
Assertion:In electrolytic refining of metal, impure metal is made cathode while a strip of pure metal is used as anode.
Reason: The pure metal gets deposited at anode as anode mud.
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and Reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Answer
243k+ views
Hint: Electrolytic refining process is used for purification of metal. Metals obtained after smelting or other methods may contain impurities like unreacted oxides, other metals, non- metals and gases.
The purification of crude metals by removing metallic and non- metallic impurities is known as refining.
Complete step by step answer:
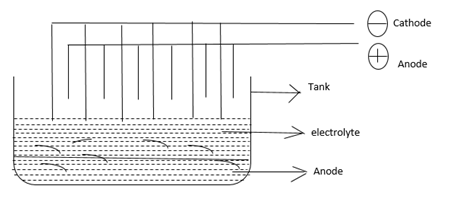
In electrolytic refining, anode [positively charged] and cathode [negatively charged] electrode is dipped into aqueous solution of their salt.
The rod of impure metal is used as anode and thin sheet of pure metal as cathode.
During electrolysis, metal from anode dissolve in the solution while the same amount of pure metal deposits on cathode.
The impurities like more reactive metals dissolve in the solution.
Less reactive metals are insoluble. They form anode mud at the bottom.
In this process $99.99\% $ pure metal is obtained.
Metals like $Ni,Al,Zn$ are refined by his method.
In the given question:
Assertion is – impure metal is made cathode while a strip of pure metal is used as anode.
But as we already discussed, impure metal is made anode and pure metal is used as cathode.
Reason is – The pure metal gets deposited at anode mud.
But pure metal gets deposited at cathode and impurities form anode mud.
Therefore, the above explanation, the correct option is [D] Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Note: Impure metal is made anode and pure metal strip is made cathode during electrolytic refining. During electrolysis pure metal from impure anode gets dissolved in the solution. As metal is always positively charged, it is migrated towards cathode and deposit. then cathodes become thick and replaced from time to time.
The purification of crude metals by removing metallic and non- metallic impurities is known as refining.
Complete step by step answer:
In electrolytic refining, anode [positively charged] and cathode [negatively charged] electrode is dipped into aqueous solution of their salt.
The rod of impure metal is used as anode and thin sheet of pure metal as cathode.
During electrolysis, metal from anode dissolve in the solution while the same amount of pure metal deposits on cathode.
The impurities like more reactive metals dissolve in the solution.
Less reactive metals are insoluble. They form anode mud at the bottom.
In this process $99.99\% $ pure metal is obtained.
Metals like $Ni,Al,Zn$ are refined by his method.

In the given question:
Assertion is – impure metal is made cathode while a strip of pure metal is used as anode.
But as we already discussed, impure metal is made anode and pure metal is used as cathode.
Reason is – The pure metal gets deposited at anode mud.
But pure metal gets deposited at cathode and impurities form anode mud.
Therefore, the above explanation, the correct option is [D] Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Note: Impure metal is made anode and pure metal strip is made cathode during electrolytic refining. During electrolysis pure metal from impure anode gets dissolved in the solution. As metal is always positively charged, it is migrated towards cathode and deposit. then cathodes become thick and replaced from time to time.
Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Different Types of Solutions in Chemistry

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

JEE Mains Result 2026 OUT Check Scorecard Percentile Cutoff and Toppers

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 2 (56/5/2) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 - The D and F Block Elements - 2025-26

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 3 56/4/3 2025 Question Paper PDF & Answer Key

CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 - Chemical Kinetics - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers




