
The pressure (P) after mixing is
(A) 5 atm
(B) 2.5 atm
(C) 2 atm
(D) 4 atm

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: To calculate the total pressure of the gas, Dalton law of partial pressure is applied. The pressure in the third chamber is the total pressure which is the sum of both the pressure pressure exerted by two chambers
Complete step by step answer:
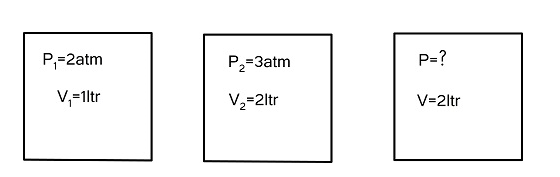
Given,
${P_1}$ is 2atm
${P_2}$ is 3atm
${V_1}$ is 1 ltr
${V_2}$ is 2 ltr
${V_{Total}}$ is 2 ltr
The Dalton law of partial pressure states that the total pressure exerted by the gaseous mixture is equal to the sum total of the individual partial pressure exerted by the gases molecule.
Example: There are two gases molecule (gas A and gas B) present having individual value of partial pressure. The total pressure exerted by the mixture of gas A and gas B is equal to the sum of the individual partial pressure exerted by both gas A and B.
The pressure exerted by the individual gas molecule present in a mixture of gases is known as partial pressure.
Dalton's law formula is given as shown below.
${P_{total}} = {P_1} + {P_2} + {P_3}$ ${P_n}$
The formula to calculate the total partial pressure is shown below.
${P_{total}} = {P_1} + {P_2}$
${P_{total}} = 2 + 3$
$\Rightarrow {P_{total}} = 5$
Thus, the total pressure after mixing of two gases present in the chamber is 5 atm.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: Dalton’s law of partial pressure helps in determining the pressure of dry gas only. Unless the individual gases present do not react chemically with each other they do not affect the pressure.
Complete step by step answer:
Given,
${P_1}$ is 2atm
${P_2}$ is 3atm
${V_1}$ is 1 ltr
${V_2}$ is 2 ltr
${V_{Total}}$ is 2 ltr
The Dalton law of partial pressure states that the total pressure exerted by the gaseous mixture is equal to the sum total of the individual partial pressure exerted by the gases molecule.
Example: There are two gases molecule (gas A and gas B) present having individual value of partial pressure. The total pressure exerted by the mixture of gas A and gas B is equal to the sum of the individual partial pressure exerted by both gas A and B.
The pressure exerted by the individual gas molecule present in a mixture of gases is known as partial pressure.
Dalton's law formula is given as shown below.
${P_{total}} = {P_1} + {P_2} + {P_3}$ ${P_n}$
The formula to calculate the total partial pressure is shown below.
${P_{total}} = {P_1} + {P_2}$
${P_{total}} = 2 + 3$
$\Rightarrow {P_{total}} = 5$
Thus, the total pressure after mixing of two gases present in the chamber is 5 atm.
So, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: Dalton’s law of partial pressure helps in determining the pressure of dry gas only. Unless the individual gases present do not react chemically with each other they do not affect the pressure.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




