
With the help of diagrams, name and describe the different types of placentation seen in angiosperms?
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: Within the ovary are ovules found in Angiosperms. Placenta is a special tissue type, linking the ovules to the ovary. The mode of placenta distribution within the ovary is called placentation.
Complete answer:
Placentation refers to how the ovules are connected to the plant's ovary and how the seeds grow. Each seed that develops will bind to the ovary wall, or to a central structure in the ovary. A plant tissue filament called a funiculus attaches the seed to the ovary wall. Similar to how an umbilical cord brings nutrients to a fetus in the womb, it transfers nutrients into the seeds. The placenta is considered the inner layer of the ovary. There are five common placentation patterns in angiosperms which define how the seeds are arranged inside the fruit. The most important placentation categories found in angiosperms are:
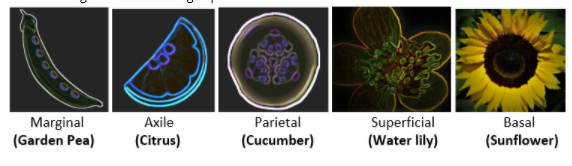
1. Marginal Placentation
This type of placentation occurs in a unilocular, monocarpellary ovary. The ovules are borne along the intersection between the two carpal margins. Marginal placentation can be found in Fabaceae (Garden Pea).
2. Axile Placentation
This form of placentation is seen in the syncarpous ovary, which is bi- or multi-carpel. In the middle of the ovary, where the placenta is shaped like a central column, the carpel walls cross. In each locule the ovules are borne on the placenta at or near the centre. Axile placentation can be seen in Rutaceae (Citrus).
3. Parietal Placentation
This form of placentation can be found in multicarpellary, syncarpous, unilocular ovaries. Here, just its margins fuse the carpels. The ovules containing placenta form at the places where the two carpels are fused. Parietal placentation can be seen in Cucurbitaceae (Cucumber).
4. Superficial Placentation
This form of placentation occurs in a multicarpellary, multilocular ovary. The ovules are borne on placentae which develops all around the partition wall's inner surface. Superficial placentation can be found in Nymphaeaceae (Water lily).
5. Basal Placentation
It is seen in the syncarpous, unilocular, bicarpellary ovary. The placenta grows directly on the receptacle at the base of the ovary, which contains a single ovule. Basal placentation can be found in Asteraceae (Sunflower).
Note: Placentation is a phenomenon occurring only in angiosperms, a group of plants which reproduce using flowers. The plant ovules are located in the ovary, at the flower base.
Complete answer:
Placentation refers to how the ovules are connected to the plant's ovary and how the seeds grow. Each seed that develops will bind to the ovary wall, or to a central structure in the ovary. A plant tissue filament called a funiculus attaches the seed to the ovary wall. Similar to how an umbilical cord brings nutrients to a fetus in the womb, it transfers nutrients into the seeds. The placenta is considered the inner layer of the ovary. There are five common placentation patterns in angiosperms which define how the seeds are arranged inside the fruit. The most important placentation categories found in angiosperms are:

1. Marginal Placentation
This type of placentation occurs in a unilocular, monocarpellary ovary. The ovules are borne along the intersection between the two carpal margins. Marginal placentation can be found in Fabaceae (Garden Pea).
2. Axile Placentation
This form of placentation is seen in the syncarpous ovary, which is bi- or multi-carpel. In the middle of the ovary, where the placenta is shaped like a central column, the carpel walls cross. In each locule the ovules are borne on the placenta at or near the centre. Axile placentation can be seen in Rutaceae (Citrus).
3. Parietal Placentation
This form of placentation can be found in multicarpellary, syncarpous, unilocular ovaries. Here, just its margins fuse the carpels. The ovules containing placenta form at the places where the two carpels are fused. Parietal placentation can be seen in Cucurbitaceae (Cucumber).
4. Superficial Placentation
This form of placentation occurs in a multicarpellary, multilocular ovary. The ovules are borne on placentae which develops all around the partition wall's inner surface. Superficial placentation can be found in Nymphaeaceae (Water lily).
5. Basal Placentation
It is seen in the syncarpous, unilocular, bicarpellary ovary. The placenta grows directly on the receptacle at the base of the ovary, which contains a single ovule. Basal placentation can be found in Asteraceae (Sunflower).
Note: Placentation is a phenomenon occurring only in angiosperms, a group of plants which reproduce using flowers. The plant ovules are located in the ovary, at the flower base.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




