NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science - Improvement in Food Resources - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Every NCERT Solution is provided to make the study simple and interesting on Vedantu. Subjects like Science, Maths, English will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 9 Science, Maths solutions and solutions of other subjects. You can also download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
The purpose of this chapter is to introduce students to the types of crops and how we can improve their production. This chapter begins with an introduction to fertilizers and how to use them. The second section of the course includes topics such as poultry farming, fish production, and beekeeping. For a better understanding of the concepts in this chapter, students are kindly requested to solve the NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science(Biology) Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which one is an oil yielding plant among the following?
(a) Lentil
(b) Sunflower
(c) Cauliflower
(d) Hibiscus
Ans: Option (b) is the correct choice.
Among the given options an oil yielding plant is sunflower. Lentils are legumes (pulses), cauliflower is a vegetable inflorescence, and Hibiscus is a blossoming plant used for decoration.
2. Which one is not a source of carbohydrate?
(a) Rice
(b) Millets
(c) Sorghum
(d) Gram
Ans: Option (d) is the correct choice.
Carbohydrates (commonly known as carbs) are a macronutrient found in a variety of foods. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and fibre. Cereals, such as rice millets and sorghum, are generally good sources of carbs.
Carbohydrates are obtained from grams also, but they are one of the major sources of protein.
3. Find out the wrong statement from the following
(a) White revolution is meant for increase in milk production
(b) Blue revolution is meant for increase in fish production
(c) Increasing food production without compromising with environmental quality is called as sustainable agriculture
(d) None of the above
Ans: Option (d) is the correct choice.
White Revolution: helped India go from being a milk-deficient country to the world's largest milk producer.
Blue Revolution: is a considerable expansion and intensification of global aquaculture production which includes fish, shellfish, aquatic plants etc.
Sustainable agriculture: is a form of agriculture that is favourable to the environment and allows for the production of crops without harming the environment.
4. To solve the food problem of the country, which among the following is necessary?
(a) Increased production and storage of food grains
(b) Easy access of people to the food grain
(c) People should have money to purchase the grains
(d) All of the above
Ans: To solve the food problem of the country all the given points are necessary as once the production of grains is increased it will be available in abundance in the market for the people, along with this stored food grains also should be easily available in the market at reasonable price and people should have money to buy the available food grains in the market.
Hence option (d) is the correct choice.
5. Find out the correct sentence
(i) Hybridisation means crossing between genetically dissimilar plants
(ii) Cross between two varieties is called as interspecific hybridisation
(iii) Introducing genes of desired character into a plant gives genetically modified crop
(iv) Cross between plants of two species is called as inter varietal hybridisation
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (a) is the correct choice.
Hybridisation is the process of obtaining offspring with desirable characters by crossing two genetically different plants or organisms.
Cross between two species is called interspecific hybridisation.
Crops which are developed by introducing new genes of desirable character are called genetically modified crops or GM crops.
Cross between two different varieties of plants of two species is called intervarietal hybridisation.
6. Weeds affect the crop plants by
(a) killing of plants in the field before they grow
(b) dominating the plants to grow
(c) competing for various resources of crops (plants) causing low availability of nutrients
(d) all of the above.
Ans: Option (c) is the correct choice.
Weeds are the unwanted plants that grow along with the main crop in the field by using the minerals and nutrients of the main crop. Thus, they compete with the main crops for minerals and nutrients.
7. Which one of the following species of honey bee is an Italian species?
(a) Apis dorsata
(b) Apis florae
(c) Apis cerana indica
(d) Apis mellifera
Ans: Option (d) is the correct choice.
Apis mellifera is an Italian species of honey bee.
8. Find out the correct sentence about manure
(i) Manure contains large quantities of organic matter and small quantities of nutrients.
(ii) It increases the water holding capacity of sandy soil.
(iii) It helps in draining out excess water from clayey soil.
(iv) Its excessive use pollutes the environment because it is made of animal excretory waste.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (a) is the correct choice.
