NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science - Carbon and Its Compounds - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds exercise questions with solutions will help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. Register Online for Class 10 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in the CBSE board examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for better solutions can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Grade 10 Science(Chemistry) Chapter No. 4 - Carbon and its Compounds
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
1. Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of
(a) carbon monoxide only
(b) carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
(c) carbon dioxide only
(d) coal
Ans: Option (c) is correct.
2. Which of the following statements are usually correct for carbon compounds? These
(i) are good conductors of electricity
(ii) are poor conductors of electricity
(iii) have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(iv) do not have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (d) is correct.
3. A molecule of ammonia $\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)$ has
(a) only single bonds
(b) only double bonds
(c) only triple bonds
(d) two double bonds and one single bond
Ans: Option (a) is correct.
4. Buckminsterfullerene is an allotropic form of
(a) phosphorus
(b) sulphur
(c) carbon
(d) tin
Ans: Option (c) is correct.
5. Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
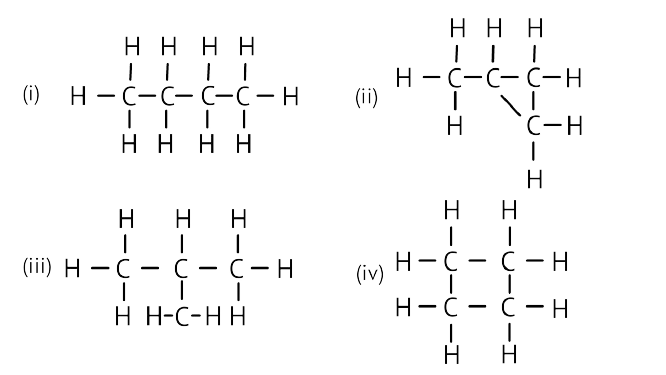
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (c) is correct.
6. ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{OH}}\mathop \to \limits^{{\text{ Alkaline KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4} + {\text{ Heat }}} {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{COOH}}$
In the above given reaction, alkaline ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$text acts as
(a) reducing agent
(b) oxidising agent
(c) catalyst
(d) dehydrating agent
Ans: Option (b) is correct.
7. Oils on treating with hydrogen in the presence of palladium or nickel catalyst form fats. This is an example of
(a) Addition reaction
(b) Substitution reaction
(c) Displacement reaction
(d) Oxidation reaction
Ans: Option (a) is correct.
8. In which of the following compounds, $- {\text{OH}}$ is the functional group?
(a) Butanone
(b) Butanol
(c) Butanoic acid
(d) Butanal
Ans: Option (b) is correct.
9. The soap molecule has a
(a) hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
(b) hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
(c) hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
(d) hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
Ans: Option (a) is correct.
10. Which of the following is the correct representation of electron dot structure of nitrogen?
(a)\[:\ddot N:\ddot N:\]
(b)\[:\mathop {\text{N}}\limits^. :\mathop {\text{N}}\limits^. :\]
(c)\[\colon \ddot{N}\vdots \vdots \dot{N} \colon\]
(d)\[\colon N\vdots \vdots N \colon\]
Ans: Option (d) is correct.
11. Structural formula of ethyne is
(a) ${\text{H}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} - {\text{H}}$
(b) ${{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} - {\text{H}}$
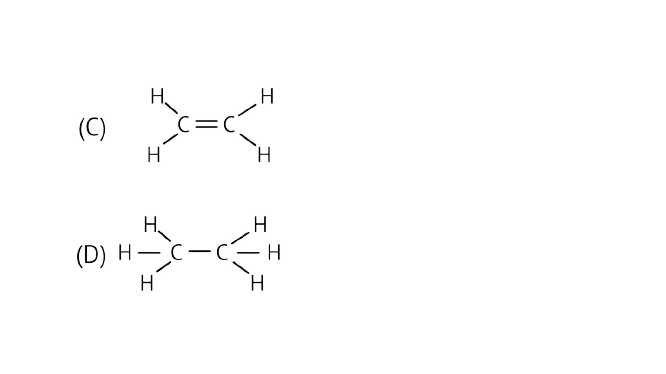
Ans: Option (a) is correct.
12. Identify the unsaturated compounds from the following
(i) Propane
(ii) Propene
(iii) Propyne
(iv) Chloropropane
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Ans: Option (d) is correct.
13. Chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbons at room temperature in the
(a) absence of sunlight
(b) presence of sunlight
(c) presence of water
(d) presence of hydrochloric acid
Ans: Option (b) is correct.
14. In the soap micelles
(a) the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
(b) ionic end of soap is in the interior of the cluster and the carbon chain is out of the cluster.
(c) both ionic end and carbon chain are in the interior of the cluster
(d) both ionic end and carbon chain are on the exterior of the cluster
Ans: Option (a) is correct.
15. Pentane has the molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_5}{{\text{H}}_{12}}$. It has
(a) $5$ covalent bonds
(b) $12$ covalent bonds
(c) $16$ covalent bonds
(d) $17$ covalent bonds
Ans: Option (c) is correct.
16. The structural formula of benzene is
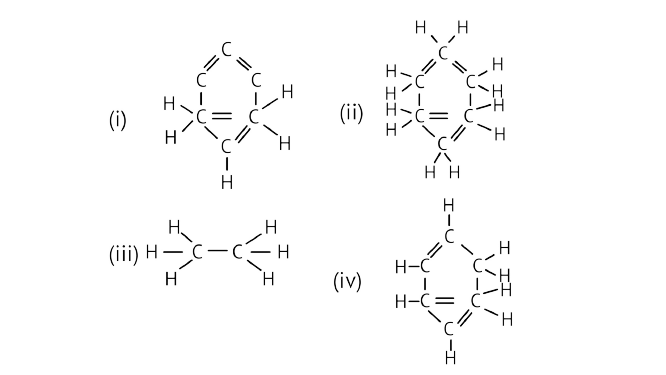
Ans: Option (c) is correct.
17. Ethanol reacts with sodium and forms two products. These are
(a) sodium ethanoate and hydrogen
(b) sodium ethanoate and oxygen
(c) sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
(d) sodium ethoxide and oxygen
Ans: Option (c) is correct.
