
The number of optically active isomer(s) of the compound $C{{H}_{3}}CHBrCHBrCOOH$ is (are):
A. Zero
B. One
C. Three
D. Four
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: To know the number of optical isomers is present in a compound first we should know the number of chiral centers is present in the given molecule. Chiral center means a carbon atom should be bonded to four different atoms. Each chiral center will produce two different optical isomers for a compound
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that we have to find the number optically active isomers possible for $C{{H}_{3}}CHBrCHBrCOOH$ .
- First of all we should draw the structure of the given compound.
- The structure of the given compound is as follows.
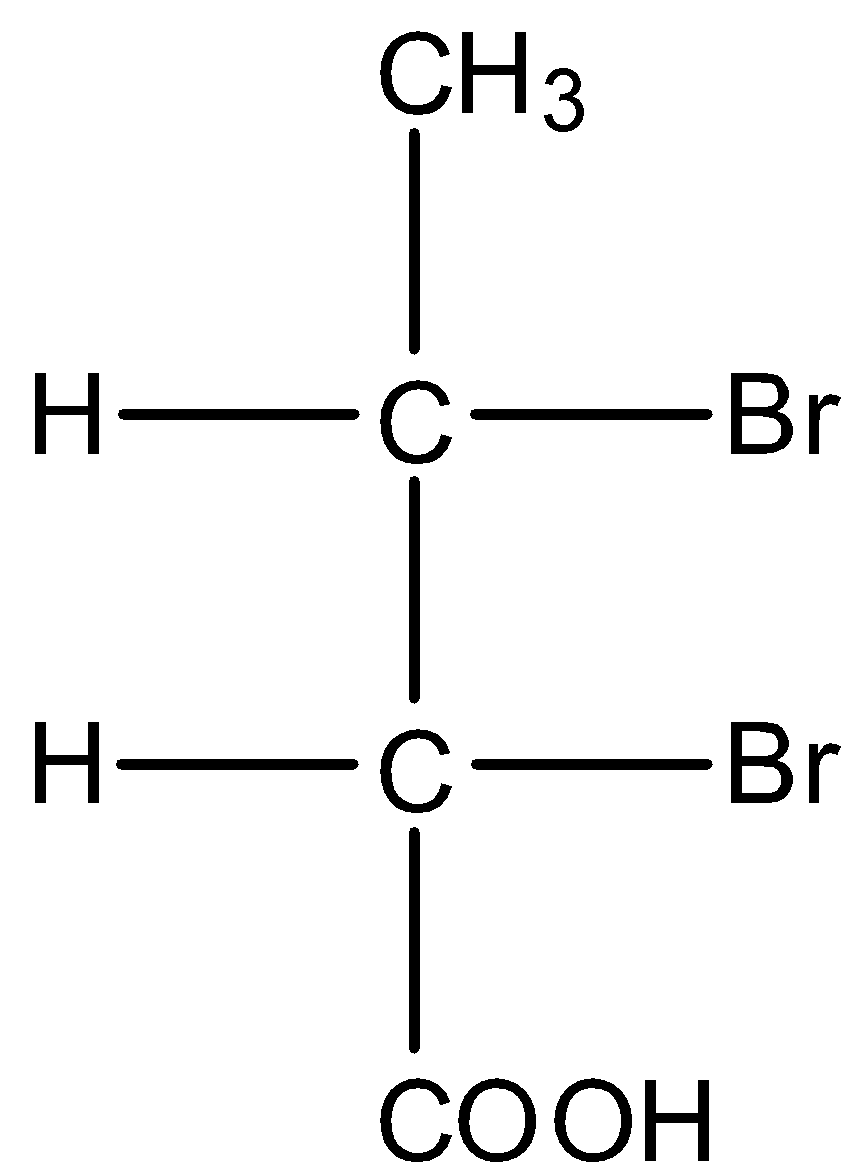
- Now we have to find the number of chiral centers in the above structure.
- The chiral centers present in the given molecule can be represented with star marks as follows.