Manure is an organic fertilizer. It is formed by the decomposition of dead plants and animals, animal excreta. It is rich in humus which helps in improving soil fertility.
9. Cattle husbandry is done for the following purposes
(i) Milk Production
(ii) Agricultural work
(iii) Meat production
(iv) Egg production
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: Option (a) is the correct choice.
Cattle husbandry is the branch of science which is involved with caring, breeding, and management of livestock. It is done for milk production, agricultural work, meat production. Egg production is related to poultry farming.
10. Which of the following are Indian cattle?
(i) Bos indicus
(ii) Bos domestica
(iii) Bos bubalis
(iv) Bos vulgaris
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (a) is the correct choice.
Indian cattles are- Bos indicus, Bos bubalis
11. Which of the following are exotic breeds?
(i) Brawn
(ii) Jersey
(iii) Brown Swiss
(iv) Jersey Swiss
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (b) is the correct choice.
Exotic breeds are those breeds which are native to other countries or foreign countries. Among the given options exotic breeds are- Jersey, Brown Swiss
12. Poultry farming is undertaken to raise following
(i) Egg production
(ii) Feather production
(iii) Chicken meat
(iv) Milk production
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (a) is the correct choice.
Poultry farming is the process of animal husbandry in which breeding, caring and rearing of birds are done for meat and egg such as; ducks, chickens, turkeys, etc.
13. Poultry fowl are susceptible to the following pathogens
(a) Viruses
(b) Bacteria
(c) Fungi
(d) All of the above
Ans: Option (a) is the correct choice.
Birds for example chickens, turkeys that are reared for their eggs and meat are called poultry fowl. They are susceptible to all the microbes such as viruses, bacteria, fungi etc.
14. Which one of the following fishes is a surface feeder?
(a) Rohus
(b) Mrigals
(c) Common carps
(d) Catlas
Ans: Option (d) is the correct choice.
Different fishes occupy different regions in the water bodies such as bottom, middle zone, surface and thus they are categorised such as, bottom feeder, middle zone feeder, surface feeder. Among the given options Catla is a surface feeder.
15. Animal husbandry is the scientific management of
(i) animal breeding
(ii) culture of animals
(iii) animal livestock
(iv) rearing of animals
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Ans: Option (c) is the correct choice.
Animal husbandry is related to animals that are reared, breed and cared for obtaining meat, milk, egg, fibre, etc.
16. Which one of the following nutrients is not available in fertilizers?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Iron
(d) Potassium
Ans: Option (a) is the correct choice.
Nitrogen is not available in the fertilizers. It is obtained from the atmosphere by nitrogen fixation with the help of nitrogen fixing bacteria.
17. Preventive and control measures adopted for the storage of grains include (a) strict cleaning
(a) strict cleaning
(b) proper disjoining
(c) fumigation
(d) all of the above
Ans: Option (d) is the correct choice. As all the above control measures are adopted for the storage of grains.
Short Answer Questions
18. Match the column A with the column B
Column A | Column B |
(a) Catla | (i) Bottom feeders |
(b) Rohu | (ii) Surface feeders |
(c) Mrigal | (iii) Middle-zone feeders |
(d) Fish farming | (iv) Culture fishery |
Ans:
Column A | Column B |
(a) Catla | (ii) Surface feeders |
(b) Rohu | (iii) Middle-zone feeders |
(c) Mrigal | (i) Bottom feeders |
(d) Fish farming | (iv) Culture fishery |
19. Fill in the blanks
(a) Pigeon pea is a good source of ________.
Ans: Pigeon pea is a good source of protein.
(b) Berseem is an important__________crop.
Ans: Berseem is an important fodder crop.
(c) The crops which are grown in the rainy season are called_________crops.
Ans: The crops which are grown in the rainy season are called kharif crops.
(d) ________are rich in vitamins.
Ans: Vegetables are rich in vitamins.
(f) _________crop grows in the winter season.