18. The correct structural formula of butanoic acid is
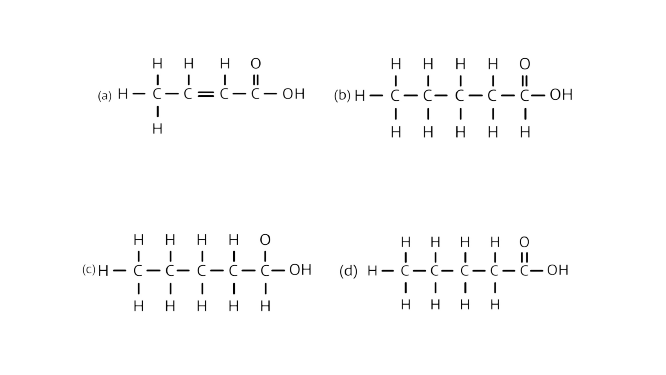
Ans: Option (d) is correct.
19. Vinegar is a solution of
(a) $50\% - 60\%$ acetic acid in alcohol
(b) $5\% - 8\%$ acetic acid in alcohol
(c) $5\% - 8\%$ acetic acid in water
(d) $50\% - 60\%$ acetic acid in water
Ans: Option (c) is correct.
20. Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because
(i) mineral acids are completely ionized
(ii) carboxylic acids are completely ionized
(iii) mineral acids are partially ionized
(iv) carboxylic acids are partially ionized
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (a) is correct.
21. Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g. hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of
(a) helium
(b) neon
(c) argon
(d) krypton
Ans: Option (b) is correct.
22. The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is
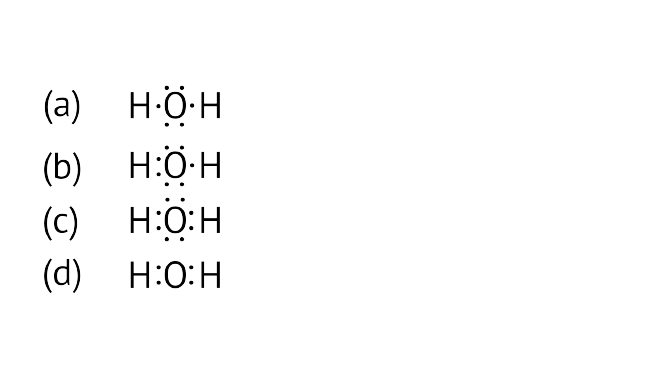
Ans: Option (c) is correct.
23. Which of the following is not a straight chain hydrocarbon?
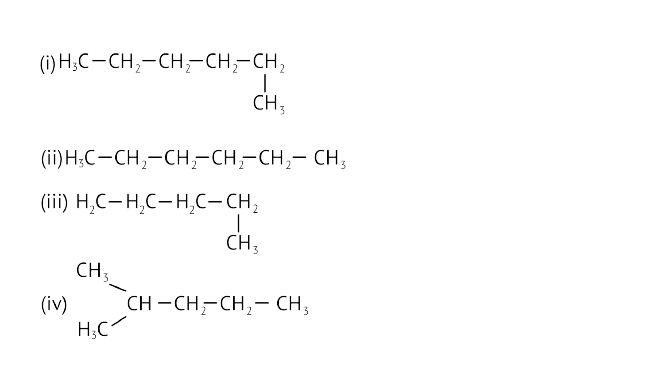
Ans: Option (d) is correct.
24. Which among the following are unsaturated hydrocarbons?
(i) ${{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$
(ii) ${{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}} - {\text{C}} \equiv {\text{C}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$
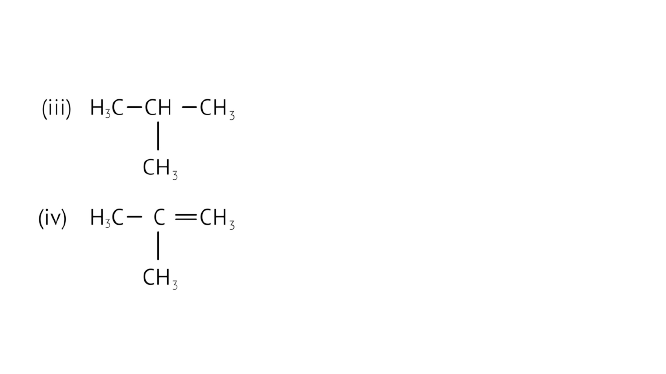
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (c) is correct.
25. Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series?
(a) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_4}$
(b) ${{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_6}$
(c) ${{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_8}$
(d) ${{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}$
Ans: Option (d) is correct.
26. The name of the compound ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{CHO}}$ is
(a) Propanal
(b) Propanone
(c) Ethanol
(d) Ethanal
Ans: Option (a) is correct.
27. The heteroatoms present in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{O}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{Cl}}$ are
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: Option (d) is correct.
28. Which of the following represents saponification reaction?
(a) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {\text{NaOH}}\mathop \to \limits^{{\text{CaO}}} {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_4} + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_3}$
(b) \[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + {{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COO}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\]
(c) $2{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + 2{\text{Na}} \to 2{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {{\text{H}}_2}$
(d) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COO}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5} + {\text{NaOH}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{OH}}$
Ans: Option (d) is correct.
29. The first member of alkyne homologous series is
(a) ethyne
(b) ethene
(c) propyne
(d) methane
Ans: Option (a) is correct.
Very Short Answers (VSA)
