
The propene reacts with \[HBr\] to form
(a) Ethane
(b) Hexane
(c) 1-bromo-propane
(d) 2-bromo propane
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Propene is a member of alkene compound. It is very reactive due to the presence of an unsymmetrical double bond. Propene readily reacts with \[HBr\] and forms bromide compounds. The reaction of \[HBr\] with propene is an example of a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Propene is an example of an unsymmetrical alkene in which three carbon atoms are present.
Propene readily reacts with \[HBr\]and forms 2-bromopropane (major product) and 1-bromopropane (minor product).
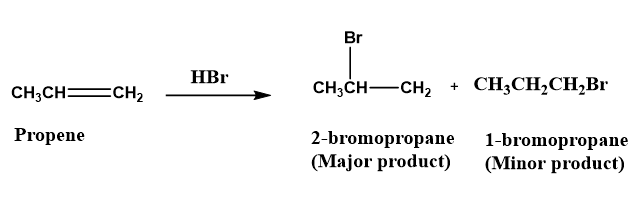
Image: Synthesis of 2-bromopropane
For the addition of \[HBr\]on an unsymmetrical alkene Marconikov rule is used to find a location at which the carbon atom of double bond the hydrogen and bromine atoms undergoes the addition.
According to the Marconikov rule the hydrogen atom of \[HBr\] prefers to bind the end of the carbon-carbon double bond which possesses the highest number of the hydrogen atom. Whereas the bromine atom prefers to bind the end of the carbon-carbon double bond which possesses the lowest number of hydrogen atoms.
Mechanism:
\[HBr\]is a polar molecule due to the electronegativity difference between hydrogen and bromine atoms.
Due to its polar nature, the \[HBr\]molecule can dissociate into \[{H^ + }\] (electrophile) and \[B{r^ - }\](nucleophile) when it approaches the alkene.
The electrophile (\[{H^ + }\]) can attack the double bond of propene and it can form a primary and secondary carbocation. Because secondary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation. Therefore, formation of secondary carbocation is observed.
After the addition of electrophile (\[{H^ + }\]) the bromide ion or nucleophile (\[B{r^ - }\]) react with formed carbocation and forms the final product i.e., 2-bromopropane (as a major product).

Image: Mechanism of the addition of hydrobromic acid over an unsymmetrical alkene.
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that option (d) will be the correct answer.
Note: When the addition of \[HBr\]to the unsymmetrical alkene takes place in the presence of peroxide then this reaction is called as anti-Markovnikov rule or peroxide effect or sometimes it is also known as the Kharasch effect. In such cases, the major product is derived from less stable carbocation.
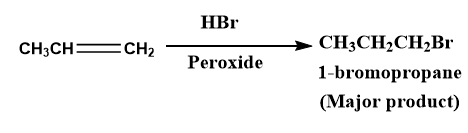
Image: addition of hydrobromic acid on alkene in the presence of peroxide.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Propene is an example of an unsymmetrical alkene in which three carbon atoms are present.
Propene readily reacts with \[HBr\]and forms 2-bromopropane (major product) and 1-bromopropane (minor product).

Image: Synthesis of 2-bromopropane
For the addition of \[HBr\]on an unsymmetrical alkene Marconikov rule is used to find a location at which the carbon atom of double bond the hydrogen and bromine atoms undergoes the addition.
According to the Marconikov rule the hydrogen atom of \[HBr\] prefers to bind the end of the carbon-carbon double bond which possesses the highest number of the hydrogen atom. Whereas the bromine atom prefers to bind the end of the carbon-carbon double bond which possesses the lowest number of hydrogen atoms.
Mechanism:
\[HBr\]is a polar molecule due to the electronegativity difference between hydrogen and bromine atoms.
Due to its polar nature, the \[HBr\]molecule can dissociate into \[{H^ + }\] (electrophile) and \[B{r^ - }\](nucleophile) when it approaches the alkene.
The electrophile (\[{H^ + }\]) can attack the double bond of propene and it can form a primary and secondary carbocation. Because secondary carbocation is more stable than primary carbocation. Therefore, formation of secondary carbocation is observed.
After the addition of electrophile (\[{H^ + }\]) the bromide ion or nucleophile (\[B{r^ - }\]) react with formed carbocation and forms the final product i.e., 2-bromopropane (as a major product).

Image: Mechanism of the addition of hydrobromic acid over an unsymmetrical alkene.
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that option (d) will be the correct answer.
Note: When the addition of \[HBr\]to the unsymmetrical alkene takes place in the presence of peroxide then this reaction is called as anti-Markovnikov rule or peroxide effect or sometimes it is also known as the Kharasch effect. In such cases, the major product is derived from less stable carbocation.

Image: addition of hydrobromic acid on alkene in the presence of peroxide.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

AssertionIn electrolytic refining of metal impure metal class 12 chemistry JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Hindi Medium (2025-26)

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 1 56/2/1 2025: Question Paper, Answers & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