Ans: Rabi crop grows in the winter season.
20. What is a GM crop? Name any one such crop which is grown in India.
Ans: Crops which are developed by introducing new genes of desirable character are called genetically modified crops or GM crops.
Example: Bt Cotton
21. List out some useful traits in an improved crop?
Ans: Some useful traits in improved crops are:
(i) Change in the time of maturity
(ii) High yielding crops
(iii) Resistance to diseases
(iv) Adaptation to wide range of temperature
22. Why is organic matter important for crop production?
Ans: Organic matter is important for crop production because:
(i) It improves the structure of the soi, allowing more water to infiltrate.
(ii) It increases the water-holding capacity of the soil.
(iii) It promotes growth of the root into more porous soil.
(iv) It improves the health of the plant by allowing more transportable nutrients to reach the root such as nitrates.
23. Why is excess use of fertilizers detrimental for the environment?
Ans: Excess use of fertilizers detrimental for environment because:
(i) The residue and unused amount of it will become pollutant.
(ii) It can be washed away to the lakes and ponds and cause eutrophication.
(iii) Large quantities of it can decrease the soil quality by killing microbes in the soil.
24. Give one word for the following
(a) Farming without the use of chemicals as fertilizers, herbicides and
pesticides are known as_________.
Ans: Farming without the use of chemicals as fertilizers, herbicides and pesticides is known as organic farming.
(b) Growing of wheat and groundnut on the same field is called as _____________.
Ans: Growing of wheat and groundnut on the same field is called as mixed cropping.
(c) Planting soyabean and maize in alternate rows in the same field is called as _________.
Ans: Planting soyabean and maize in alternate rows in the same field is called as inter cropping.
(d) Growing different crops on a piece of land in pre-planned succession is known as_________.
Ans: Growing different crops on a piece of land in pre-planned succession is known as crop rotation.
(e) Xanthium and Parthenium are commonly known as___________.
Ans: Xanthium and Parthenium are commonly known as weeds
(f) Causal organisms of any disease are called as _________.
Ans: Causal organisms of any disease are called pathogens.
25. Match the following A and B
Column A | Column B |
(a) Cattle used for tilling and carting | (i) Milk producing female |
(b) Indian breed of chicken | (ii) Broiler |
(c) Sahiwal, Red Sindhi | (iii) Drought animals |
(d) Milch | (iv) Local breed of cattle |
(e) Chicken better fed for obtaining | (v) Aseel |
Ans:
Column A | Column B |
(a) Cattle used for tilling and carting | (iii) Drought animals |
(b) Indian breed of chicken | (v) Aseel |
(c) Sahiwal, Red Sindhi | (iv) Local breed of cattle |
(d) Milch | (i) Milk producing female |
(e) Chicken better fed for obtaining | (ii) Broiler |
26. If there is low rainfall in a village throughout the year, what measures will you suggest to the farmers for better cropping?
Ans: Following measures can be suggested to the farmers for better cropping:
(i) They should use drought resistant plants.
(ii) They should add organic manure which is rich in humus.
(iii) They should use a water harvesting method by which they can store water for future use.
27. Group the following and tabulate them as energy yielding, protein yielding, oil yielding and fodder crop.
Wheat, rice, berseem, maize, gram, oat, pigeon gram, sudan grass, lentil, soyabean, groundnut, castor and mustard.
Ans: Energy yielding: Wheat, Rice, Maize
Protein yielding: Gram, Pigeon gram, Lentil, Soybean
Oil yielding: Groundnut, Castor, Mustard, Soyabean.
Fodder Crops: Berseem, Oat, Sudan grass
28. Define the term hybridization and photoperiod.
Ans: Hybridisation: It is the process of obtaining offspring with desirable characters by crossing two genetically different plants or organisms.
Photoperiod: It is the duration or length of day and night which results in physiological reactions of organisms.
29. Fill in the blanks
(a) Photoperiod affect the__________.
Ans: Photoperiod affect the flowering.
