
The maximum value of refractive index of a material of prism which allows the passage of light through it when the angle of prism is $A$ is:
A. $\sqrt {1 + {{\sin }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} $
B. $\sqrt {1 + {{\cos }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} $
C. $\sqrt {1 + {{\tan }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} $
D. $\sqrt {1 + {{\cot }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} $
Answer
553.2k+ views
Hint:For the maximum value of refractive index, the angle of incident is with respect to the surface of the prism and since there is only refraction of light takes place so there will not be total internal reflection and use Snell’s law and thermodynamic property.
Formula used:
According to the Snell’s law, the refractive index is given by $\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
where, $i$ is the angle of incident of light and $r$ is the angle of refraction.
Complete step by step answer:
From the question, we know that the angle of the prism is $A$.Since there is only refraction of light and no total internal reflection. So,
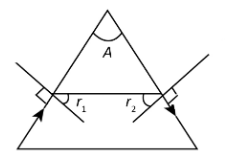
\[{r_1} = {r_2}\]
We know that the angle of prism is equal to the sum of angle of refraction and the angle of emergence. Thus,
$A = {r_1} + {r_2}$
The above equation can be written as,
$
A = {r_1} + {r_1}\\
\Rightarrow{r_1} = \dfrac{A}{2}
$
Now we using Snell’s law, the refractive index of the material of the prism will be,
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin {r_1}}}$
Here, $i$ is the angle of incident, which is equal to $90^\circ $ as there is no total internal reflection.
$
\mu = \dfrac{{\sin 90^\circ }}{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}}\\
\Rightarrow\mu = \dfrac{1}{{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}}
$
Rewrite the above equation,
\[\mu = \dfrac{{\sqrt 1 }}{{\sqrt {{{\sin }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} }}\]
Now we use the thermodynamic property, ${\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = 1$
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\sin }^2}\dfrac{A}{2} + {{\cos }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} }}{{\sqrt {{{\sin }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} }}$
After further simplifying the above equation, we have,
$\therefore\mu = \sqrt {1 + {{\cot }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} $
Thus, the maximum value of refractive index of a material of prism which allows the passage of light through it when the angle of prism is $A$ is $\sqrt {1 + {{\cot }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} $.
Hence option D is correct.
Note:The relation between the refractive index and angle of minimum deviation is expressed as, $\mu = \dfrac{{\sin \dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}}}{{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}}$
where ${\delta _m}$ is the minimum deviation and $A$ is the angle of prism. In the case of minimum deviation, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence and symmetrical refraction takes place.
Formula used:
According to the Snell’s law, the refractive index is given by $\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
where, $i$ is the angle of incident of light and $r$ is the angle of refraction.
Complete step by step answer:
From the question, we know that the angle of the prism is $A$.Since there is only refraction of light and no total internal reflection. So,

\[{r_1} = {r_2}\]
We know that the angle of prism is equal to the sum of angle of refraction and the angle of emergence. Thus,
$A = {r_1} + {r_2}$
The above equation can be written as,
$
A = {r_1} + {r_1}\\
\Rightarrow{r_1} = \dfrac{A}{2}
$
Now we using Snell’s law, the refractive index of the material of the prism will be,
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin {r_1}}}$
Here, $i$ is the angle of incident, which is equal to $90^\circ $ as there is no total internal reflection.
$
\mu = \dfrac{{\sin 90^\circ }}{{\sin \left( {\dfrac{A}{2}} \right)}}\\
\Rightarrow\mu = \dfrac{1}{{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}}
$
Rewrite the above equation,
\[\mu = \dfrac{{\sqrt 1 }}{{\sqrt {{{\sin }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} }}\]
Now we use the thermodynamic property, ${\sin ^2}A + {\cos ^2}A = 1$
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sqrt {{{\sin }^2}\dfrac{A}{2} + {{\cos }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} }}{{\sqrt {{{\sin }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} }}$
After further simplifying the above equation, we have,
$\therefore\mu = \sqrt {1 + {{\cot }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} $
Thus, the maximum value of refractive index of a material of prism which allows the passage of light through it when the angle of prism is $A$ is $\sqrt {1 + {{\cot }^2}\dfrac{A}{2}} $.
Hence option D is correct.
Note:The relation between the refractive index and angle of minimum deviation is expressed as, $\mu = \dfrac{{\sin \dfrac{{A + {\delta _m}}}{2}}}{{\sin \dfrac{A}{2}}}$
where ${\delta _m}$ is the minimum deviation and $A$ is the angle of prism. In the case of minimum deviation, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence and symmetrical refraction takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




