
The mid points of two small magnetic dipoles of length $ d $ in end-on positions, are separated by a distance $ x $, \[\left( {x > > d} \right)\]. The force between them is proportional to $ {x^{ - n}} $ where $ n $ is:
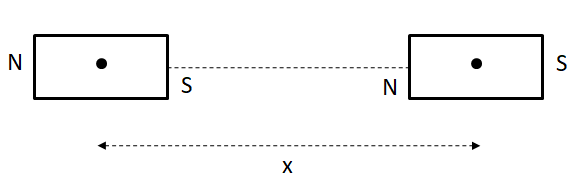
(A) $ 1 $
(B) $ 2 $
(C) $ 3 $
(D) $ 4 $
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint To solve this question, we have to use the formula for the magnetic field at the axial position due to a magnet. The parameters of the magnets are given in the question, which can be used to get the final answer.
Formula Used: The formulae used to solve this question are given by
$ \Rightarrow {B_A} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\left( {2m} \right)}}{{4\pi {r^3}}} $
Here $ m $ is the magnetic dipole moment, $ r $ is the distance from the centre of the magnet, and $ {\mu _0} $ is the magnetic permeability in vacuum.
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dr}} $
Here $ U $ is the potential energy corresponding to the conservative force $ F $, and $ r $ is the distance.
Complete step by step answer
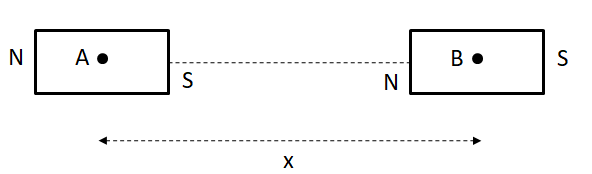
As both the dipoles are placed axially, they will exert force on each other due to the axial magnetic field.
We know that the axial magnetic field is given by
$ \Rightarrow {B_A} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\left( {2m} \right)}}{{4\pi {r^3}}} $
Here, according to the question, the dipoles are of length $ d $ and their mid points are separated by a distance $ x $. But it is also given that \[\left( {x > > d} \right)\]. So the length of the dipoles can be neglected and approximately we take $ r = x $. So, we have the magnetic field
$ \Rightarrow {B_A} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\left( {2m} \right)}}{{4\pi {x^3}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {B_A} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}m}}{{2\pi {x^3}}} $ ……...(i)
Now, the magnetic potential energy is given by
$ \Rightarrow U = - mB $
Substituting (i), we get
$ \Rightarrow U = - \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{m^2}}}{{2\pi {x^3}}} $ ……...(ii)
Also, as the magnetic force is conservative in nature, so it is related to the potential energy by $ F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dr}} $
Here $ r = x $
$ \therefore F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}} $
Substituting $ U $ from (ii), we have
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{{d\left[ { - \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{m^2}}}{{2\pi {x^3}}}} \right]}}{{dx}} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{{3{\mu _0}{m^2}}}{{2\pi {x^4}}} $
As we can see from the final expression of the force that it is proportional to $ \dfrac{1}{{{x^4}}} $ or $ {x^{ - 4}} $ .
Comparing $ {x^{ - n}} $, we get $ n = 4 $ .
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note
If we do not remember the formula for the equatorial magnetic field, then we can take the help of the electrostatic analogy. We know that the electric field due to a dipole at its equatorial position is given by $ E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{2p}}{{{r^3}}} $. Replacing the electric field $ E $ with the magnetic field $ B $, the electric dipole moment $ p $ with the magnetic dipole moment $ m $ and the constant $ \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} $ with the constant $ \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} $ we can get the corresponding expression for the axial magnetic field.
Formula Used: The formulae used to solve this question are given by
$ \Rightarrow {B_A} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\left( {2m} \right)}}{{4\pi {r^3}}} $
Here $ m $ is the magnetic dipole moment, $ r $ is the distance from the centre of the magnet, and $ {\mu _0} $ is the magnetic permeability in vacuum.
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dr}} $
Here $ U $ is the potential energy corresponding to the conservative force $ F $, and $ r $ is the distance.
Complete step by step answer

As both the dipoles are placed axially, they will exert force on each other due to the axial magnetic field.
We know that the axial magnetic field is given by
$ \Rightarrow {B_A} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\left( {2m} \right)}}{{4\pi {r^3}}} $
Here, according to the question, the dipoles are of length $ d $ and their mid points are separated by a distance $ x $. But it is also given that \[\left( {x > > d} \right)\]. So the length of the dipoles can be neglected and approximately we take $ r = x $. So, we have the magnetic field
$ \Rightarrow {B_A} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}\left( {2m} \right)}}{{4\pi {x^3}}} $
$ \Rightarrow {B_A} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}m}}{{2\pi {x^3}}} $ ……...(i)
Now, the magnetic potential energy is given by
$ \Rightarrow U = - mB $
Substituting (i), we get
$ \Rightarrow U = - \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{m^2}}}{{2\pi {x^3}}} $ ……...(ii)
Also, as the magnetic force is conservative in nature, so it is related to the potential energy by $ F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dr}} $
Here $ r = x $
$ \therefore F = - \dfrac{{dU}}{{dx}} $
Substituting $ U $ from (ii), we have
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{{d\left[ { - \dfrac{{{\mu _0}{m^2}}}{{2\pi {x^3}}}} \right]}}{{dx}} $
$ \Rightarrow F = - \dfrac{{3{\mu _0}{m^2}}}{{2\pi {x^4}}} $
As we can see from the final expression of the force that it is proportional to $ \dfrac{1}{{{x^4}}} $ or $ {x^{ - 4}} $ .
Comparing $ {x^{ - n}} $, we get $ n = 4 $ .
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note
If we do not remember the formula for the equatorial magnetic field, then we can take the help of the electrostatic analogy. We know that the electric field due to a dipole at its equatorial position is given by $ E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}}\dfrac{{2p}}{{{r^3}}} $. Replacing the electric field $ E $ with the magnetic field $ B $, the electric dipole moment $ p $ with the magnetic dipole moment $ m $ and the constant $ \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} $ with the constant $ \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} $ we can get the corresponding expression for the axial magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




