NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current (Book Solutions)
1. What are the components present in NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current?
Components in Chapter 13 of NCERT for class 10:
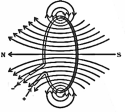
What is the magnetic field and what are magnetic field lines?
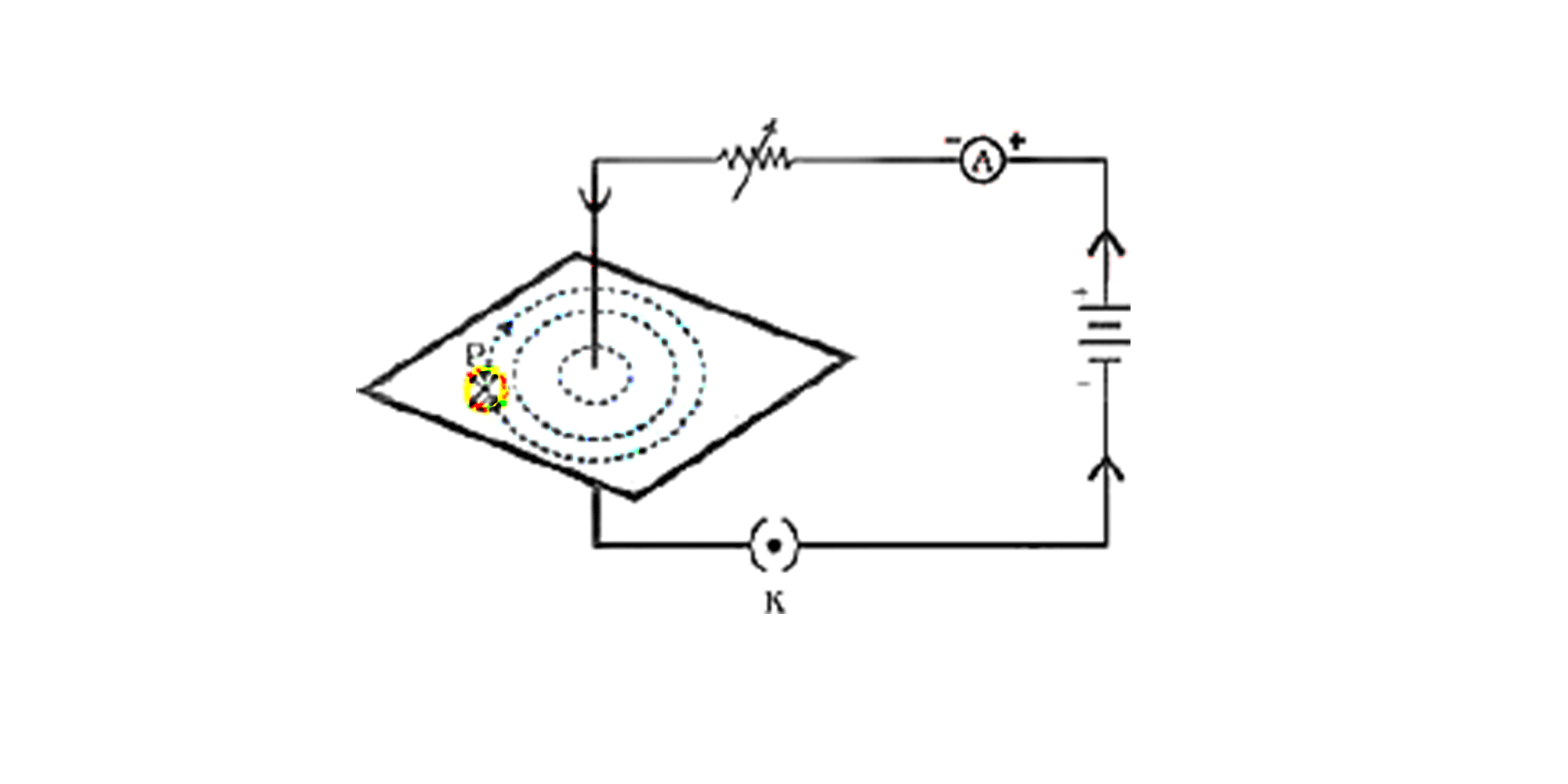
Magnetic field lines due to current carrying conductor
