
Which of the following complexes possess meridional isomer?
[A].$[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C{{l}_{3}}]$
[B].$[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]$
[C].$[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C{{l}_{4}}]$
[D].$[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{5}}Cl]$
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: Meridional isomer is a type of geometrical isomer. Geometrical isomers are a type of stereoisomers and they have the same chemical formula and chemical bonds but different spatial arrangements of atoms. Generally, meridional isomerism is shown by complexes of type $\left[ M{{X}_{3}}{{Y}_{3}} \right]$.
Complete answer:
Isomers are the compounds possessing the same atoms and bonds but in different spatial orientations. There are various types of isomerism in coordination compounds.
If three ligands of a compound occupy the same face, they are called facial isomers. However, if these three ligands lie on the same plane, the isomer is said to be meridional isomers.
Meridional isomerism is generally shown by octahedral complexes when the position of the three donor atoms of the ligands occupies the position around the meridian of the octahedron formed.
Meridional isomers are optically inactive as they possess a centre of symmetry.
Now let us check which of the given complexes will form meridional isomers.
In option [D] we have $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{5}}Cl]$ we can draw this as-
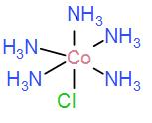
It cannot form meridional isomers, it has 5 identical ligands.
Next in option [C] we have, $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C{{l}_{4}}]$
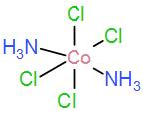
As we can see it does not have three identical isomers in the meridian, therefore it cannot possess meridional isomers.
In option [B] we have $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]$
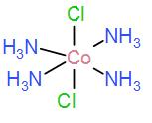
Even this complex does not have three
Lastly, we have [A] $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C{{l}_{3}}]$
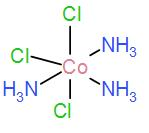
As it contains the three $N{{H}_{3}}$ groups in the meridional position, it has a meridional isomer.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [A] $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C{{l}_{3}}]$
Note: Octahedral complexes i.e. the complexes containing six ligands generally show meridional isomers. Complexes of the type $\left[ M{{X}_{3}}{{Y}_{3}} \right]$ exhibit two isomers facial as well as meridional. They show facial isomerism when the ligands are placed adjacent to each other and meridional isomerism by such complexes is shown above.
Complete answer:
Isomers are the compounds possessing the same atoms and bonds but in different spatial orientations. There are various types of isomerism in coordination compounds.
If three ligands of a compound occupy the same face, they are called facial isomers. However, if these three ligands lie on the same plane, the isomer is said to be meridional isomers.
Meridional isomerism is generally shown by octahedral complexes when the position of the three donor atoms of the ligands occupies the position around the meridian of the octahedron formed.
Meridional isomers are optically inactive as they possess a centre of symmetry.
Now let us check which of the given complexes will form meridional isomers.
In option [D] we have $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{5}}Cl]$ we can draw this as-

It cannot form meridional isomers, it has 5 identical ligands.
Next in option [C] we have, $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}C{{l}_{4}}]$

As we can see it does not have three identical isomers in the meridian, therefore it cannot possess meridional isomers.
In option [B] we have $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{4}}C{{l}_{2}}]$

Even this complex does not have three
Lastly, we have [A] $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C{{l}_{3}}]$

As it contains the three $N{{H}_{3}}$ groups in the meridional position, it has a meridional isomer.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [A] $[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C{{l}_{3}}]$
Note: Octahedral complexes i.e. the complexes containing six ligands generally show meridional isomers. Complexes of the type $\left[ M{{X}_{3}}{{Y}_{3}} \right]$ exhibit two isomers facial as well as meridional. They show facial isomerism when the ligands are placed adjacent to each other and meridional isomerism by such complexes is shown above.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




