
Which of the following is a purine?
(a) Cytosine
(b) Guanine
(c) Thymine
(d) Uracil
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Purines and pyrimidines are heterocyclic nitrogen- containing compounds that make up the building blocks of nucleic acids such as Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and Ribonucleic acid RNA. These compounds are also known as nitrogen bases and exist as base pairs in the nucleic acid structure.
Complete Answer:
Purines are compounds that contain a six- membered ring that has nitrogen in it as well. This ring is further fused with an imidazole ring. Thus, purines are structures that have two rings. Purines that are found in the nucleic acids are Adenine (A) and Guanine (G).
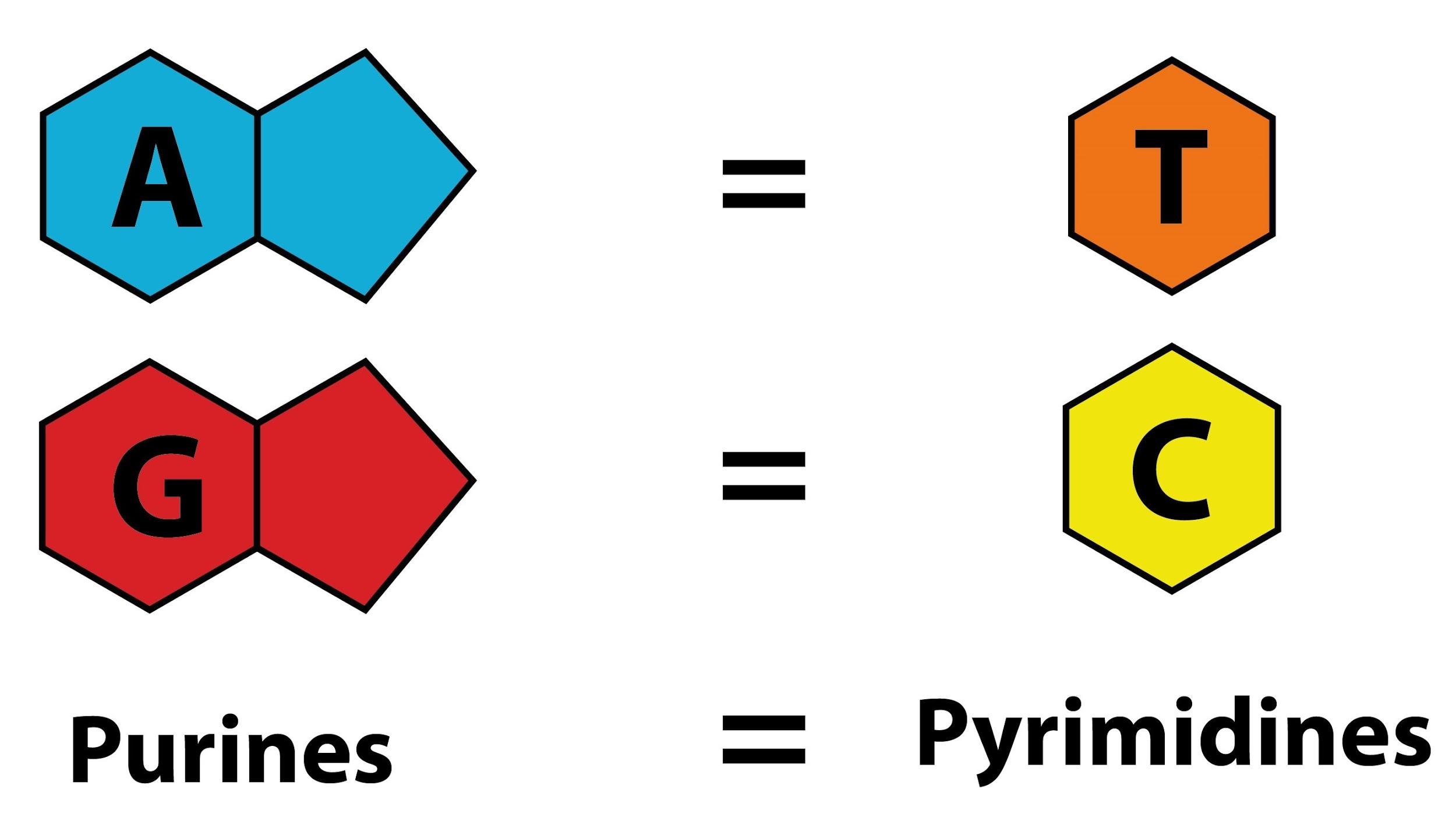
Pyrimidines are compounds that have only the six- membered ring. Thus, pyrimidines are structures that contain only one ring in them. Pyrimidines that are found in nucleic acids are Cytosine (C) , Thymine (T) , and Uracil (U) .
Additional information: Let us study more about purines and pyrimidines.
- The nitrogenous bases purines and pyrimidines make a glycosidic bond with sugars (Ribose sugar and deoxyribose sugar) to form a structure known as Nucleoside.
- Examples of nucleosides include adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, etc.
- Nucleosides form a phospho- ester bond with a phosphate group to form a structure known as nucleotides.
- These nucleotides combine with each other to give rise to nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
- In nucleic acids, the nitrogenous bases are joined together by hydrogen bonds and are known as base pairs.
- A purine always combines with a pyrimidine.
- Adenine bonds with Thymine with the help of two hydrogen bonds.
- Whereas Cytosine bonds with guanine with the help of three hydrogen bonds.
- Uracil is found in RNA where it bonds with adenine in place of thymine.
So, the correct option is ‘(b) Guanine’.
Note:
- Nitrogen bases are aromatic in nature.
- Erwin Chargaff studied the nitrogenous bases found in nucleic acids and proposed a rule which states that the ratios of the amount of Adenine and Thyme as well as Cytosine and Guanine is constant and equals 1.
- This also means that the number of purines is equal to the number of pyrimidines in DNA and RNA.
Complete Answer:
Purines are compounds that contain a six- membered ring that has nitrogen in it as well. This ring is further fused with an imidazole ring. Thus, purines are structures that have two rings. Purines that are found in the nucleic acids are Adenine (A) and Guanine (G).

Pyrimidines are compounds that have only the six- membered ring. Thus, pyrimidines are structures that contain only one ring in them. Pyrimidines that are found in nucleic acids are Cytosine (C) , Thymine (T) , and Uracil (U) .
Additional information: Let us study more about purines and pyrimidines.
- The nitrogenous bases purines and pyrimidines make a glycosidic bond with sugars (Ribose sugar and deoxyribose sugar) to form a structure known as Nucleoside.
- Examples of nucleosides include adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, etc.
- Nucleosides form a phospho- ester bond with a phosphate group to form a structure known as nucleotides.
- These nucleotides combine with each other to give rise to nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
- In nucleic acids, the nitrogenous bases are joined together by hydrogen bonds and are known as base pairs.
- A purine always combines with a pyrimidine.
- Adenine bonds with Thymine with the help of two hydrogen bonds.
- Whereas Cytosine bonds with guanine with the help of three hydrogen bonds.
- Uracil is found in RNA where it bonds with adenine in place of thymine.
So, the correct option is ‘(b) Guanine’.
Note:
- Nitrogen bases are aromatic in nature.
- Erwin Chargaff studied the nitrogenous bases found in nucleic acids and proposed a rule which states that the ratios of the amount of Adenine and Thyme as well as Cytosine and Guanine is constant and equals 1.
- This also means that the number of purines is equal to the number of pyrimidines in DNA and RNA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




