
The number of neighbours around each particle in a face-centred cubic lattice is:
A.4
B.6
C.12
D.8
Answer
594k+ views
Hint:
In a face centred cubic (fcc) lattice, the atoms of the given substance are located on all 6 sides of the cubic structure as well as on all the 8 vertices of the cube.
Complete step by step answer:
The geometrical representation or the structure of a face centred cubic lattice can be visually represented as follows:
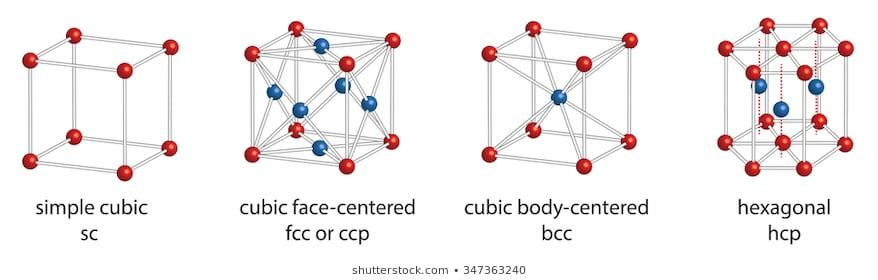
As the name suggests, a Face Centred Cubic (fcc) lattice structure has atoms on all the sides of the cubic structure as well as all the vertices. There is no atom present in the centre of the cube. This brings the total count of the total number of atoms present in a Face Centred Cubic structure to 12. Considering that each vertex contains \[{\dfrac{1}{8}^{th}}\]of an atom and each face contains half an atom, the total number of atoms present in face centred cubic lattice is :
= \[\dfrac{1}{8}\](number of vertices) + \[\dfrac{1}{2}\](number of sides)
= \[\dfrac{1}{8}\](8) + \[\dfrac{1}{2}\](6)
\[ = {\text{ }}1{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}3\]
\[ = {\text{ }}4 \]atoms
Hence in FCC, there are 4 atoms per unit cell.
-In order to understand the number of neighbours around each particle in a face-centred cubic, we must understand a concept known as Coordination number.
-In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it.
-The coordination number is fixed for a certain type of lattice structure. And for Face Centred Cubic lattice structure, the coordination number is 12.
-Hence, by definition, the number of neighbours around each particle in a face-centred cubic lattice is 12.
Hence, Option C is the correct option.
Note:
The coordination number for the various types of cubic arrangements are as follows:
Simple cubic lattice: 6
Body centred cubic lattice: 8
Face centred cubic lattice: 12
In a face centred cubic (fcc) lattice, the atoms of the given substance are located on all 6 sides of the cubic structure as well as on all the 8 vertices of the cube.
Complete step by step answer:
The geometrical representation or the structure of a face centred cubic lattice can be visually represented as follows:

As the name suggests, a Face Centred Cubic (fcc) lattice structure has atoms on all the sides of the cubic structure as well as all the vertices. There is no atom present in the centre of the cube. This brings the total count of the total number of atoms present in a Face Centred Cubic structure to 12. Considering that each vertex contains \[{\dfrac{1}{8}^{th}}\]of an atom and each face contains half an atom, the total number of atoms present in face centred cubic lattice is :
= \[\dfrac{1}{8}\](number of vertices) + \[\dfrac{1}{2}\](number of sides)
= \[\dfrac{1}{8}\](8) + \[\dfrac{1}{2}\](6)
\[ = {\text{ }}1{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}3\]
\[ = {\text{ }}4 \]atoms
Hence in FCC, there are 4 atoms per unit cell.
-In order to understand the number of neighbours around each particle in a face-centred cubic, we must understand a concept known as Coordination number.
-In chemistry, crystallography, and materials science, the coordination number, also called ligancy, of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of atoms, molecules or ions bonded to it.
-The coordination number is fixed for a certain type of lattice structure. And for Face Centred Cubic lattice structure, the coordination number is 12.
-Hence, by definition, the number of neighbours around each particle in a face-centred cubic lattice is 12.
Hence, Option C is the correct option.
Note:
The coordination number for the various types of cubic arrangements are as follows:
Simple cubic lattice: 6
Body centred cubic lattice: 8
Face centred cubic lattice: 12
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




