
With reference to flower colour in snapdragon, explain incomplete dominance.
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: Antirrhium is the generic name of the snapdragon. The Snapdragon flower is also called the dragon flower because of its resemblance to the face of a dragon.
Complete Answer:
Incomplete dominance: Incomplete dominance is also called partial dominance or semi-dominance.
- In incomplete dominance, both the alleles in heterozygous condition partially express themselves. Here the dominant allele can not completely mask the effect of recessive allele.
- The physical appearance of the organism shows the blending of both the two alleles i.e. dominant allele as well as recessive allele.
Example of incomplete dominance:
- Cross pollination between red snapdragon and white snapdragon result in pink snapdragon.
Here, neither the white allele or red allele is dominant.
- The pink colour results from the blending of both the two alleles that are white allele or white and red allele.
- RR represents the dominant red allele and rr represents the recessive allele.
- In F1 ( filial 1 ) generation, all the offspring will be of pink colour having genotype Rr.
- And in F2 generation when two heterozygotes are crossed and results in 1 red coloured snapdragon, 2 pink coloured snapdragon and 1 white coloured snapdragon in the ratio 1:2:1.
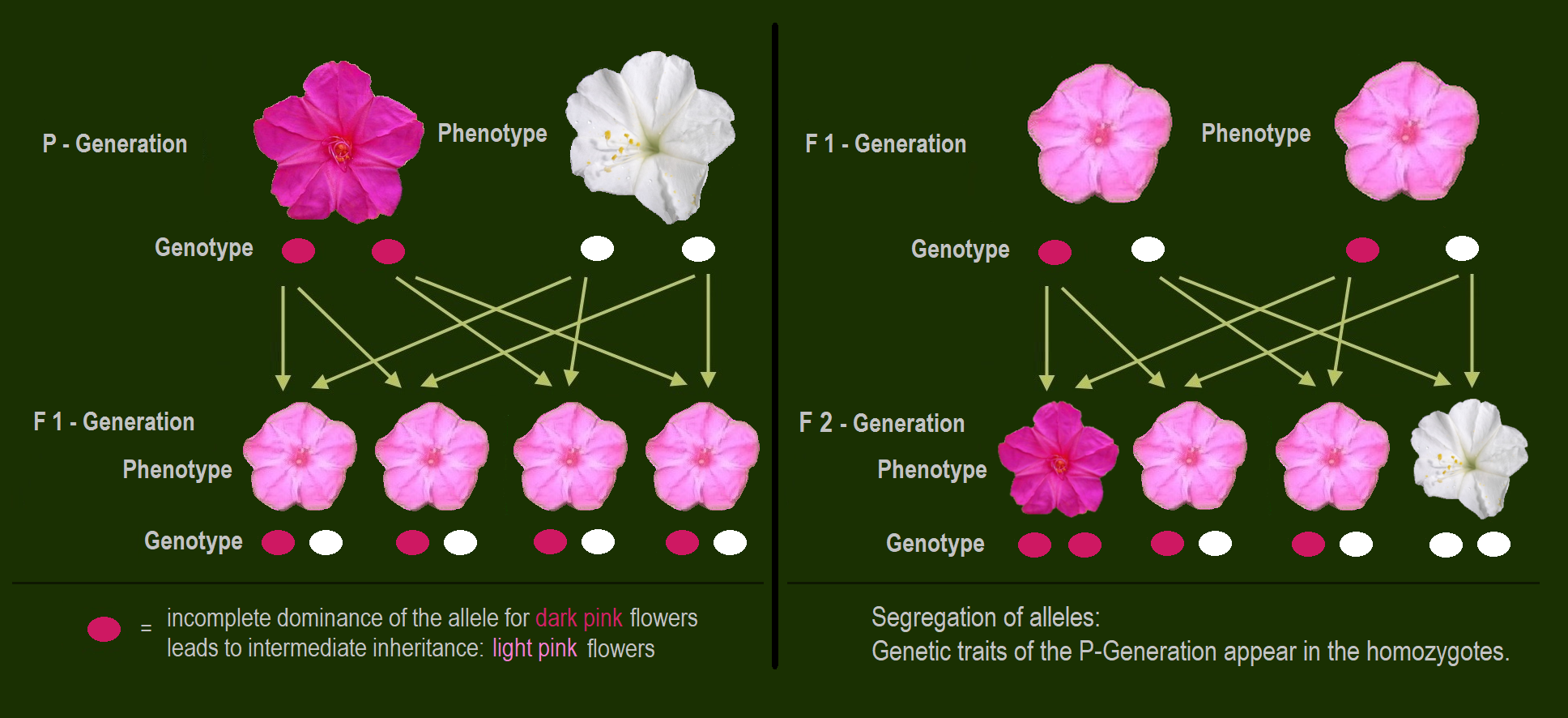
Note: Incomplete dominance does not follow the Mendel’s dominance law which states that the dominant character will completely mask the effect of the recessive character.
Complete Answer:
Incomplete dominance: Incomplete dominance is also called partial dominance or semi-dominance.
- In incomplete dominance, both the alleles in heterozygous condition partially express themselves. Here the dominant allele can not completely mask the effect of recessive allele.
- The physical appearance of the organism shows the blending of both the two alleles i.e. dominant allele as well as recessive allele.
Example of incomplete dominance:
- Cross pollination between red snapdragon and white snapdragon result in pink snapdragon.
Here, neither the white allele or red allele is dominant.
- The pink colour results from the blending of both the two alleles that are white allele or white and red allele.
- RR represents the dominant red allele and rr represents the recessive allele.
- In F1 ( filial 1 ) generation, all the offspring will be of pink colour having genotype Rr.
- And in F2 generation when two heterozygotes are crossed and results in 1 red coloured snapdragon, 2 pink coloured snapdragon and 1 white coloured snapdragon in the ratio 1:2:1.

Note: Incomplete dominance does not follow the Mendel’s dominance law which states that the dominant character will completely mask the effect of the recessive character.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