The magnetic field through a straight conductor
The right hand thumb rule
The magnetic field in a circular loop
The magnetic field in a solenoid
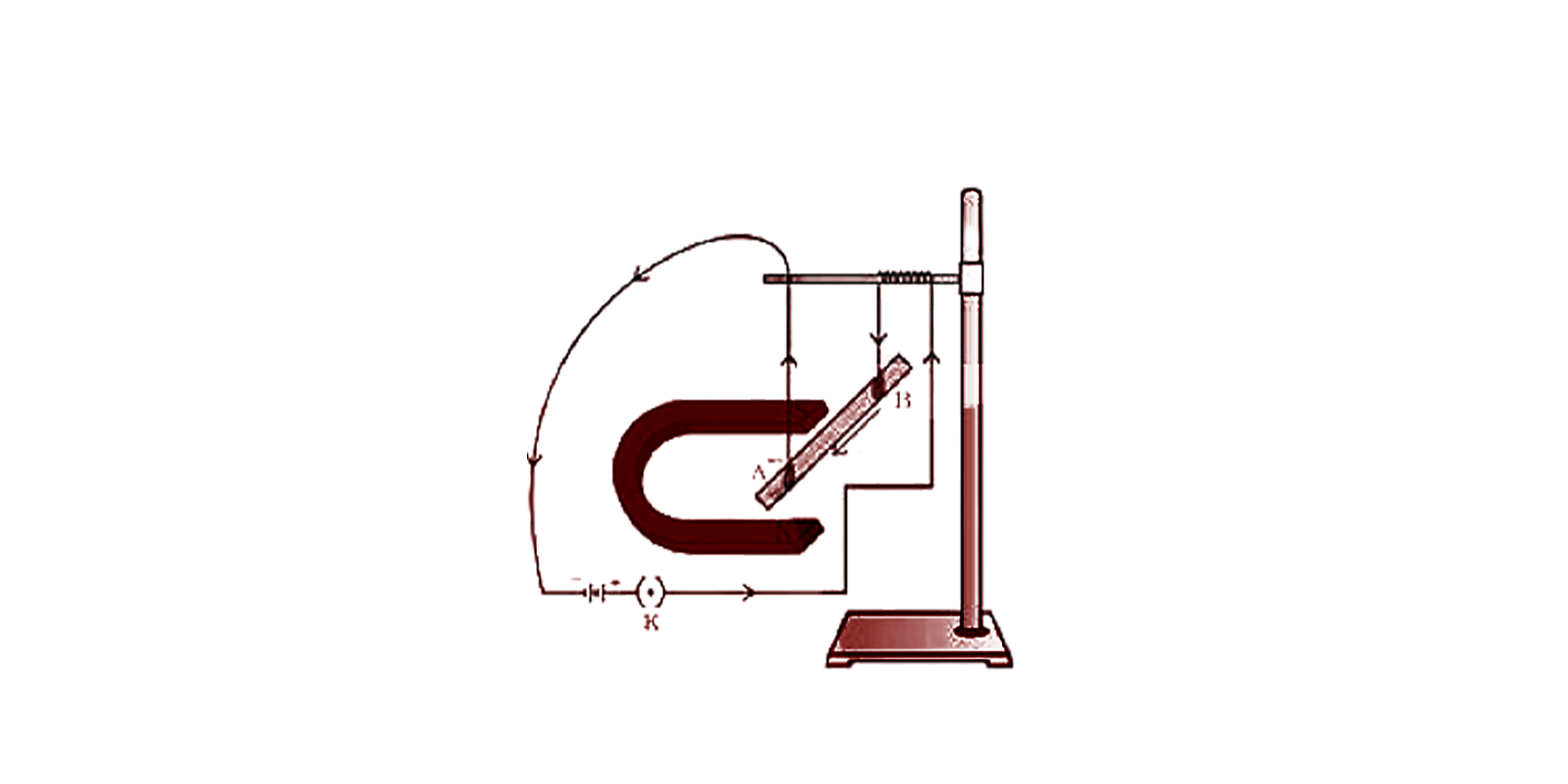
Force on a current-carrying conductor in the magnetic field
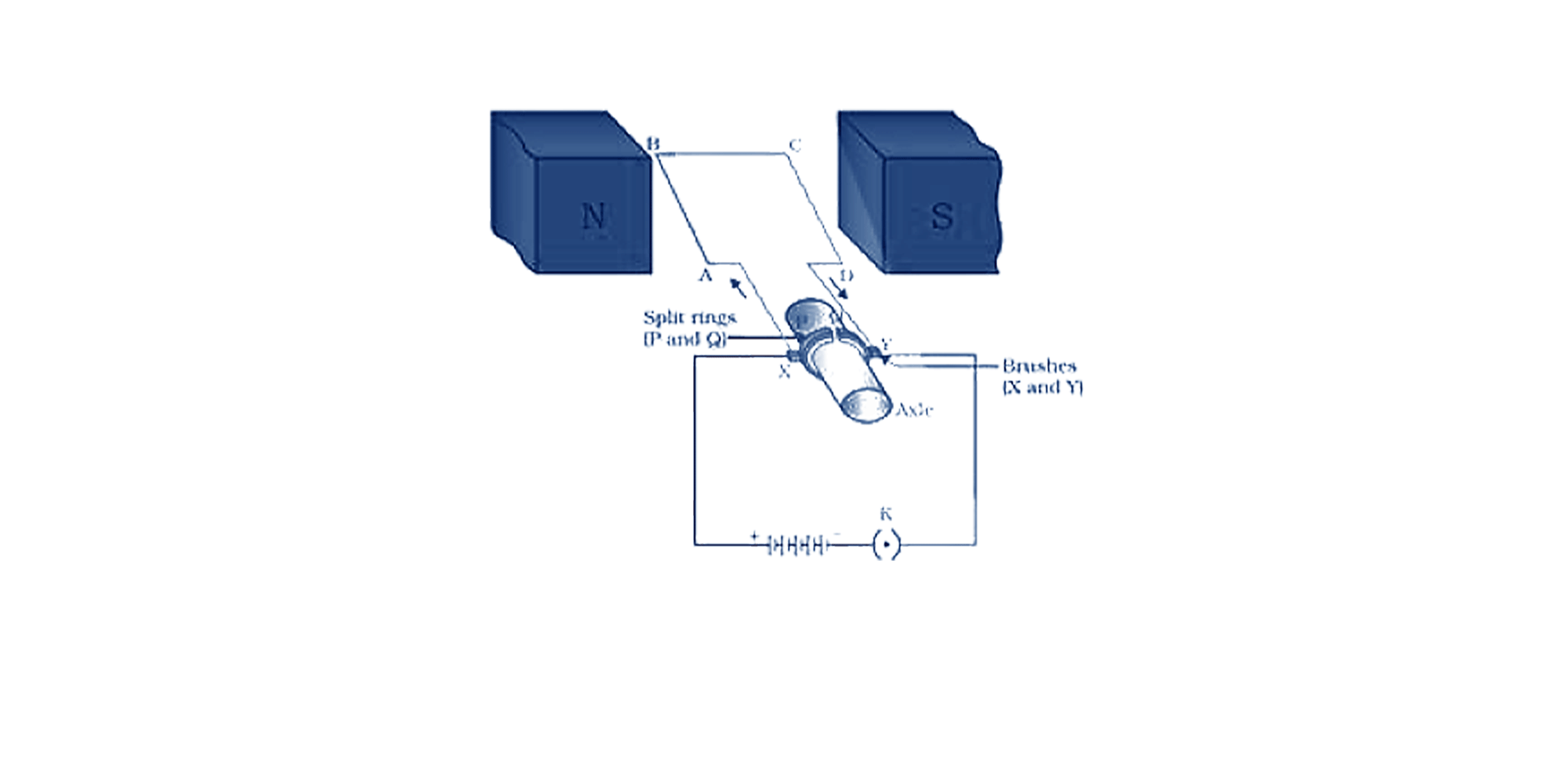
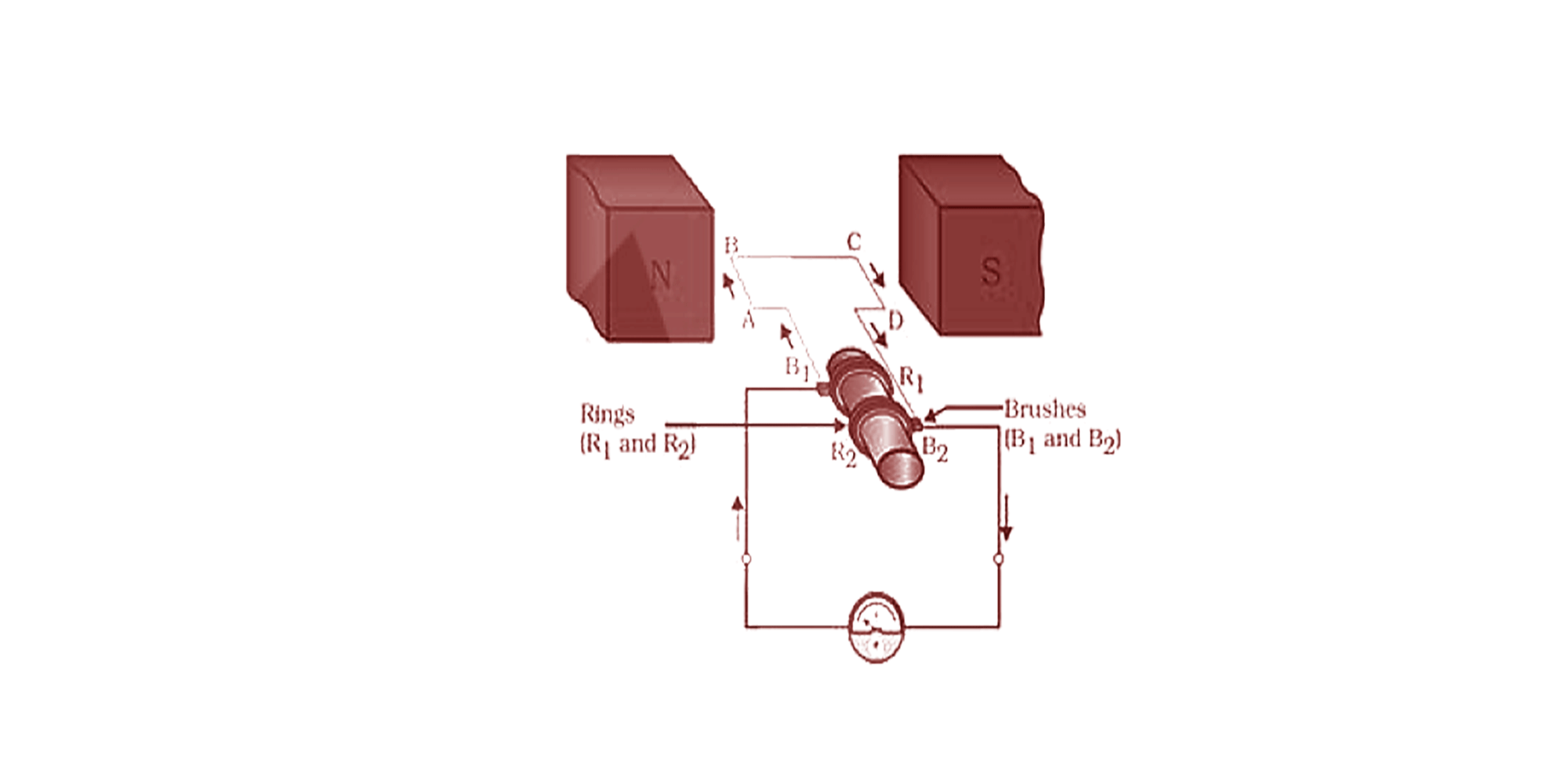
Electric motor and electric generator
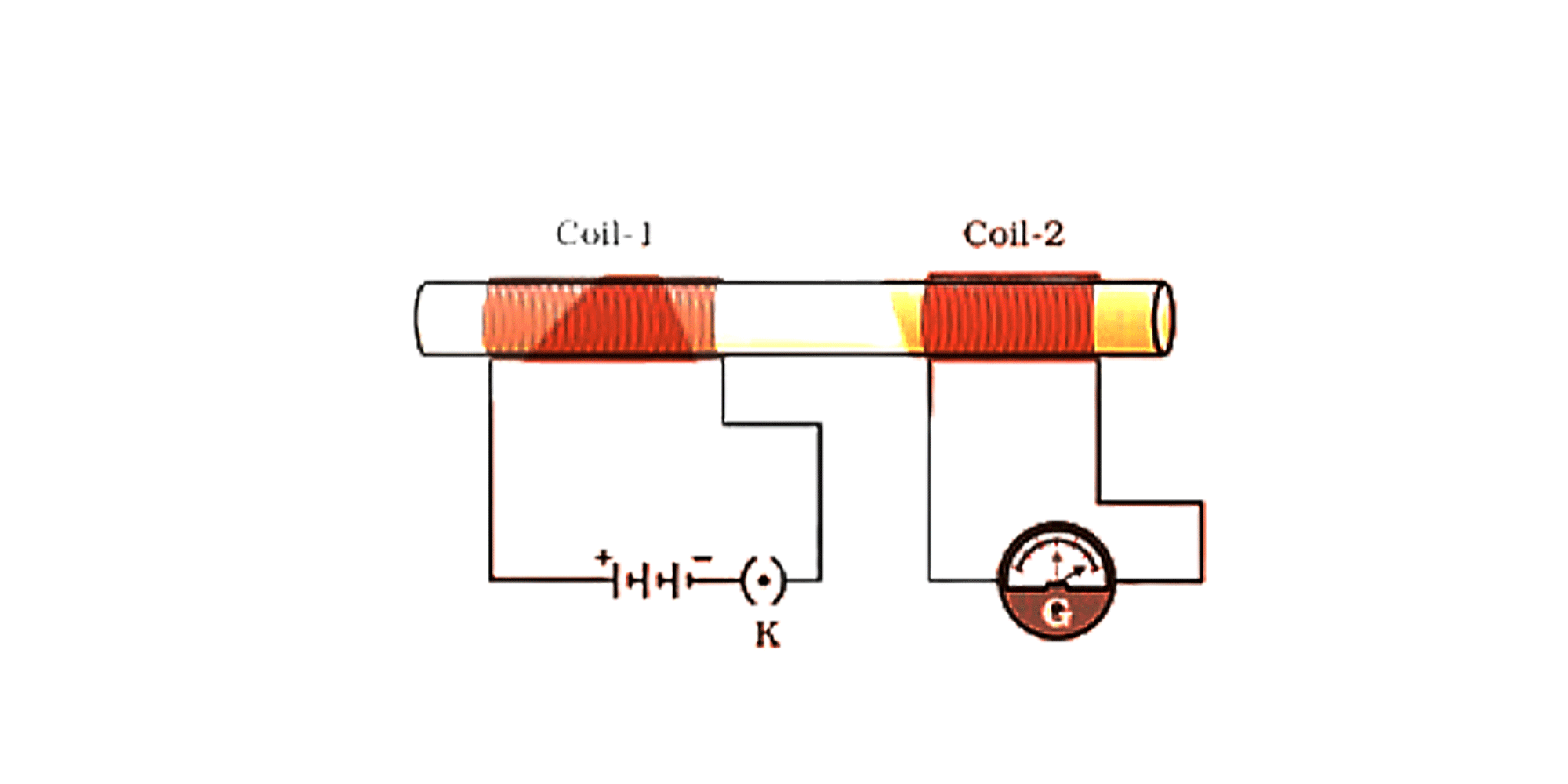
