
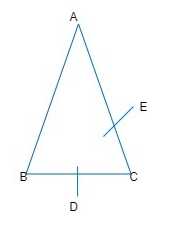
Three charges each have $ +q $ charge, are placed at the corner of an isosceles triangle ABC of sides BC and AC, 2a.D and E are the mid points of BC and CA. The work done in taking a charge Q from D to E is:
(A) $ \dfrac{eqQ}{8\pi {{\in }_{0}}a} $
(B) $ \dfrac{qQ}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}a} $
(C) Zero
(D) $ \dfrac{3qQ}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}a} $

Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: To find out the work done is taking charge Q from one point to another, we will find electrostatic potential at those points using
$ V=\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}r} $
$ V $ is the potential generated between the charges
$ q $ is the charge due to which our test charge is affected
r is the distance between the charges.
Complete step by step solution
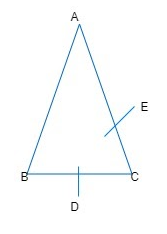
Here,
$ AC=BC=2a $
As D and E are midpoints of BC and AC (given).
$ \therefore $ $ AE=EC=a $
And,
$ BD=DC=a $
In $ \Delta ADC, $
$ \begin{align}
& {{(AD)}^{2}}={{(AC)}^{2}}-{{(DC)}^{2}} \\
& ={{(2a)}^{2}}-{{(a)}^{2}}={{(4a)}^{2}}-{{(a)}^{2}}={{(a)}^{2}} \\
& AD=a\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align} $
Similarly, potential at points D due to the given charge distribution is
$ {{V}_{D}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}[\dfrac{q}{BD}+\dfrac{q}{DC}+\dfrac{q}{AD}] $
$ \begin{align}
& =\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\left[ \dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}a} \right] \\
& =\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}a}\left[ 2+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right] \\
\end{align} $ ...........................(1)
Potential at point E due to given charge configuration is
$ {{V}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\left[ \dfrac{1}{q}+\dfrac{1}{q}+\dfrac{1}{a\sqrt{3}} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}a}\left[ 2+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right] $ ...........................(2)
From (1) and (2), it is clear that
The work done in taking a charge Q from D to E is
$ W=Q({{V}_{E}}-{{V}_{D}})=0 $ $ (\because {{V}_{D}}={{V}_{E}}) $
Therefore, option (C) is correct.
Note
Electric potential due to single charge is spherically symmetric. It should be clearly borne in mind that due to single charge,
$ F\propto \dfrac{1}{{{r}^{2}}} $ ; $ E\propto \dfrac{1}{{{r}^{2}}} $ but $ V\propto \dfrac{1}{r} $ ,
where r is the distance from the charge.
$ V=\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}r} $
$ V $ is the potential generated between the charges
$ q $ is the charge due to which our test charge is affected
r is the distance between the charges.
Complete step by step solution

Here,
$ AC=BC=2a $
As D and E are midpoints of BC and AC (given).
$ \therefore $ $ AE=EC=a $
And,
$ BD=DC=a $
In $ \Delta ADC, $
$ \begin{align}
& {{(AD)}^{2}}={{(AC)}^{2}}-{{(DC)}^{2}} \\
& ={{(2a)}^{2}}-{{(a)}^{2}}={{(4a)}^{2}}-{{(a)}^{2}}={{(a)}^{2}} \\
& AD=a\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align} $
Similarly, potential at points D due to the given charge distribution is
$ {{V}_{D}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}[\dfrac{q}{BD}+\dfrac{q}{DC}+\dfrac{q}{AD}] $
$ \begin{align}
& =\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\left[ \dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}a} \right] \\
& =\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}a}\left[ 2+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right] \\
\end{align} $ ...........................(1)
Potential at point E due to given charge configuration is
$ {{V}_{E}}=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}}\left[ \dfrac{1}{q}+\dfrac{1}{q}+\dfrac{1}{a\sqrt{3}} \right] $
$ =\dfrac{q}{4\pi {{\in }_{0}}a}\left[ 2+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \right] $ ...........................(2)
From (1) and (2), it is clear that
The work done in taking a charge Q from D to E is
$ W=Q({{V}_{E}}-{{V}_{D}})=0 $ $ (\because {{V}_{D}}={{V}_{E}}) $
Therefore, option (C) is correct.
Note
Electric potential due to single charge is spherically symmetric. It should be clearly borne in mind that due to single charge,
$ F\propto \dfrac{1}{{{r}^{2}}} $ ; $ E\propto \dfrac{1}{{{r}^{2}}} $ but $ V\propto \dfrac{1}{r} $ ,
where r is the distance from the charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