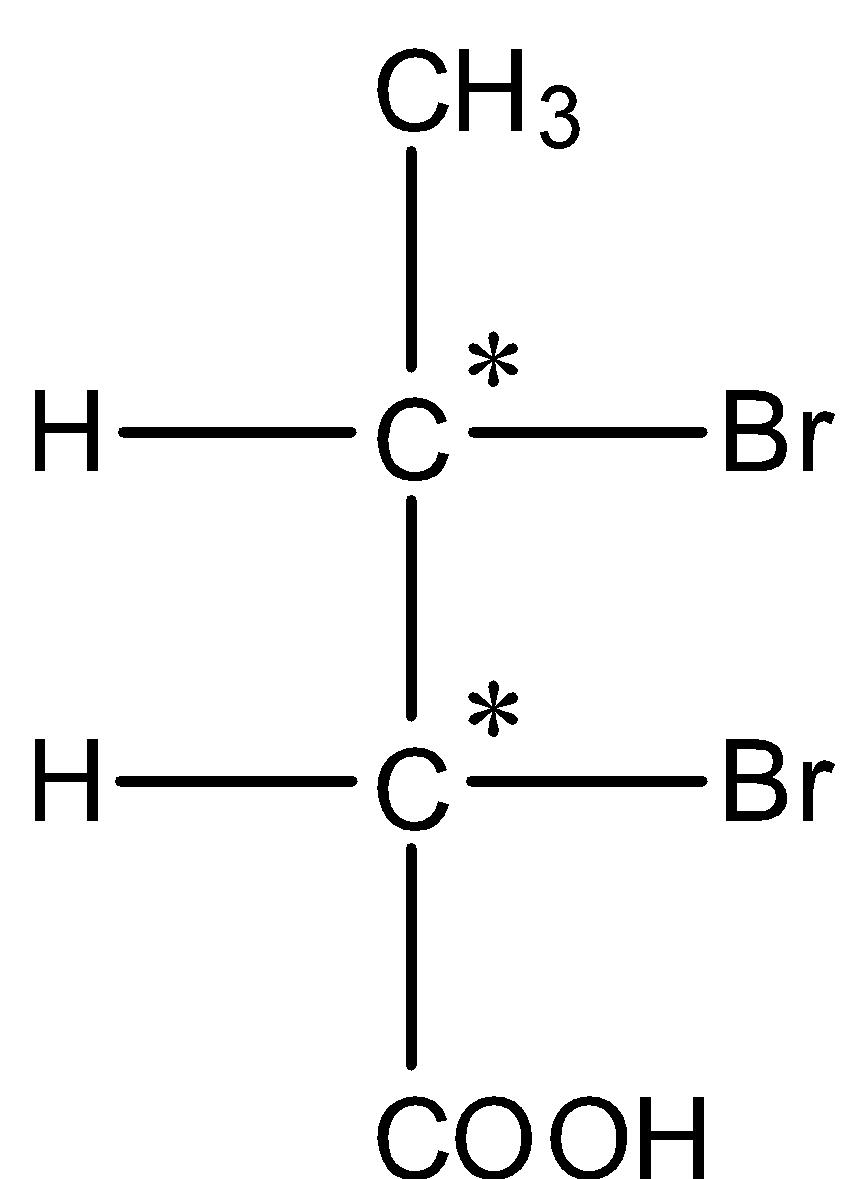
- Means in the given compound there are two chiral centers.
- The formula to calculate the number of optically active isomers from the number of chiral centers is as follows.
- Total number of optically active isomers = ${{2}^{n}}$
Here n = number of chiral centers present for a particular molecule.
- We know that in the given molecule there are two chiral centers then substitute it in the above equation to get a number of optically active isomers.
- Total number of optically active isomers for the given compound $={{2}^{n}}={{2}^{2}}=4$ .
- Therefore the given molecule contains 4 optically active isomers.
- So, the correct option is D.
Note: We have to check which carbon is chiral and which carbon is achiral during the calculation of number of optically active isomers. Optically active means they will rotate the plane polarized light from one direction to another.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that we have to find the number optically active isomers possible for $C{{H}_{3}}CHBrCHBrCOOH$ .
- First of all we should draw the structure of the given compound.
- The structure of the given compound is as follows.

- Now we have to find the number of chiral centers in the above structure.
- The chiral centers present in the given molecule can be represented with star marks as follows.

- Means in the given compound there are two chiral centers.
- The formula to calculate the number of optically active isomers from the number of chiral centers is as follows.
- Total number of optically active isomers = ${{2}^{n}}$
Here n = number of chiral centers present for a particular molecule.
- We know that in the given molecule there are two chiral centers then substitute it in the above equation to get a number of optically active isomers.
- Total number of optically active isomers for the given compound $={{2}^{n}}={{2}^{2}}=4$ .
- Therefore the given molecule contains 4 optically active isomers.
- So, the correct option is D.
Note: We have to check which carbon is chiral and which carbon is achiral during the calculation of number of optically active isomers. Optically active means they will rotate the plane polarized light from one direction to another.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