(b) Kharif crops are cultivated from________to_________.
Ans: Kharif crops are cultivated from June to October.
(c) Rabi crops are cultivated from___________to_________.
Ans: Rabi crops are cultivated from November to April.
(d) Paddy, maize, green gram and black gram are____________crops.
Ans: Paddy, maize, green gram and black gram are Kharif crops.
(e) Wheat, gram, pea, mustard are___________crops.
Ans: Wheat, gram, pea, mustard are Rabi crops.
30. Cultivation practices and crop yield are related to environmental conditions. Explain.
Ans: Cultivation practices and crop yield are related to environmental conditions as different crops and their cultivation practices need different climatic conditions such as temperature, duration of sunlight, duration of time for maturity.
31. Fill in the blanks
(a) A total of__________nutrients are essential to plants.
Ans: A total of 16 nutrients are essential to plants.
(b)_________and________are supplied by air to plants.
Ans: Carbon di-oxide and Oxygen are supplied by air to plants.
(c) ________is supplied by water to plants.
Ans: Hydrogen is supplied by water to plants.
(d) Soil supply_________nutrients to plants.
Ans: Soil supplies 13 nutrients to plants.
(e) __________nutrients are required in large quantity and called as_________.
Ans: 6 nutrients are required in large quantity and called macronutrients.
(f) ________ nutrients are needed in small quantity for plants and are called_______.
Ans: 7 nutrients are needed in small quantity for plants and are called micronutrients.
32. Differentiate between compost and vermicompost?
Ans:
Compost | Vermicompost |
It is a natural process. | It is done with the help of earthworms. |
It is a high temperature process. | It is a low temperature process. |
This compost is produced by decomposition of organic matter. | This earthworm degrades organic matter. |
This process is accomplished by microbes such as bacteria. | This process is accomplished by worms such as earthworms. |
33. Arrange these statements in the correct sequence of preparation of green manure.
(a) Green plants are decomposed in soil.
(b) Green plants are cultivated for preparing manure or crop plant parts are used.
(c) Plants are ploughed and mixed into the soil.
(d) After decomposition it becomes green manure.
Ans: Step 1- (b) Green plants are cultivated for preparing manure or crop plant parts are used.
Step 2- (c) Plants are ploughed and mixed into the soil.
Step 3- (a) Green plants are decomposed in soil.
Step 4- (d) After decomposition it becomes green manure.
34. An Italian bee variety A. mellifera has been introduced in India for honey production. Write about its merits over other varieties.
Ans: Merits of A. mellifera over other varieties are:
(i) It is sting less.
(ii) It stays in an artificial or the given beehive for a very long time.
(iii) It breeds easily and at a faster rate.
(iv) It has a high honey collection capacity.
35. In agricultural practices, higher input gives higher yield. Discuss how?
Ans: In agricultural practices, higher input gives higher yield means that if farmers would have higher money input they can take up different farming practices and technologies. Their capacity of inputs decides cropping type and improved production practices and types of seed they choose (for eg. HYV seeds). Along with that latest agricultural machine, nutrient supply etc require high cost input and knowledge of new techniques and their improvements.
Long Answer Questions
36. Discuss the role of hybridisation in crop improvement.
Ans: Hybridisation is a process in which two genetically dissimilar plants are crossed to produce offspring with desirable characters.
The hybridisation process can be performed in between two different varieties, species or genera.
By hybridisation method crop yield can be improved, it can be made disease resistant, etc.
37. Define
(i) Vermicompost
Ans: It is the composting process done with the help of worms such as earthworms. In this process earthworms degrade the biodegradable waste and convert it into manure.
(ii) Green manure
Ans: The plants that are used as manure are called green manure. They are planted in the soil to prevent leaching and erosion, provide nutrients to the soil, improve soil structure, etc.
(iii) Bio fertilizer
Ans: When living organisms are used as fertilizer to provide nutrients to the plants they are called as biofertilizers such as blue green algae that do nitrogen fixation.