Electromagnetic induction
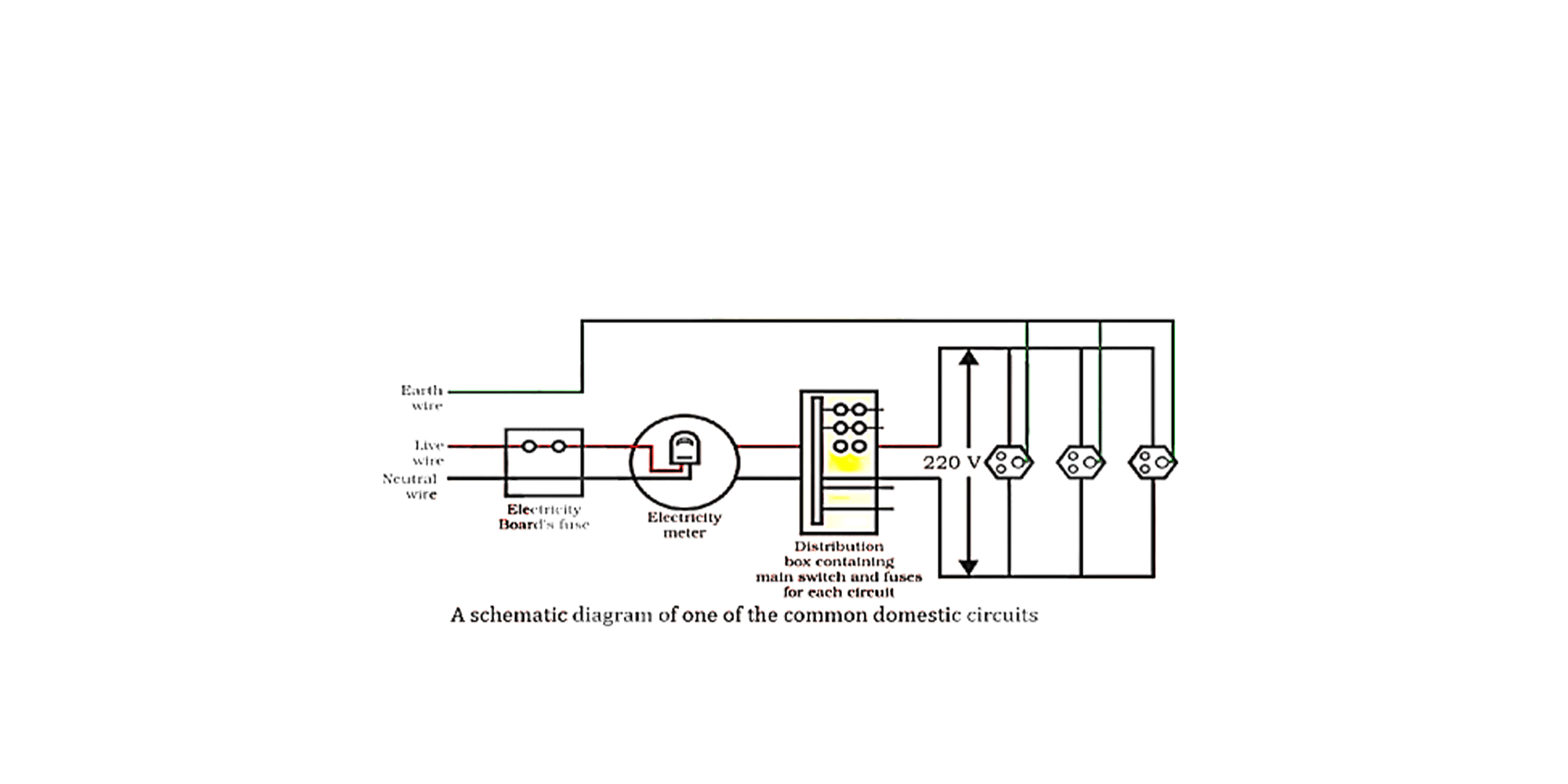
Domestic electric circuits
Students are advised to study all the topics without leaving any of them for a better understanding of the concepts. It will not only help in improving your scores but also helps you understand complex topics.
2. How can students improve scores in board exams using NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current?
The NCERT exemplar is prepared by the experts after carefully making a detailed survey of the exam pattern and needs. They all have made extensive research into these concepts. It gives a comprehensive understanding of all the topics in the chapter. Practising these questions along with the regular study of their textbooks will improve students’ scores. Students can study them online or offline from Vedantu. They can also download free PDFs from the links provided
3. What is a fuse and how is it important in a circuit?
Fuse is a safety component used in an electric circuit. It has been used in electrical engineering for ages. It protects the circuit from shutting down in case of an overload of electric current. It is also known as a “sacrificial device” in the circuit. The working principle behind it is the heating effect of the current. A metallic wire is used in the fuse and when there is an overload of electricity, it gets melted due to an increase in temperature. Melting of the wire will break down the circuit. Generally, copper is used infused. They are always connected in series to let the current flow through them. Current rating, voltage rating, temperature are some of the important components to be considered while selecting a fuse.