30. Draw the electron dot structure of ethyne and also draw its structural formula.
Ans:

$H - C \equiv C - H$
31. Write the names of the following compounds
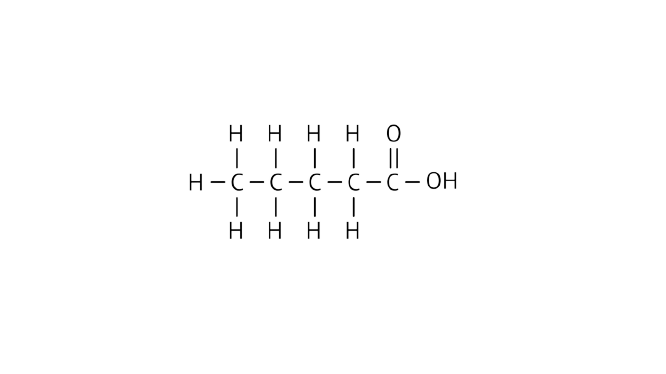
Ans: Pentanoic acid
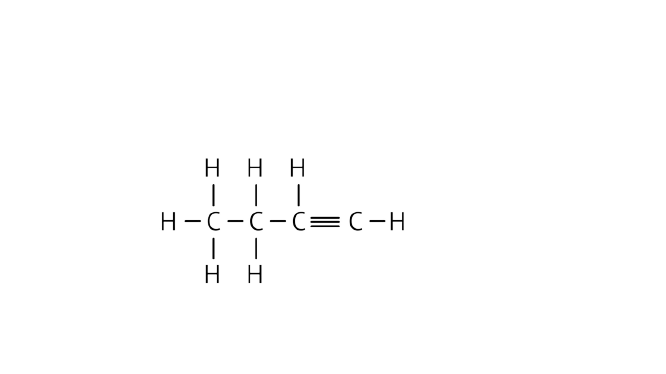
Ans: Butyne
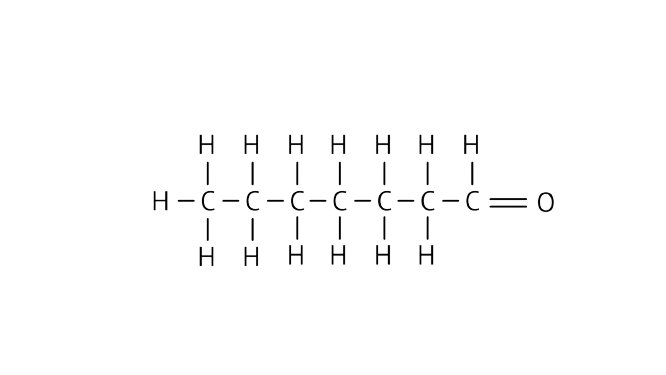
Ans: Heptanal
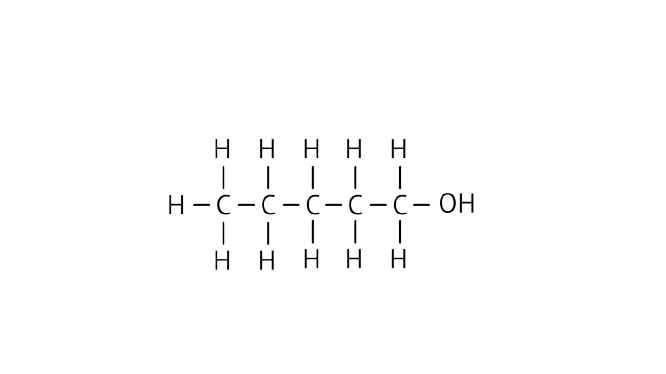
Ans: Pentanol
32. Identify and name the functional groups present in the following compounds.
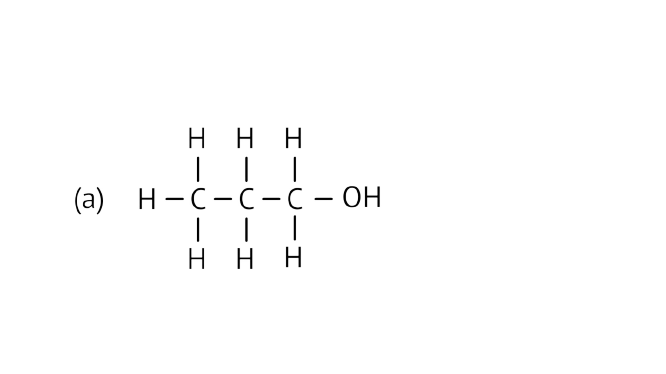
Ans: Alcohol
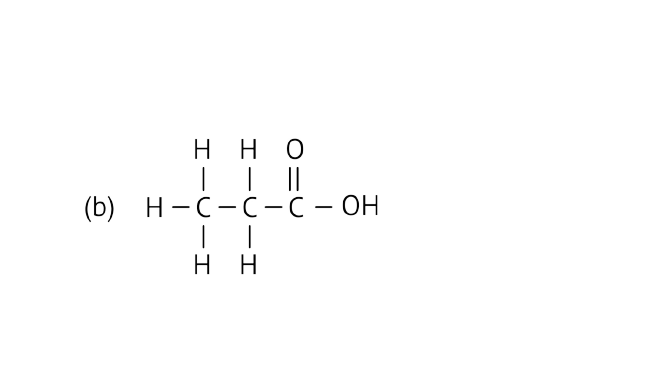
Ans: Carboxylic acid
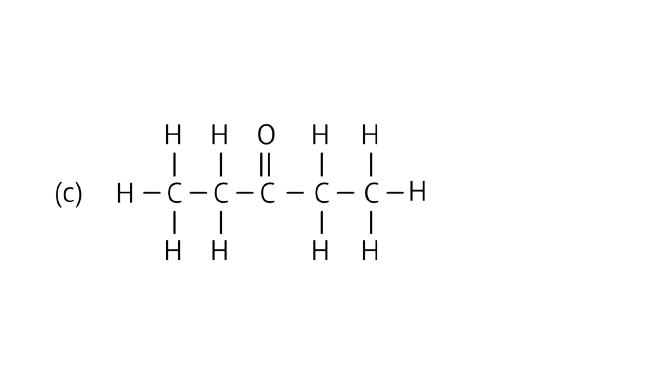
Ans: Ketone
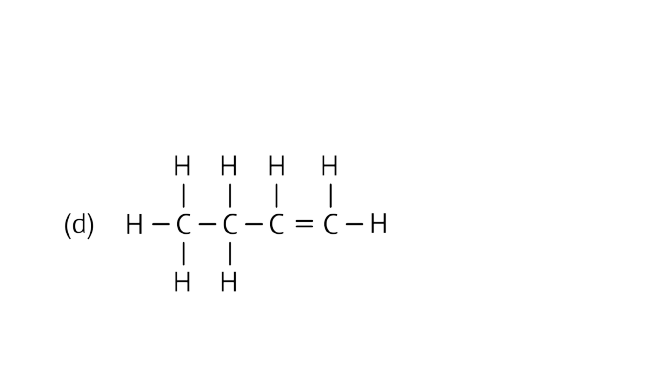
Ans: Alkene
33. A compound X is formed by the reaction of a carboxylic acid ${{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_4}{{\text{O}}_2}$ and an alcohol in presence of a few drops of ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ followed by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid as used in this reaction. Give the names and structures of following,
(a) carboxylic acid
Ans: Name: Ethanoic acid
Structure:
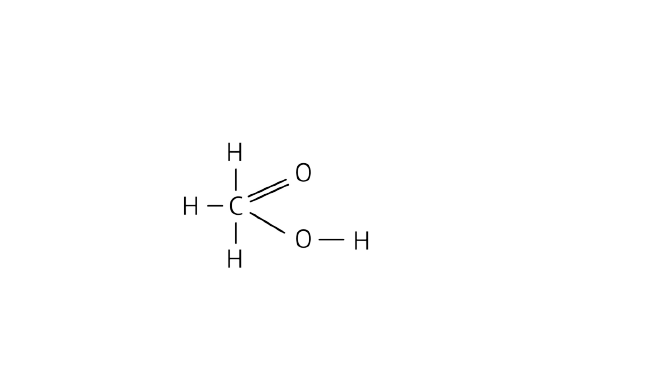
(b) alcohol
Ans: Name: Ethanol
Structure:
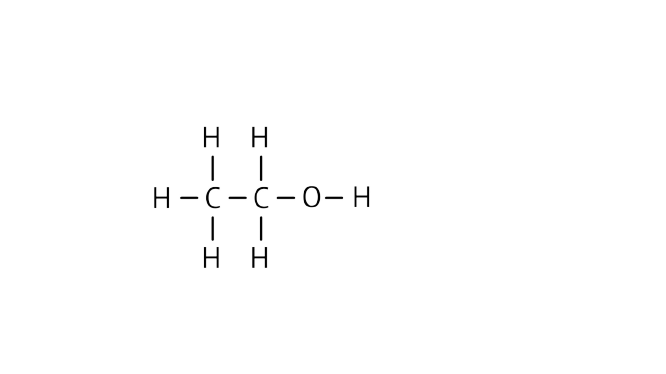
(c) the compound X.
