
Which one is a vital stain?
A. Janus green
B. Methylene blue
C. Neutral red
D. All the above
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: Vital stain is a technique in which a harmless dye is used to stain living tissue for microscopic observation. The stain may be injected into living animals. Subsequently, stained microscopic organisms such as protozoa may be completely immersed in the dye solution.
Complete answer:
-Vital stain includes trypan blue, vital red, and the Janus green the latter being especially suitable for observing mitochondria.
-The term vital stain is used by some authors to refer to an intravital stain and by others interchangeably with a supravital stain, the core concept being that the cell being examined is still alive. In a more strict sense, the term vital staining has a meaning contrasting with supravital staining. While in supravital staining the living cells take up the stain, on the other hand in vital staining the living cells stain negatively and only the dead cells stain positively. Thus, viability can be assessed by counting the percentage of total cells that stain negatively that is the unstained live cells.
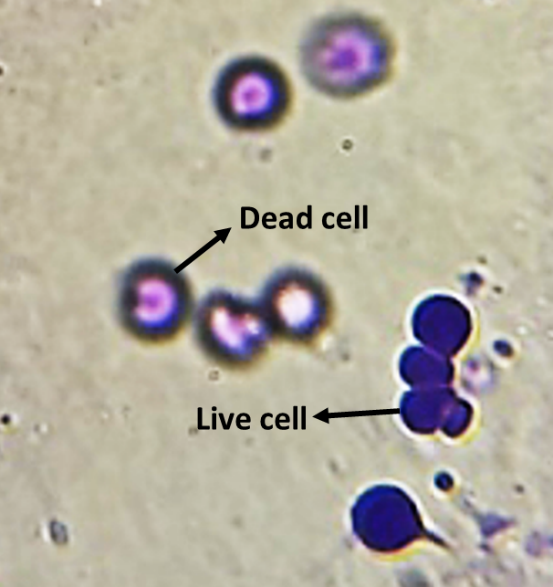
- Janus green stains the cell based on the presence or absence of oxygen. It is an oxidizing stain that stains the cells blue in the presence of oxygen (in case of live cells) and stains the cell pink in the absence of oxygen (in case of a dead cell).
Figure 1: Janus green-stained cells
Additional information:
- Vital stains and dyes are frequently used in histology and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses disease at the microscopic level.
- Stains can be used to define biological tissues, muscle fibers, and connective tissue cell populations or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific (DNA, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify the presence of a specific compound.
- Very bulks or highly charged stains that do not cross live plasma membranes are used as vital stains and supravital stains are those that are either small or are pumped actively into live cells. Since the supravital and intravital nature of the staining depends on the dye a combination of supravital and vital dyes can also be used in a sophisticated way to better classify cells into distinct subsets (eg. Dead, dying, and viable cells).
- Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in a flow cytometer and to flag proteins or nucleic acid in gel electrophoresis. Staining is not limited to biological material it can also be used to study the structure of the other materials for example the lamellar structure of semi-crystalline polymer or the domain structure of the block copolymer.
Note:
Different stains react in different parts of the cells and these properties are used as an advantage to reveal specific parts. Methylene blue is used to stain animal cells such as human cheek cells to make their nuclei more observable. Also used to stain blood films in cytology. The neutral red stain is also called toluylene red. Neutral stain stains the substance red. It is usually used as a counterstain in combination with other dyes.
Complete answer:
-Vital stain includes trypan blue, vital red, and the Janus green the latter being especially suitable for observing mitochondria.
-The term vital stain is used by some authors to refer to an intravital stain and by others interchangeably with a supravital stain, the core concept being that the cell being examined is still alive. In a more strict sense, the term vital staining has a meaning contrasting with supravital staining. While in supravital staining the living cells take up the stain, on the other hand in vital staining the living cells stain negatively and only the dead cells stain positively. Thus, viability can be assessed by counting the percentage of total cells that stain negatively that is the unstained live cells.
- Janus green stains the cell based on the presence or absence of oxygen. It is an oxidizing stain that stains the cells blue in the presence of oxygen (in case of live cells) and stains the cell pink in the absence of oxygen (in case of a dead cell).
Figure 1: Janus green-stained cells

Additional information:
- Vital stains and dyes are frequently used in histology and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses disease at the microscopic level.
- Stains can be used to define biological tissues, muscle fibers, and connective tissue cell populations or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific (DNA, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify the presence of a specific compound.
- Very bulks or highly charged stains that do not cross live plasma membranes are used as vital stains and supravital stains are those that are either small or are pumped actively into live cells. Since the supravital and intravital nature of the staining depends on the dye a combination of supravital and vital dyes can also be used in a sophisticated way to better classify cells into distinct subsets (eg. Dead, dying, and viable cells).
- Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in a flow cytometer and to flag proteins or nucleic acid in gel electrophoresis. Staining is not limited to biological material it can also be used to study the structure of the other materials for example the lamellar structure of semi-crystalline polymer or the domain structure of the block copolymer.
Note:
Different stains react in different parts of the cells and these properties are used as an advantage to reveal specific parts. Methylene blue is used to stain animal cells such as human cheek cells to make their nuclei more observable. Also used to stain blood films in cytology. The neutral red stain is also called toluylene red. Neutral stain stains the substance red. It is usually used as a counterstain in combination with other dyes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