38. Discuss various methods for weed control.
Ans: Various methods of weed control are:
1. Mechanical method: This method includes uprooting, weeding, scraping, burning, and flooding.
2. Biological method: In this method specific insects are used which feed on these weeds and by consuming the weed plant they destroy them.
3. Chemical method: In this method various chemicals are used such as herbicides, weedicides. These chemicals are sprayed on the weeds to kill them.
4. Cultural method: This method includes intercropping, crop rotation.
39. Differentiate between the following
(i) Capture fishery and Culture fishery
Ans:
Capture Fishery | Culture Fishery |
It is the method in which fishes are obtained from natural resources. | It is the method in which fishes are obtained by fish farming. |
Special care is not required. | Special care is required. |
In this mature and immature both types of fishes are captured. | In this only mature fishes are captured. |
(ii) Mixed cropping and Inter cropping
Ans:
Mixed Cropping | Inter Cropping |
In this type of cropping two or more crops are simultaneously grown on the same field. | In this type of cropping two or more crops are simultaneously grown on the same field but in a definite pattern |
This is done to reduce the chances of crop failure. | This is done to increase the production of crops per unit area. |
Seeds are mixed up before sowing | Seeds are not mixed before sowing. |
(iii) Bee keeping and Poultry farming
Ans:
Bee Keeping | Poultry Farming |
It is the method of rearing, caring and managing honey bees. | It is the method of rearing, caring and managing birds like chickens. |
It is done for the production of honey. | It is done for the production of meat and egg. |
It is also called apiculture. | It is also called Ranch or valley farming. |
40. Give the merits and demerits of fish culture?
Ans: Merits of fish culture:
(i) In pisciculture, different types of fishes are cultured together.
(ii) The meat of fish is highly nutritive. It is one of the major sources of protein, vitamins, minerals and useful fats.
(iii) Pisciculture made possible the natural breeding process with our choice of breed.
(iv) With the help of improved pisciculture technique, large amounts of fish can be obtained from a small area.
Demerits of fish culture are:
(i) It is a major threat to biodiversity.
(ii) It is a great threat of disease because of the loss of natural habitat.
41. What do you understand by composite fish culture?
Ans: It is a technique to obtain maximum yield of fish from a small pond area. In this type of culture, 5-6 species of fishes are cultured together. The selection of species is done by making sure that they do not compete for food. As a result food available in all the parts of the pond are used.
Example; Catla is surface feeder, Rohu is middle zone feeder, Mrigal is bottom feeder.
42. Why beekeeping should be done in good pasturage?
Ans: Good pasturage provides nectar to honeybees in good quantity and quality as different types of flowers are available, which at the end will result in yield of good quality honey.
43. Write the modes by which insects affect the crop yield.
Ans: The modes by which insect affect the crop yield are:
(i) Cutting: Few insects chew different plant parts like flower, fruit, leaf, stem.
(ii) Borers: Few insects create a burrow in different plant parts and live inside.
(iii) Suckers: Few insects use their proboscis to suck cell sap from different plant parts.
44. Discuss why pesticides are used in very accurate concentration and in very appropriate manner?
Ans: Pesticides are used in very accurate concentration and in very appropriate manner because:
(i) It can harm the soil and can lose the fertility of the soil.
(ii) It can kill the microbes which are good for soil.
(iii) It can be responsible for air, water, and soil pollution.
45. Name two types of animal feed and write their functions.
Ans: The two types of animal feed are fodder and forage.
(i) Fodder helps in digestion of the food and keeps the nutrients in its fresh form.
(ii) Forage is rich in vitamins, fiber and proteins, it increases the metabolic activity of the animals.
46. What would happen if poultry birds are larger in size and have no summer adaptation capacity? In order to get small sized poultry birds, having summer adaptability, what method will be employed?
Ans: If poultry birds are larger in size then it would create a problem in housing and feeding as they will require a large area and more feeding and maintenance of temperature is required for better production of eggs. If they would not have summer adaptation then it may cause decline in egg production.