Ans: Name: Ester (ethyl ethanoate)
Structure:
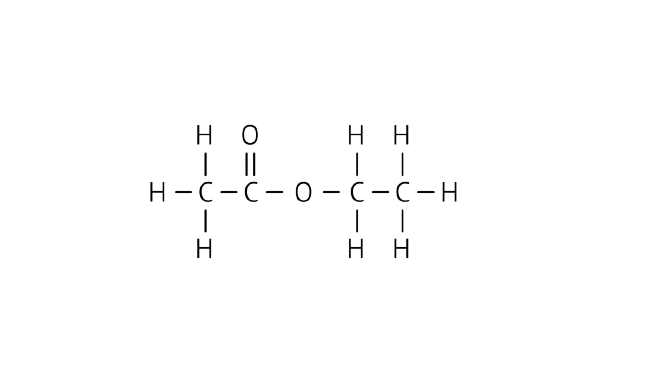
34. Why detergents are better cleansing agents than soaps? Explain.
Ans: Detergents are big chain carboxylic acid ammonium or sulphonate salts. With calcium or magnesium ions, the charged ends of these compounds do not produce an insoluble precipitate. $Ca$ and $Mg$ ions are present in hard water.
As a result, detergents perform well even in hard water. As a result, detergents outperform soaps as cleaning agents.
35. Name the functional groups present in the following compounds
(a)${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COC}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$
Ans: Ketone
(b) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}}$
Ans: Carboxylic acid
(c)${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHO}}$
Ans: Aldehyde
(d) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}$
Ans: Alcohol
36. How is ethene prepared from ethanol? Give the reaction involved in it.
Ans: To obtain ethene, ethanol is heated at 443 k in the presence of an excess of concentrated sulphuric acid.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}\mathop {\xrightarrow{{{\text{Conc}}{\text{. H}},{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}}\limits^{\text{ }} {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
37. Intake of small quantity of methanol can be lethal. Comment.
Ans: In the liver, methanol is converted to methane. Methanal coagulates the cytoplasm of cells, killing them. Methanal also has an effect on the visual nerves, causing blindness. As a result, even a little amount of methanal can be fatal.
38. A gas is evolved when ethanol reacts with sodium. Name the gas evolved and also write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Ans: Hydrogen gas is evolved in this equation.
$2{\text{Na}} + 2{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}} \to 2{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{ONa}} + {{\text{H}}_2}$
39. Ethene is formed when ethanol at $443\;{\text{K}}$ is heated with excess of concentrated sulphuric acid. What is the role of sulphuric acid in this reaction? Write the balanced chemical equation of this reaction.
Ans: The role of sulphuric acid in this reaction is like a catalyst and a dehydrating agent.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow{{\operatorname{C} onc.{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
40. Carbon, Group ($14$) element in the Periodic Table, is known to form compounds with many elements.
Write an example of a compound formed with
(a) chlorine (Group $17$ of Periodic Table)
Ans: Carbon tetrachloride $CC{l_4}$.
(b) oxygen (Group $16$ of Periodic Table)
Ans: Carbon Dioxide $(C{O_2})$.
41. In electron dot structure, the valence shell electrons are represented by crosses or dots.
(a) The atomic number of chlorine is $17$. Write its electronic configuration.
Ans: Electronic configuration: $2,8,7$.
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of chlorine molecule.
Ans:
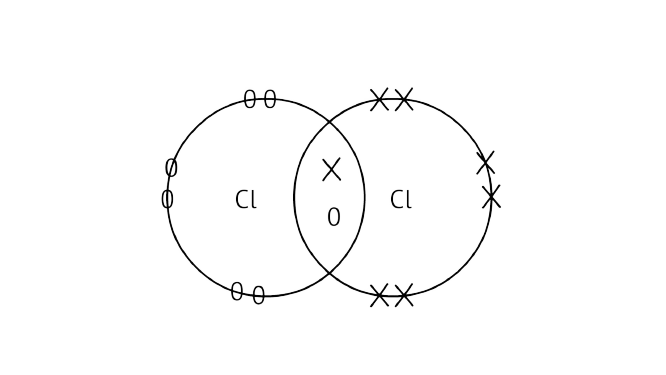
42. Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Compare the ability of catenation of the two elements. Give reasons.
Ans: Catenation occurs in both carbon and silicon. However, silicon compounds are reactive and less stable. Carbon bonds, on the other hand, are extremely strong, making organic chemicals more stable than silicon compounds. Carbon is thought to be more capable of catenation than silicon.
43. Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain multiple bonds between the two C-atoms and show addition reactions. Give the test to distinguish ethane from ethene.
Ans: Saturated hydrocarbons burn with a clear flame in most cases. Unsaturated hydrocarbons create a lot of soot when they burn with a yellow flame. As a result, when ethane is burned, it produces a clean flame with no soot. When ethene is burned, it generates a yellow flame and a lot of soot.
44. Match the reactions given in Column (A) with the names given in column (B).
Column (A) | Column (B) |
(a) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}}\mathop \to \limits^{{{\text{H}}^ + }} {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOC}}{{\text{H}}_3} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ | (i) Addition reaction |
(b) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Ni}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$ | (ii) Substitution reaction |
(c) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_4} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}\mathop \to \limits^{{\text{ Sunlight }}} {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{Cl}} + {\text{HCl}}$ | (iii) Neutralisation reaction |
(d) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + {\text{NaOH}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ | (iv) Esterification reaction |
Ans:
Column (A) | Column (B) |
(a) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}}\mathop \to \limits^{{{\text{H}}^ + }} {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOC}}{{\text{H}}_3} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ | (iv) Esterification reaction |
(b) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Ni}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$ | (i) Addition reaction |
(c) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_4} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}\mathop \to \limits^{{\text{ Sunlight }}} {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{Cl}} + {\text{HCl}}$ | (ii) Substitution reaction |
(d) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + {\text{NaOH}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$ | (iii) Neutralisation reaction |
45. Write the structural formulae of all the isomers of hexane.
Ans:
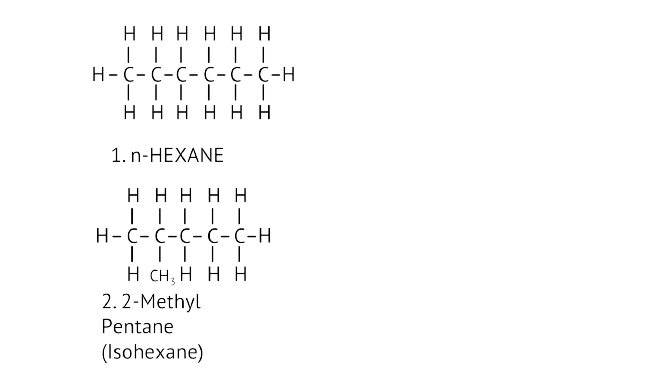

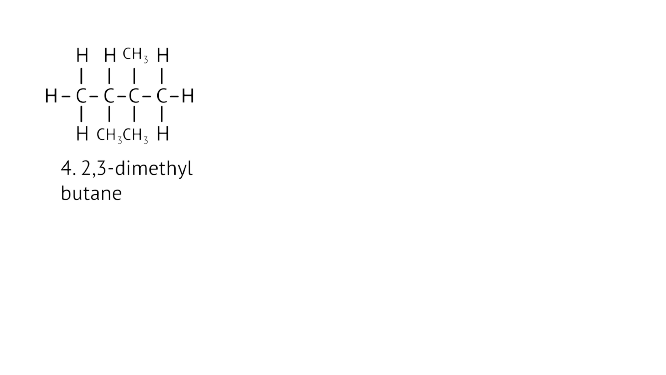
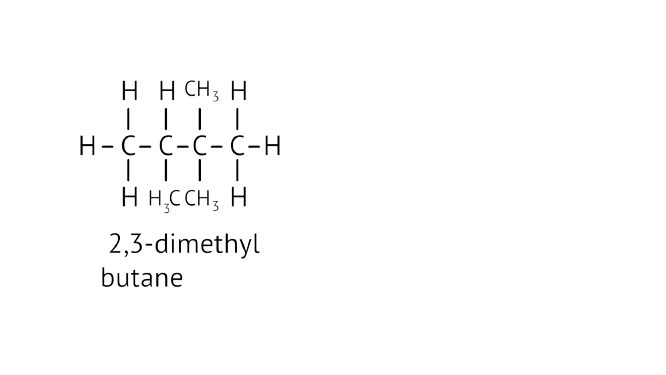
46. What is the role of metal or reagents written on arrows in the given chemical reactions?
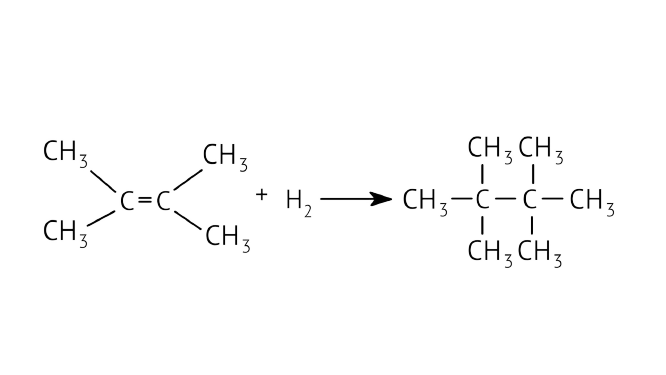
Ans: Catalyst
(b) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow{{Conc.{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COO}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Ans: Catalyst
(c) ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow[{Heat}]{{{\text{Alk}}.{\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}}$
Ans: Oxidizing Agent
Long Answer Questions (LAQ)
47. A salt X is formed and a gas is evolved when ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate. Name the salt X and the gas evolved. Describe an activity and draw the diagram of the apparatus to prove that the evolved gas is the one which you have named. Also, write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
Ans: The salt 'X' is sodium ethanoate$\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}}} \right)$, and the evolved gas is carbon dioxide $\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}} \right)$.
Fill a test tube halfway with ethanoic acid (${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}}$). To the acid, add sodium bicarbonate $\left( {{\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_3}} \right)$. Close the test tube's mouth with a cork and connect a delivery tube to it. Put lime water in another test tube and connect it to the other end of the delivery tube.

As the lime water changes to milky which indicates that $C{O_2}$ gas is present.
So, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + {\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
48. (a) What are hydrocarbons? Give examples.
Ans: Hydrocarbons are hydrogen and carbon compounds such as methane, ethane, ethene, and others.
(b) Give the structural differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with two examples each.
Ans:
Saturated Hydrocarbons | Unsaturated Hydrocarbons |
1. All of the bonds in saturated hydrocarbons are single bonds. | 1. All of the bonds in unsaturated hydrocarbons are double or triple bonds. |
2. Examples are Ethane and methane. | 2. Examples are Ethyne and ethene. |
(c) What is a functional group? Give examples of four different functional groups.
