
Which rubber is not polydiene?
(a) Polyisoprene
(b) Polychloroprene
(c) Thiokol rubber
(d) Nitrile rubber
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: Polydienes are polymers which have their monomer as a diene, which is essentially two carbon-carbon double bonds ($C = C$) occurring in the same molecule. Therefore, by examining structures of each compound, we can identify the rubber which doesn’t have diene in their monomer.
Complete step by step answer:
To approach this problem, let us have a close look at the structures of each rubber mentioned in the options.
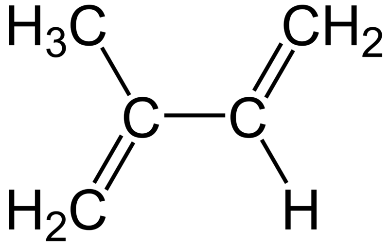
The first rubber, polyisoprene, has the compound isoprene as its monomer (shown in figure). We can clearly see that this compound has two carbon-carbon double bonds and therefore, when polymerized, forms a polydiene.
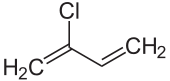
The next compound, polychloroprene, has chloroprene as its monomer. The structure of chloroprene is shown in the figure below. As we can see, this molecule is a diene too as it has two carbon-carbon double bonds.
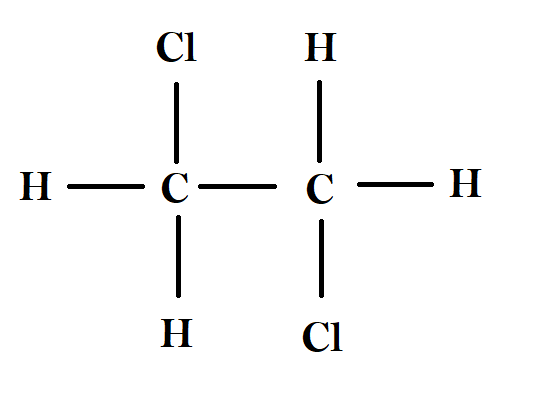
The third compound is Thiokol rubber, is formed from two monomers, namely 1,2-dichloroethane and sodium polysulphide. Sodium polysulphide consists only of sodium and sulphur atoms, and the structure of 1,2-dichloroethane is shown below. As we can see, even this molecule is not a diene as it doesn’t even have a double bond. Hence, Thiokol rubber is not a polydiene.
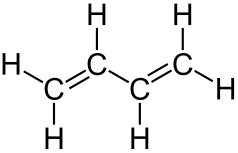
The last compound, nitrile rubber, is formed from two monomers, acrylonitrile and 1,3-butadiene. Out of these, the structure of 1,3-butadiene is shown below. As we can clearly see, this molecule has two carbon-carbon double bonds too. Therefore, when polymerized with acrylonitrile, it forms a polydiene.
As we can see from above, Thiokol rubber is the only polymer which does not have a diene monomer.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Dienes are constituents of the monomers of most natural and synthetic polymers. Presence of a diene molecule in any monomer will make its polymer a polydiene. Thiokol rubber has a branched chain structure of sulphur, which gives it added strength and more resistance to wear and tear. The process of adding cross-linked sulphur chains into natural rubber for enhancing its properties is known as vulcanization.
Complete step by step answer:
To approach this problem, let us have a close look at the structures of each rubber mentioned in the options.
The first rubber, polyisoprene, has the compound isoprene as its monomer (shown in figure). We can clearly see that this compound has two carbon-carbon double bonds and therefore, when polymerized, forms a polydiene.

The next compound, polychloroprene, has chloroprene as its monomer. The structure of chloroprene is shown in the figure below. As we can see, this molecule is a diene too as it has two carbon-carbon double bonds.

The third compound is Thiokol rubber, is formed from two monomers, namely 1,2-dichloroethane and sodium polysulphide. Sodium polysulphide consists only of sodium and sulphur atoms, and the structure of 1,2-dichloroethane is shown below. As we can see, even this molecule is not a diene as it doesn’t even have a double bond. Hence, Thiokol rubber is not a polydiene.

The last compound, nitrile rubber, is formed from two monomers, acrylonitrile and 1,3-butadiene. Out of these, the structure of 1,3-butadiene is shown below. As we can clearly see, this molecule has two carbon-carbon double bonds too. Therefore, when polymerized with acrylonitrile, it forms a polydiene.

As we can see from above, Thiokol rubber is the only polymer which does not have a diene monomer.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: Dienes are constituents of the monomers of most natural and synthetic polymers. Presence of a diene molecule in any monomer will make its polymer a polydiene. Thiokol rubber has a branched chain structure of sulphur, which gives it added strength and more resistance to wear and tear. The process of adding cross-linked sulphur chains into natural rubber for enhancing its properties is known as vulcanization.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE




