 1FAD+3CO2+1FADH2+4NADH2+1ATP
1 ATP= 1ATP
3×4NADH2 = 12ATP
2×1FAD2 = 2ATP
Total =15 ATP
Thus 2 Pyruvic acid in glycolysis yield, $15 \times 2 = 30$ ATP.
2. Explain ETS.
Ans: The mechanism of the Electron transport system is as follows:
Glucose is completely oxidized towards the end of the citric acid cycle. Energy is not released unless NADH and FADH are oxidized through ETS.
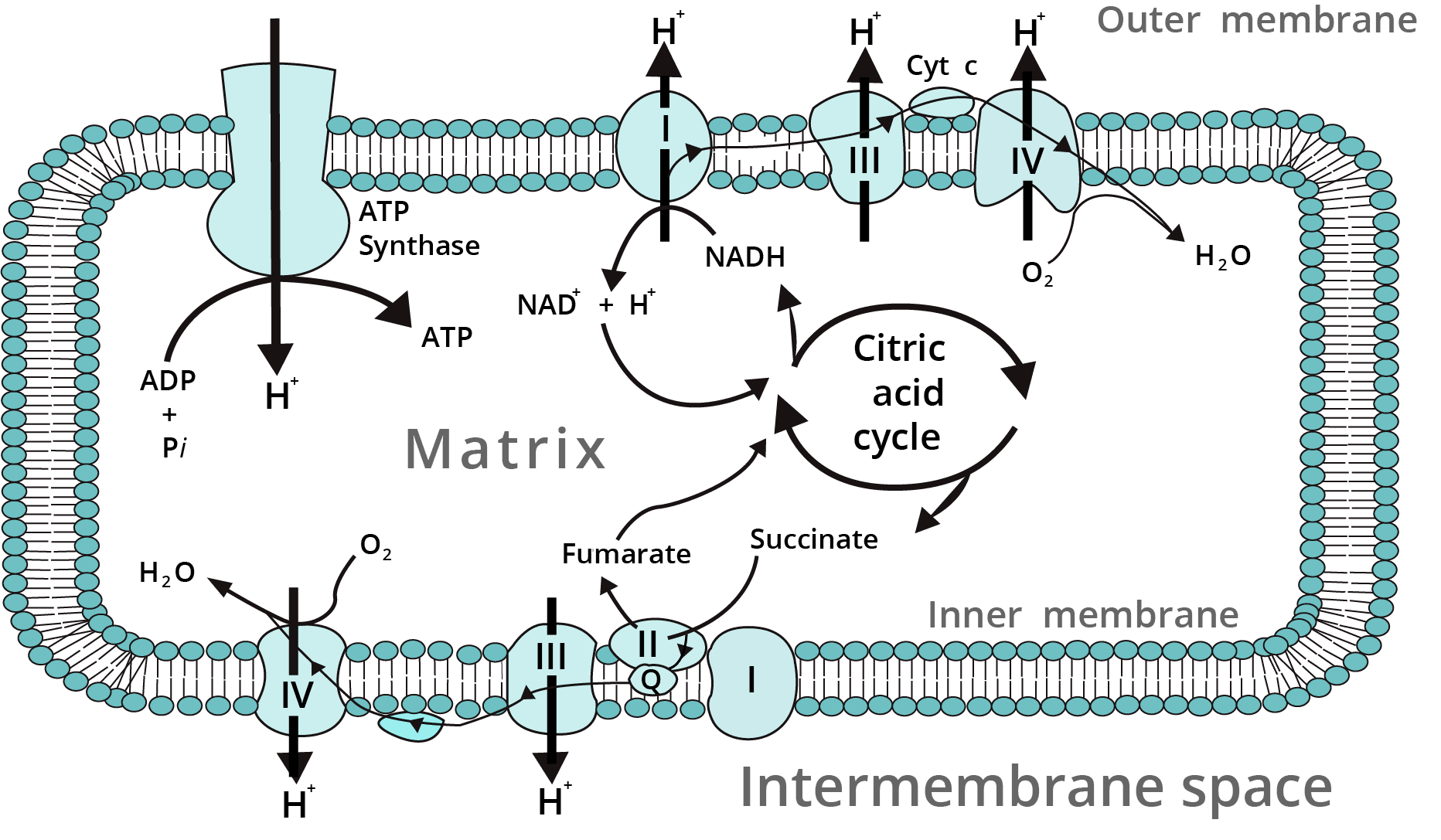
Electron Transport System
The ETS is operative in the inner mitochondria membrane. Electrons from NADH produced in the mitochondrial matrix are oxidized by an NADH dehydrogenase (complex I) and electrons are then transferred to ubiquinone located within the inner membrane also receives reducing equivalents via FADH which is generated during oxidation of succinate, through the activity of an enzyme named succinate dehydrogenase (complex II). Reduced ubiquinone is then oxidized with the transfer of electrons to cytochrome complex (complex III).
Cytochrome is a small protein attached to the outer surface of the inner membrane and acts as a mobile carrier for the transfer of electrons between complex III and complex IV. (complex IV) is cytochromes ‘c’ oxidize complex having cytochromes ‘a’ and a3. When electrons pass from one carrier to another via complex I to IV in ETS, they are coupled to ATP synthase (complex V) for the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. Oxidation of one molecule of NADH, gives rise to 3 molecules of ATP, while that of FADH, produces 2 molecules of ATP. Electrons are curried by cytochromes and recombine with their protons before the final stage when the hydrogen atom is accepted by oxygen to form water. O2 acts as the final hydrogen acceptor. The whole process by which oxygen allows the production of ATP by phosphorylation of ADP is called ‘oxidative phosphorylation’.
3. Give the various steps involved in Glycolysis.
Ans: The steps are as follows
Glucose is phosphorylated in the presence of ATP, catalyzed by the enzyme hexokinase.
Glucose – 6 – phosphate is changed into fructose – 6 – phosphate catalyzed by phosphohexose isomers.
Fructose – 6 – phosphate is phosphorylated in the presence of ATP to form Fructose 1, 6 biphosphates.
Fructose 1, 6 biphosphates is split into two molecules of triose phosphate one of 3 – phosphoglycerate dehyde and one of dihydroxyacetone phosphate, which is interconvertible. This reaction is catalyzed by phosphofructokinase.
3 – phosphoglyceraldehyde is oxidized to 1,3 biphosphoglycerate, with the reduction of NAD to NADH.
Phosphoglycerate kinase catalyzes the formation of 3-phosphoglycerate to 1,3 biposphoglycerate and 1 molecule of ATP is produced directly (substrate phosphation).
3-phosphoglycerate is converted into 2-phosphoglycerate and then into phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
PEP is converted into pyruvate along with the formation of one molecule of ATP directly. The enzyme pyruvate kinase catalyzes this step.
The end products of glycolysis are 2 molecules of pyruvic acid + 2 NADH + 2ATP
Related Study Materials for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12
S.No | Important Other Links for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 |
1. | |
2. |
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter-wise Important Questions
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter-wise Important Questions and Answers cover topics from all other chapters, helping students prepare thoroughly by focusing on key topics for easier revision.
Additional Study Materials for Class 11 Biology
S.No | Study Materials for Class 11 Biology |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Papers |

