47. Suggest some preventive measures for the diseases of poultry birds.
Ans: Some preventive measures for the diseases of poultry birds are:
(i) Poultry farms should be cleaned.
(ii) Poultry farms should be properly sanitised.
(iii) Disinfectants should be sprayed at regular intervals.
(iv) Birds should be vaccinated.
48. Figure15.1 shows the two crop fields [Plots A and B] have been treated by manures and chemical fertilizers respectively, keeping other environmental factors the same. Observe the graph and answer the following questions.
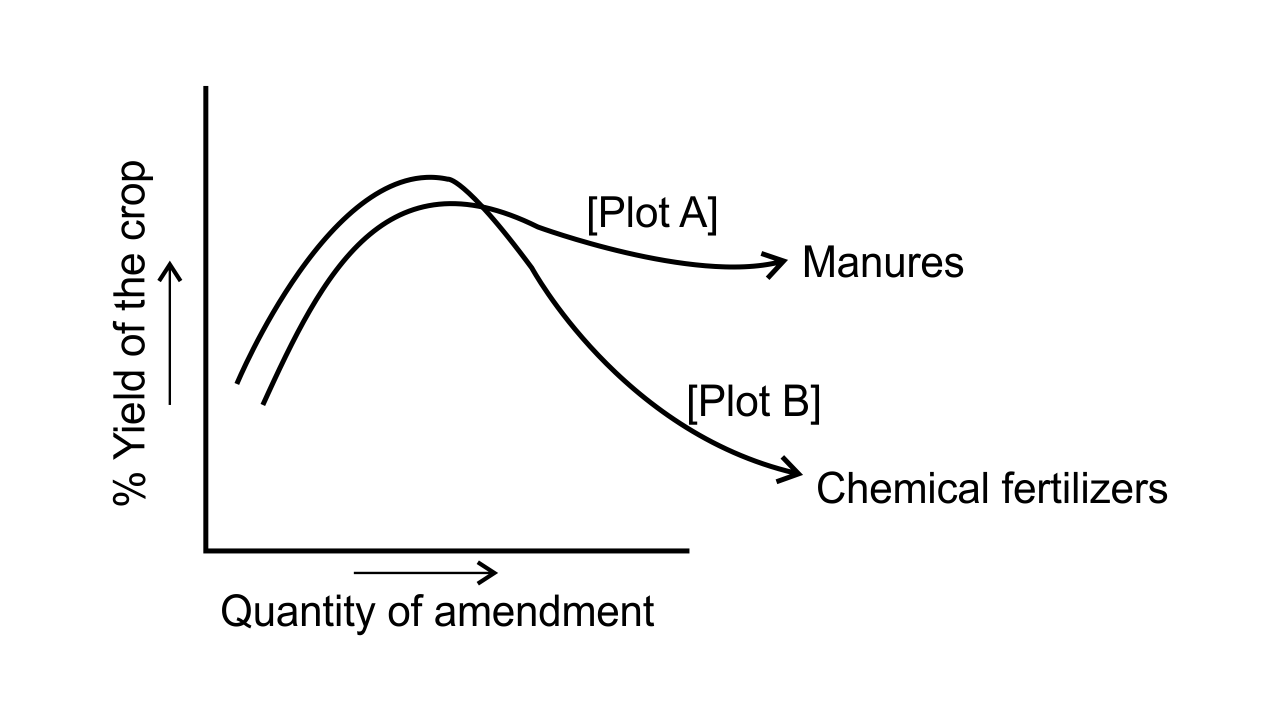
(i) Why does plot B show sudden increase and then gradual decrease in yield?
Ans: Sudden increase in yield is due to release of nutrients by chemical fertilizers and the gradual decline in the graph indicates that continuous use of high quantities of chemicals kills the useful microbes who are responsible for restoring organic matter in the soil. This decreases the soil fertility.
(ii) Why is the highest peak in plot A graph slightly delayed?
