
Which of the following is homologue of
$C{{H}_{3}}NHC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$ ?
(A) $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}NHC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$
(B) $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}$
(C)
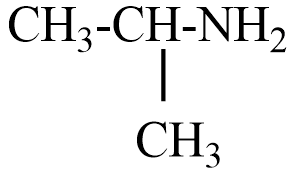
(D) $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}NHC{{H}_{3}}$
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: Based on the structure and chemical properties of all organic compounds have been divided into different families or groups. These classifications of organic compounds will be useful to study the properties of some organic compounds. Generally, most organic compounds are poor electricity due to the covalent bond between carbon-carbon atoms.
Complete step by step solution:
A family or group structurally similar organic compounds with the same functional group exhibit gradation in physical and chemical properties, two adjacent members of which differ by $-C{{H}_{2}}$ functional groups are known as homologous series. The members in this series are expected to metamerism.
The individual member of the series is called homologous and this phenomenon is named homology.
An important class of organic compound derived by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of $N{{H}_{3}}$ a molecule with alkyl or aryl groups are amines. Regarding the derivatives of ammonia in which one, two, or three atoms are replaced with alkyl groups formed alkylamines, those are primary, secondary, or tertiary amines respectively.
Given compounds, $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}NHC{{H}_{3}}$ (which is a secondary amine) only a homologue of a given compound$C{{H}_{3}}NHC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$. Because homologue means the difference of $-C{{H}_{2}}$ group.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: As the molecular mass increases in homologous series, physical properties gradation will be observed. Because increasing molecular mass then increasing boiling points and melting points in the series. But the chemical properties are defined by the functional group in this series.
Complete step by step solution:
A family or group structurally similar organic compounds with the same functional group exhibit gradation in physical and chemical properties, two adjacent members of which differ by $-C{{H}_{2}}$ functional groups are known as homologous series. The members in this series are expected to metamerism.
The individual member of the series is called homologous and this phenomenon is named homology.
An important class of organic compound derived by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms of $N{{H}_{3}}$ a molecule with alkyl or aryl groups are amines. Regarding the derivatives of ammonia in which one, two, or three atoms are replaced with alkyl groups formed alkylamines, those are primary, secondary, or tertiary amines respectively.
Given compounds, $C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}NHC{{H}_{3}}$ (which is a secondary amine) only a homologue of a given compound$C{{H}_{3}}NHC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}$. Because homologue means the difference of $-C{{H}_{2}}$ group.
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: As the molecular mass increases in homologous series, physical properties gradation will be observed. Because increasing molecular mass then increasing boiling points and melting points in the series. But the chemical properties are defined by the functional group in this series.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




