NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings (Book Solutions)
1. Where do I find the explanation for Matter for class 9 Science?
NCERT Exemplar for class 9 science Chapter 1 – Matter in our surroundings has the entire explanation that’s needed for students to learn. It is available on Vedantu.com and has been created in tandem with the NCERT guidelines. The book has beautiful illustrations to help one understand the concepts in their entirety. By posing real-life situations, the author makes one ponder about the topics so that they can apply them to their everyday lives and relate to them. Refer to the book on a continual basis to clarify doubts.
2. How do I know which online site to trust when it comes to preparing for class 9 science examinations?
Students can check out Vedantu before they start prepping for class 9 science examinations. This site has the study material that’s needed for not just examinations but also for the sake of personal learning and absorption. The material present has been crafted carefully so that the students find it interesting to read and practice. You will be able to secure better and higher grades if you read these regularly. Vedantu’s notes have benefitted millions of children and they’re one of the most trustworthy academic portals.
3. Where can I find a proper explanation of the concept of Condensation for Class 9 Science NCERT?
A proper explanation of the concept of condensation can be found on NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings as well as the Vedantu website.
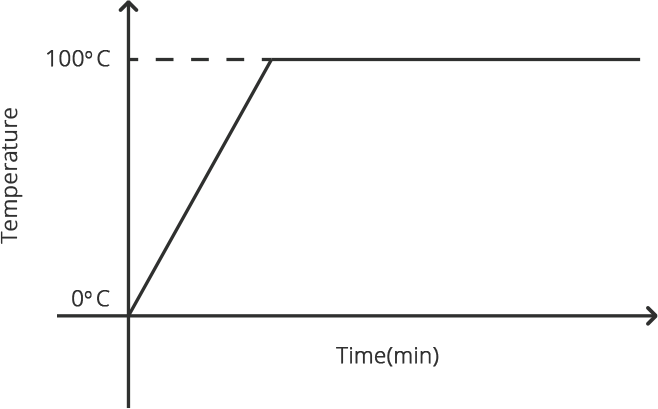
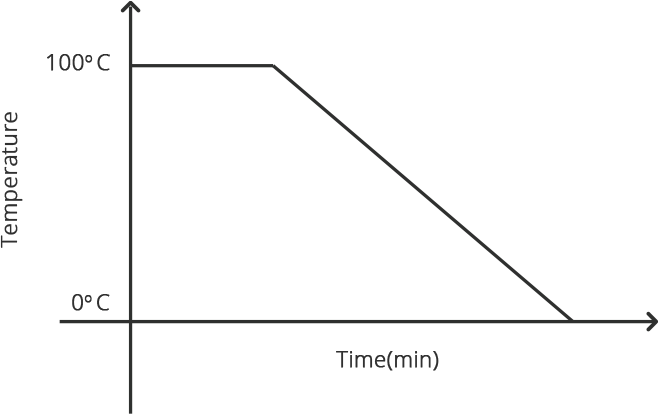
When any gas or vapor gets cooled sufficiently, the process of it turning into liquid is termed condensation. It is the polar opposite of vaporization or boiling.
Various experts in the field of Science have together come up with the book and so, the explanations of all the concepts are very simplified for the pupils.
4. How do I revise for NCERT Class 9 Science?
You can go to NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings on Vedantu.com. The site has the subject matter as per the CBSE guidelines and so, everything has been covered. You can either refer to the notes in the online mode or download it into a PDF format and then read later on. Either way, these notes are of great help for those seeking to learn in-depth and do well in their examinations. You can even make your own notes after reading these and study from them.
5. Are all the important aspects covered in NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings?
Yes, all the vital topics and the sub-topics have been taken care of in NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 1- Matter in our surroundings. Before one sits for examinations, one should go through the book as it will help him/her revise all that has been taught. Moreover, the solutions provided in the book are challenging enough, and solving them will see to it that you score really well. You can find the book on Vedantu.com as it is a bankable site for students looking to learn.