Ans: Manures are organic fertilisers and it takes time to supply a small quantity of nutrients to the soil comparatively inorganic fertiliser. This may be the reason why the highest peak in plot A graph is slightly delayed.
(iii) What is the reason for the different pattern of the two graphs?
Ans: The difference in the pattern of two graphs shows that the use of manure (plot A) is good for a long time as the yield remains high when the quantity of manure increases. On the other hand, when chemical fertilizers (plot B) are used continuously for a long time it leads to loss of microbes which are helpful in maintaining soil fertility, thus resulting in loss of fertility.
49. Complete the crossword puzzle (Fig.15.2)
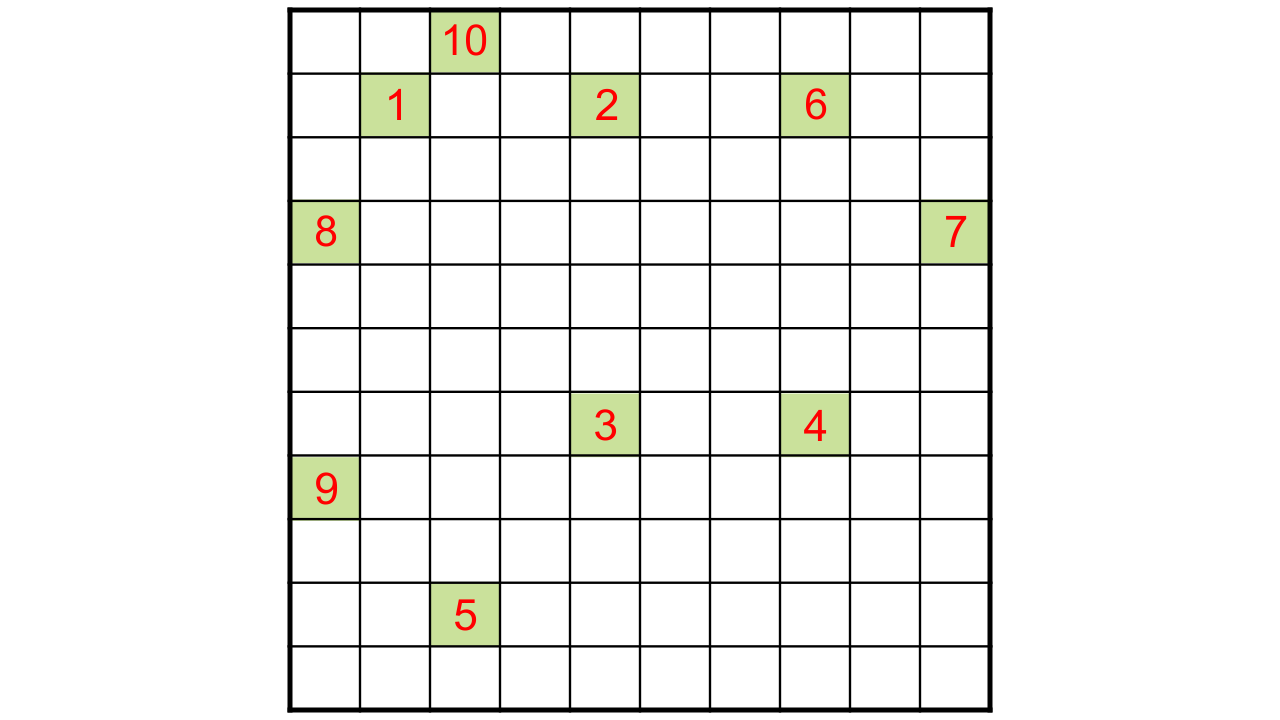
Across
1. Oil yielding plant (9)
3. Crop grown in winter season (4)
5. Fixed by Rhizobium (8)
9. Common honey bee (4)
Downward
2. Animal feed (6)
4. A micronutrient (5)
6. Unwanted plant in crop fields (4)
7. An exotic breed of chicken(7)
8. Bottom feeders in fish pond(7)
10. A marine fish (4)
Ans:

Improvement in Food Resources
The breeding and selection of plants and animals for quality improvement and management, the use of fertilizers, manures, the prevention of pests and diseases, and organic farming.