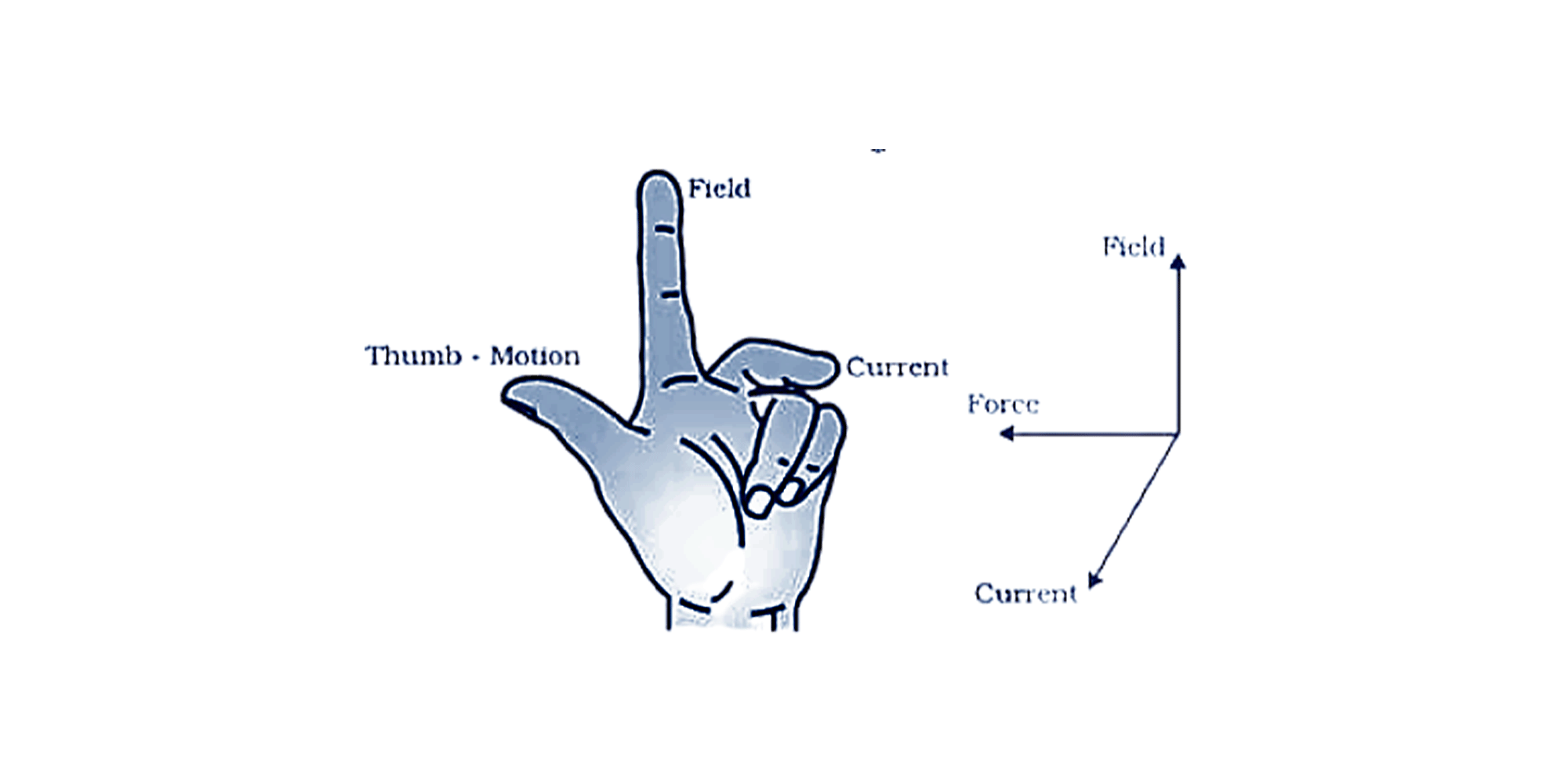
4. What is right - hand thumb rule?
This rule is also known as Fleming’s right-hand thumb rule, named after the person who invented it. It's a simple technique used in maths and physics to understand vectors in 3 dimensions. It was invented for use in electromagnetism in the 19th century by a British Physicist. It is used to determine the cross-product of velocity. It is used to calculate the angular velocity of a rotating object and the rotational velocity of any point on the rotating object. It is also used to measure induced current from motion into a magnetic field.
5. What is electromagnetic induction?
It is a process in which a conductor is put in a particular position and the magnetic field varies or the magnetic field is static but the conductor moves. It produces electromotive force in the conductor. This law was discovered by Michael Faraday in the 19th century. Debit and credit cards which we use while shopping work on this principle of electromagnetic induction. Transformers, ac generators also use this principle to function.