
Which of the following is a monomer of Dacron?
(A)
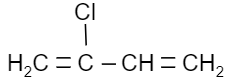
(B)
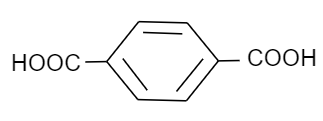
(C)
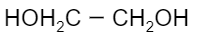
(D)
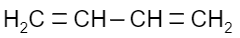
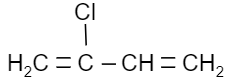

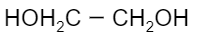
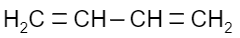
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, think about the common name of Dacron, which is generally called terylene. It is used regularly in the production of various fabrics. This name will give you an idea about the monomer units that are involved in the production of this polymer.
Complete step by step solution:
Before proceeding to answer this question, let us first know about what is a monomer. Monomers are the unit molecules involved in the formation of long chain polymers.
Now coming to dacron, we know that the common name of dacron is terylene. The name is derived from one of the molecules involved in the making of its monomer. The monomeric units involved in the production of dacron are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. These monomers undergo a condensation reaction to form the monomeric unit of dacron. Following is the reaction that ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid undergo to form dacron:
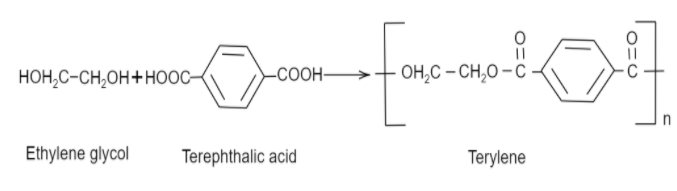
Thus, we can see that the monomers involved are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid.
Hence, the correct option is B and C.
Additional Information:
Dacron is a polymer that has a fairly widespread use in fabrics. It has high tensile strength and is slightly strong to stretch whether the fabric is wet or dry. It has a high resistance from being degraded by chemical bleaches and abrasive materials. It is often used in curtains, firefighter hoses, formal shirts and mixing with other woollen wear.
Note: Possibly you may get confused between phthalic and terephthalic acid, as they have the same molecular formula but are structural isomers of each other and both have two acid groups that are attached to a benzene ring. The only difference is that terephthalic acid is a para-isomer while phthalic acid is an ortho-isomer.
Complete step by step solution:
Before proceeding to answer this question, let us first know about what is a monomer. Monomers are the unit molecules involved in the formation of long chain polymers.
Now coming to dacron, we know that the common name of dacron is terylene. The name is derived from one of the molecules involved in the making of its monomer. The monomeric units involved in the production of dacron are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. These monomers undergo a condensation reaction to form the monomeric unit of dacron. Following is the reaction that ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid undergo to form dacron:

Thus, we can see that the monomers involved are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid.
Hence, the correct option is B and C.
Additional Information:
Dacron is a polymer that has a fairly widespread use in fabrics. It has high tensile strength and is slightly strong to stretch whether the fabric is wet or dry. It has a high resistance from being degraded by chemical bleaches and abrasive materials. It is often used in curtains, firefighter hoses, formal shirts and mixing with other woollen wear.
Note: Possibly you may get confused between phthalic and terephthalic acid, as they have the same molecular formula but are structural isomers of each other and both have two acid groups that are attached to a benzene ring. The only difference is that terephthalic acid is a para-isomer while phthalic acid is an ortho-isomer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




