
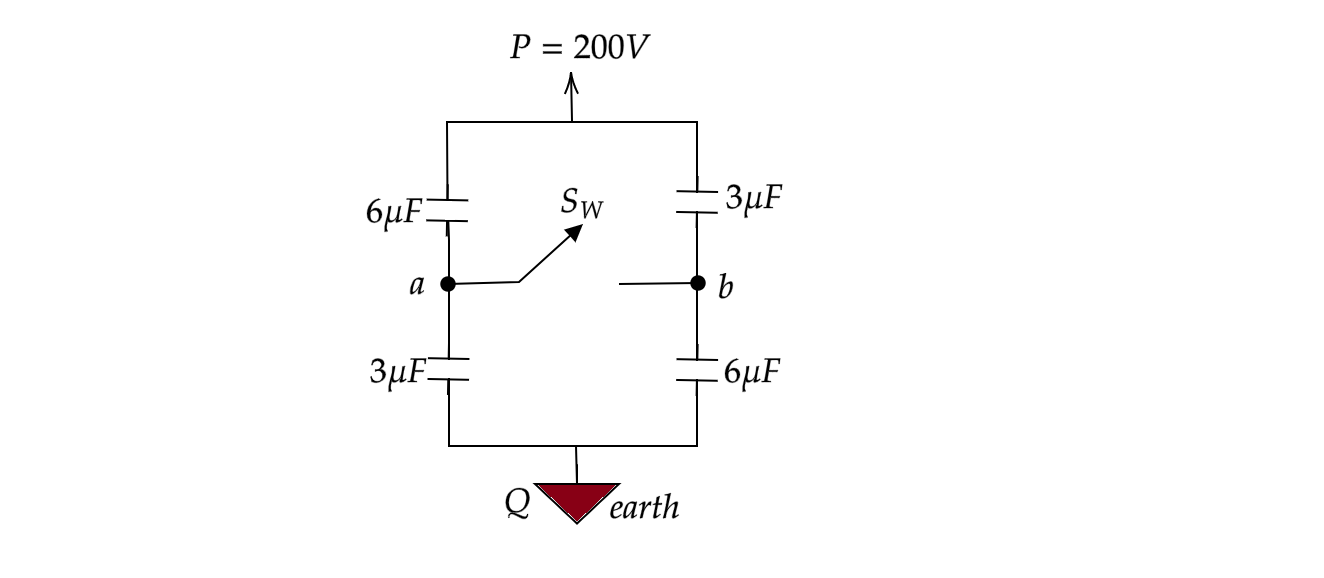
The potential difference between \[a\] and \[b\] when the switch is open is given as \[\dfrac{200}{x}V\] .
Find \[x\] .

Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: If the switch is left open, it means that the points \[a\] and \[b\] are not connected and the two arms of the circuits having two capacitors in each arm are connected in parallel across the \[200V\] source. The circuit is completed because of the earth connection shown, the potential of the earth is taken as \[0V\] .
Complete step by step answer:
As discussed above, the capacitors in the left arm are in series and the capacitors in the right arm are also in series. Since both the arms connected across PQ are in parallel, the voltage across both the arms is the same. Since we need to find the voltage across points \[a\] and \[b\] , we need to find the voltage drop caused by the \[6\mu F\] capacitor in the left arm and the voltage drop caused by the \[3\mu F\] capacitor in the right arm.
Hence voltage drop caused by the \[6\mu F\] capacitor is given as \[{{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{a}}\] where
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{a}}=\dfrac{3}{3+6}{{V}_{PQ}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{a}}=\dfrac{3}{3+6}\times 200V=\dfrac{200}{3}V--equation(1) \\
\end{align}\]
The denominator in the above calculation is the sum of both the capacitors in that arm.
Similarly, we can calculate the voltage drop caused by the \[3\mu F\] capacitor in the right arm,
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{b}}=\dfrac{6}{3+6}{{V}_{PQ}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{b}}=\dfrac{6}{3+6}\times 200V=\dfrac{400}{3}V--equation(2) \\
\end{align}\]
Subtracting the above two equations, that is, \[equation(2)-equation(1)\] , we get
\[{{V}_{a}}-{{V}_{b}}=\dfrac{400}{3}V-\dfrac{200}{3}V=\dfrac{200}{3}V\]
This is the required potential difference.
Therefore, the value of \[x\] is equal to \[3\].
Note: In the above calculation, you must have noticed that while calculating the potential drop due to a capacitor we used the value of its adjacent capacitor in the numerator and not the value of the capacitor itself; this is because the voltage is divided in a capacitive DC voltage divider according to the formula \[V=\dfrac{Q}{C}\] , which establishes that voltage is inversely proportional to the capacitance value of the capacitor.
Complete step by step answer:
As discussed above, the capacitors in the left arm are in series and the capacitors in the right arm are also in series. Since both the arms connected across PQ are in parallel, the voltage across both the arms is the same. Since we need to find the voltage across points \[a\] and \[b\] , we need to find the voltage drop caused by the \[6\mu F\] capacitor in the left arm and the voltage drop caused by the \[3\mu F\] capacitor in the right arm.
Hence voltage drop caused by the \[6\mu F\] capacitor is given as \[{{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{a}}\] where
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{a}}=\dfrac{3}{3+6}{{V}_{PQ}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{a}}=\dfrac{3}{3+6}\times 200V=\dfrac{200}{3}V--equation(1) \\
\end{align}\]
The denominator in the above calculation is the sum of both the capacitors in that arm.
Similarly, we can calculate the voltage drop caused by the \[3\mu F\] capacitor in the right arm,
\[\begin{align}
& {{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{b}}=\dfrac{6}{3+6}{{V}_{PQ}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{V}_{P}}-{{V}_{b}}=\dfrac{6}{3+6}\times 200V=\dfrac{400}{3}V--equation(2) \\
\end{align}\]
Subtracting the above two equations, that is, \[equation(2)-equation(1)\] , we get
\[{{V}_{a}}-{{V}_{b}}=\dfrac{400}{3}V-\dfrac{200}{3}V=\dfrac{200}{3}V\]
This is the required potential difference.
Therefore, the value of \[x\] is equal to \[3\].
Note: In the above calculation, you must have noticed that while calculating the potential drop due to a capacitor we used the value of its adjacent capacitor in the numerator and not the value of the capacitor itself; this is because the voltage is divided in a capacitive DC voltage divider according to the formula \[V=\dfrac{Q}{C}\] , which establishes that voltage is inversely proportional to the capacitance value of the capacitor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