Ans: Functional group - An atom or group of atoms that are connected in a certain way and are responsible for the chemical characteristics of organic molecules. Hydroxyl groups \[\left( { - OH} \right)\], aldehyde groups \[\left( { - CHO} \right)\], carboxylic groups \[\left( { - COOH} \right)\], and so on are examples.
49. Name the reaction which is commonly used in the conversion of vegetable oils to fats. Explain the reaction involved in detail.
Ans: In the conversion of vegetable oils to fats, the addition reaction is employed. This is referred to as oil hydrogenation. Long chains of unsaturated carbons are found in vegetable oils, whereas long chains of saturated carbons are found in animal fats.
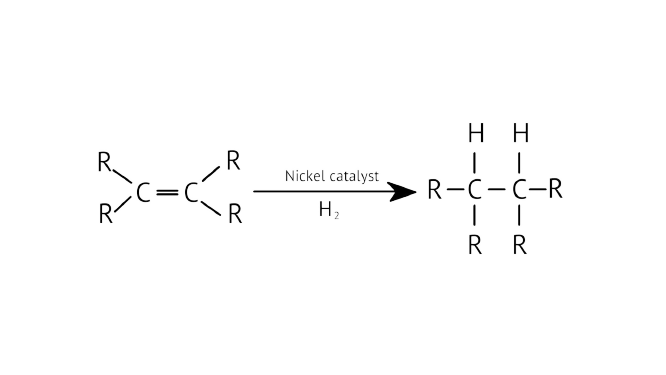
Unsaturated fat is beneficial to one's diet. Saturated fat, on the other hand, is harmful.
50. (a) Write the formula and draw the electron dot structure of carbon tetrachloride.
Ans: Formula: $CC{l_4}$
Electron dot structure:
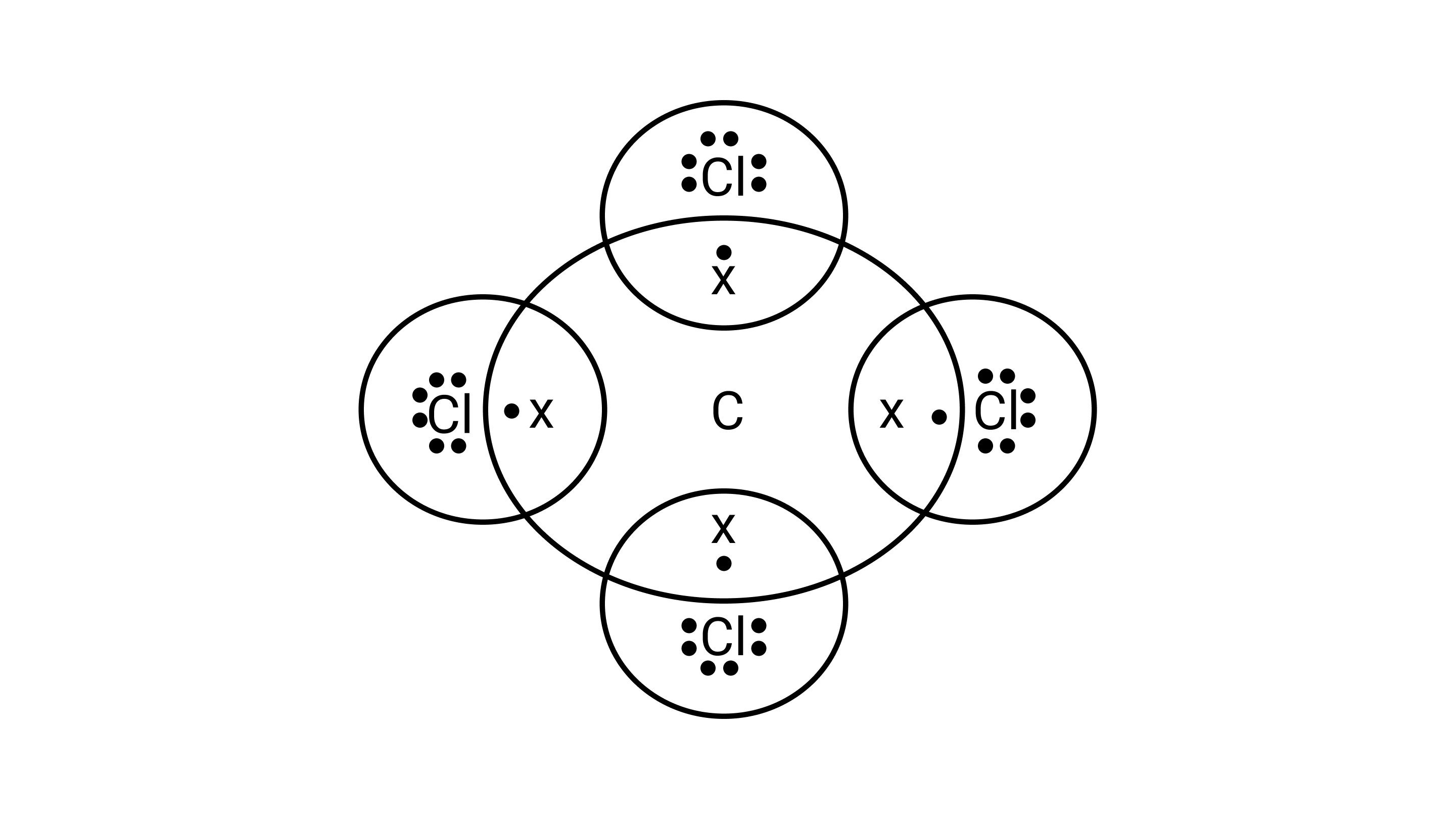
(b) What is saponification? Write the reaction involved in this process.
Ans: When an ester reacts with an alkali, it produces ethanol and sodium ethanoate. This reaction is known as the saponification reaction because it serves as the foundation for the production of soap.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COO}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5} + {\text{NaOH}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{OH}}$
51. Esters are sweet-smelling substances and are used in making perfumes. Suggest some activity and the reaction involved for the preparation of an ester with well labeled diagram.
Ans:
In a test tube, combine $1$ ml ethanol and $1$ml glacial acetic acid. Fill the test tube with a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid. Warm the test tube gently in a water bath for about $5$ minutes. After that, remove the test tube and place the contents in a beaker. Consider the fragrance of the content. The pleasant aroma indicates that ester has been produced.
\[\left ( \underset{Ethanoic~Acid}~CH_{3}COOH \right ) + \left (\underset{Ethanal}~CH_{3}CH_{2}OH \right) \overset{Acid}{\rightarrow} \left (\underset{Ethanal}~CH_{3}COCH_{2}CH_{3} \right)\]
52. A compound C (molecular formula,${{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_4}{{\text{O}}_2}$) reacts with Na- metal to form a compound R and evolves a gas which burns with a pop sound. Compound C on treatment with an alcohol A in presence of an acid forms a sweet smelling compound S (molecular formula,${{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_6}{{\text{O}}_2}$). On addition of ${\text{NaOH}}$ to C, it also gives R and water. S on treatment with ${\text{NaOH}}$ solution gives back R and A.
Identify C, R, A, S and write down the reactions involved.
Ans: Compound 'C' is ethanoic acid. When it interacts with sodium, it produces sodium ethanoate. As a result, component 'R' is either sodium ethanoate or sodium acetate. We already know that hydrogen gas burns with a popping sound. The following equation may be used to describe this reaction:
$2{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + 2{\text{Na}} \to 2{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {{\text{H}}_2}$
When ethanoic acid interacts with methanol in the presence of an acid, we obtain (methyl ethanoate) ester, which has a pleasant odour. As a result, chemical S is methyl ethanoate while molecule A is methanol. This reaction is:
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow{{Acid}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
When sodium hydroxide is introduced to ethanoic acid, sodium ethanoate and water are formed.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + {\text{NaOH}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Methanol and sodium ethanoate are produced when methyl ethanoate is treated with $\[NaOH\]$ solution.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COO}} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} + {\text{NaOH}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{OH}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}}$
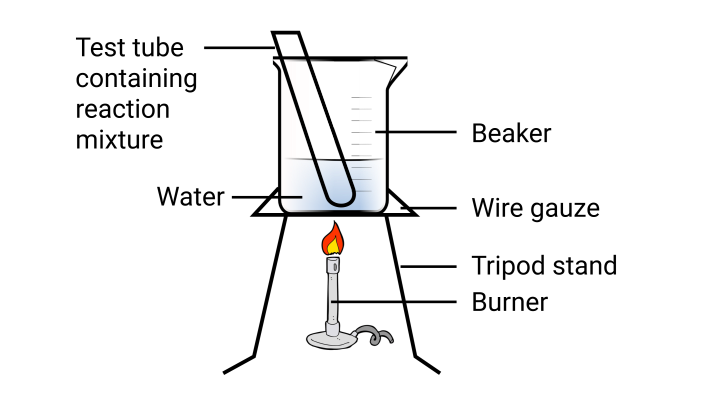
53. Look at Figure \[{\mathbf{4}}.{\mathbf{1}}\] and answer the following questions:

(a) What change would you observe in the calcium hydroxide solution taken in tube B?
Ans: The calcium hydroxide solution in test tube B turns milky.
(b) Write the reaction involved in test tubes A and B respectively.
Ans: In test tube A, Reaction is,
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH}} + {\text{NaHC}}{{\text{O}}_3} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
In test tube B, Reaction is,
${\text{Ca}}{({\text{OH}})_2} + {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{CaC}}{{\text{O}}_3} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
(c) If ethanol is given instead of ethanoic acid, would you expect the same change?
Ans: Ethanol do not react with $NaHC{O_3}$. As a result, the same modification cannot be noticed.
(d) How can a solution of lime water be prepared in the laboratory?
Ans: Fill a beaker halfway with distilled water and add calcium carbonate powder. Wait for the mixture to settle after carefully stirring it. Take the clear liquid from the beaker and decant it. Lime water is the name of this beverage.
54. How would you bring about the following conversions? Name the process and write the reaction involved. Write the reactions.
(a) ethanol to ethene.
Ans: In the presence of an excess of conc. sulphuric acid, ethanol is heated to 443 k. Dehydrogenation is the name given to this reaction. The following equation may be used to describe this reaction:
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{ Conc}}{\text{.H S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
(b) propanol to propanoic acid.
Ans: Propanoic acid is produced by treating propanol with alkaline potassium permanganate or acidified potassium dichromate.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{alk KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}{\text{/ acidified }}{{\text{K}}_2}C{r_2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}}$
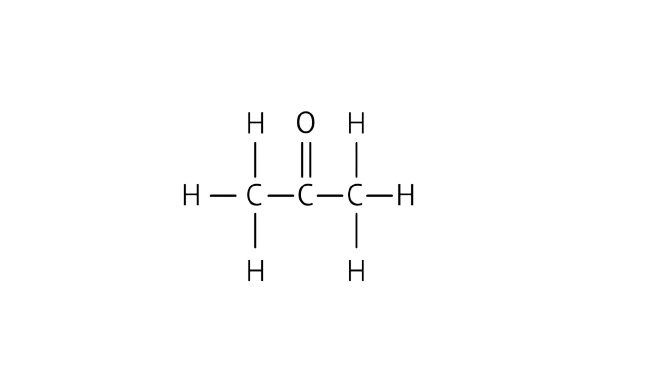
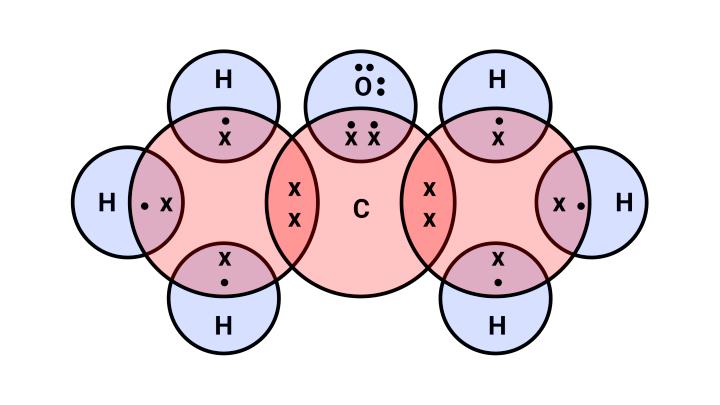
55. Draw the possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_6}{\text{O}}$ and also give their electron dot structures.