The Acts You Need to Know
We need food for growth, development, and health because it contains proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
The growth and completion of each crop's life cycle are influenced by climatic conditions, temperature, and photoperiods- A photoperiod is the length of time it takes the sun to shine. Sunlight is essential for plants and flowers.
There are Many Factors That Affect Crop Production, Such as:
Understanding the growth and development of crops.
The effect of various nutrients, climates, and water on plant growth.
Modifying and managing each factor to maximize crop production.
Crops grown during the rainy season (between June and October) are classified as Kharif crops.
Example: Paddy, soybean, pigeon pea, maize, cotton, green gram, and black gram are all Kharif crops.
Crops grown during the winter season (from November to April) are classified as rabi crops.
Example: In India, rabi crops include wheat grain, peas, mustard, and linseed.
What is the Need for Improved Food Resources?
There are several reasons why we need to improve food resources:
To increase the nutritional value and quality of food.
To increase crop productivity.
To prevent the spread of diseases and pests among food products and crops.
To reduce the cost of food products and to make them more widely available.
What other Characteristics are Desired in Plants?
There are many different regions in India. There are some that have abundant rainfall, while others are dry and have not much rainfall. As a result, not all crops can grow in every region. Consequently, high-yielding crop plants need to be developed for every region and every condition.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources (Book Solutions)
1. What is organic farming?
Organic farming involves using little or no chemicals (fertilizers, herbicides, pesticides, etc.) and making use of natural manures, recycled farm waste (straw and livestock excreta), use of bio-agents (cultured algae for biofertilizers, neem leaves for pest control in grain storage, etc.) which are coupled with healthy cropping systems (mixed cropping, inter-cropping, and crop rotation). In addition to providing nutrients, these cropping systems also control insects, pests, and weeds.
2. Summer ploughing can be described as follows:
This method involves ploughing the field deeply in summer to destroy both weeds and pests. The management of livestock animals is known as animal husbandry. Animal husbandry encompasses a range of activities including feeding, breeding, and disease control. Farming of animals such as cattle, goats, sheep, poultry, and fish is an animal-based industry.
A dairy animal is called a milk animal (dairy animal), whereas a draft animal is one used for farm work.
3. In NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science, Chapter 15, what type of questions will be asked?
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science, Chapter 15 asks students the following questions:
MCQ's
Very short answer
Short answer
Long answer
Fill in the blanks
Match the following
In Chapter 15 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science, there are 17 multiple-choice questions (MCQs), 5 fill-in-the-blank questions, 1 very short answer, 4 short answers, and 11 long answers questions. Short answer questions can be answered in one sentence by students.
4. Is it possible to download free NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15?
Vedantu offers free access to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 15. They are created according to the latest NCERT guidelines and are updated regularly. Students can access chapter-by-chapter PDF files for exam preparation. The answers are all based solely on the NCERT textbook. In addition to improving logical reasoning and analytical thinking skills, PDF solutions help students prepare for exams.
5. What are the concepts discussed in Chapter 15 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science?
In Chapter 15 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science, concepts are discussed as follows.
15.1 Improvement In Crop Yields
15.1.1 Crop Variety Improvement
15.1.2 Crop Production Management
15.1.3 Crop Protection Management
15.2 Animal Husbandry
15.2.1 Cattle Farming
15.2.2 Poultry Farming
15.2.3 Fish Production
15.2.4 Bee-keeping
Experts at Vedantu have designed solutions for Chapter 15 while considering students' understanding abilities. Downloading the solutions PDF available in Vedantu will help students better understand the concepts covered in this chapter.




