Ans: The possible isomers of the compound:
Propanone
Electron dot structure:
2) Propanal
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3} - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} - {\text{CHO}}$
Electron dot structure:
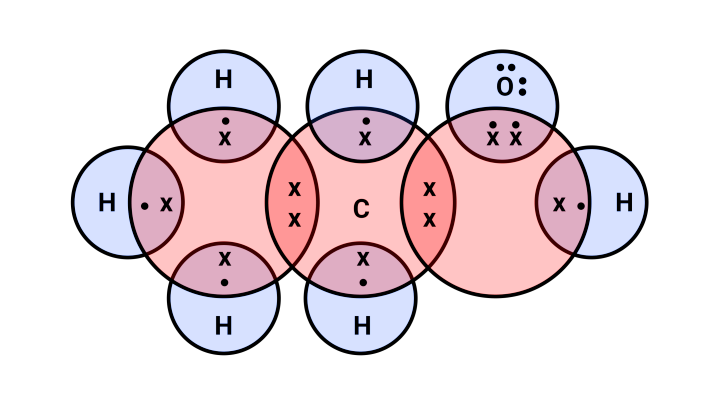
56. Explain the given reactions with the examples
(a) Hydrogenation reaction
Ans: The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to produce a saturated hydrocarbon is referred to as a hydrogenation reaction. The process of turning unsaturated vegetable oil into fat is known as hydrogenation.
\[R_{2}C = RC_{2} + H_{2}\overset{Ni}{\rightarrow}R_{2}C - RC_{2}\]
(b) Oxidation reaction
Ans: The addition of oxygen to alcohol to produce carboxylic acid is referred to as an oxidation reaction. The following is an example of alcohol oxidation.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{alk KMn}}{{\text{O}}_4}{\text{/ acidified }}{{\text{K}}_2}C{r_2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{COOH}}$
(c) Substitution reaction
Ans: Saturated hydrocarbons are relatively inert. However, in the presence of sunshine, chlorine replaces hydrogen one by one.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_4} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}\xrightarrow{{Sunlight}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{Cl}} + {\text{HCl}}$
(d) Saponification reaction
Ans: When ester reacts with an alkali, it produces ethanol and sodium ethanoate.
This reaction is known as the saponification reaction since it is the foundation of soap production.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COO}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5} + {\text{NaOH}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COONa}} + {{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{OH}}$
(e) Combustion reaction
Ans: The reaction that occurs when a material burns in the presence of oxygen is known as combustion. For example;
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_4} + {{\text{O}}_2} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {\text{ heat + light }}$
57. An organic compound A on heating with concentrated ${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}$ forms a compound B which on addition of one mole of hydrogen in presence of Ni forms a compound C. One mole of compound C on combustion forms two moles of ${\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2}$ and \[3\] moles of${{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$Identify the compounds A, B and C and write the chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Ans: Ethanol is compound A. We get ethene when we heat it with strong sulphuric acid. As a result, compound B is ethene. The following equation demonstrates this.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Conc}}{\text{. }}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_4}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Ethane is formed when ethene is heated in the presence of nickel. The following equation demonstrates this.
${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2} = {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Ni}}}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_6}$ (Compound C)
When we burn one mole of ethane, we receive two moles of carbon dioxide and three moles of water, as demonstrated by the equation below.
$2{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_6} + 7{{\text{O}}_2} \to 4{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_2} + 6{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Concepts in Class 10 NCERT Science Chapter 4
The students of Class 10 get to study a lot of concepts that are useful for higher Classes in the NCERT Chapter-4, Carbon and its Compounds. They learn about the Covalent bonds and how they are formed. Then they study the three types of allotropes and their structures named Graphite, Buckminsterfullerene, and diamond.
Then, they come to terms with the versatile nature of carbon in which students learn about the Unsaturated and Saturated compounds, organic compounds. Eventually, they learn about the Chains, Rings, and Branches of the organic compounds and a little about the Homologous series. They should understand the Nomenclature of Carbon compounds, the chemical properties of carbon, and study some important carbon compounds and their properties in detail.
Download this solution file today and get the best answers framed by top subject matter experts of Vedantu. Find out how to answer the specific questions of this chapter and learn how to score better in the board exam.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 - Carbon and Its Compounds (Book Solutions)
1. Where can I find the solutions to NCERT Exemplar for Class 10?
Students of Class 10 can find the Solutions to Class 10 NCERT questions and NCERT Exemplar solutions among many other important study materials only at Vedantu.com for free. These PDFs are accessible to everyone and can be easily downloaded from websites and apps through Vedantu just by signing in. These solutions are easy to understand and are beneficial to every Class 10 student for their board preparation. These Pdfs can be downloaded and then studied offline, hard copy, and soft copy. If you download Class 10 Science - Carbon and Its Compounds solutions, you will understand how it can boost your studies.
2. How can NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science help in getting better marks?
The students of Class 10 will find that as compared to NCERT questions, the questions from NCERT Exemplar require more practice and conceptual in order to solve them. When the students practice for Class 10 Science using the NCERT Exemplar then their concepts become better and this shows they can even practice questions that require higher order thinking ( or HOTs). Being able to solve all these questions helps a student to prepare for the boards in the best way and ensures that the student gets better marks in the Class 10 board examination.
3. What can I do to understand the NCERT Class 10 Chapter-4, Carbon and its Compounds?
The students of Class 10 who are preparing the Chapter-4 NCERT, Carbon and its compounds should be at ease with all the concepts and should have a clear idea about why Carbon forms covalent bonds and other theoretical questions which should be understood and remembered. The names of the allotropes are also important for the students to remember and their properties among other things. They are also supposed to know about what nomenclature is and how it is applied for different compounds of carbon.
4. Are the Questions provided in NCERT and NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter-4 Carbon and its compound important?
Yes, all the questions present in NCERT and NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter-4 Carbon and its compound are important as they are important for every Class 10 student appearing for boards. All the questions are based on the Chapter and in the CBSE exams of Class 10 nothing comes from outside and every question is based on these two books. In order to practice smart and better, each child should be introduced to every question and should learn the meaning of each term, definition, or property with clarity. To make it better, they need to download the solutions for the exercises of these books one after the other. For this, Vedantu is the best portal to access to find the ideal solutions for Class 10 science chapters.






































