
The main cause of zener breakdown is
A. the base semiconductor being germanium.
B. production of electron-hole pairs due to thermal excitation.
C. low doping.
D. high doping.
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: A zener diode performs voltage regulation when it undergoes breakdown. Breakdown is a condition which occurs in reverse bias, under which, excessive minority carrier flow causes large current variation for almost no variation in voltage.
Complete step by step answer:
The main cause of zener breakdown is high doping concentrations. The breakdown is a condition when upon increasing the voltage in small amounts; we experience a massive current flow in the device. Zener breakdown occurs when we apply reverse bias to a heavily doped diode. In a reverse bias situation, ideally no current flows for a p-n junction diode, the diode acts as an open switch. But, when we increase the amount of doping the junction seems to narrow down.
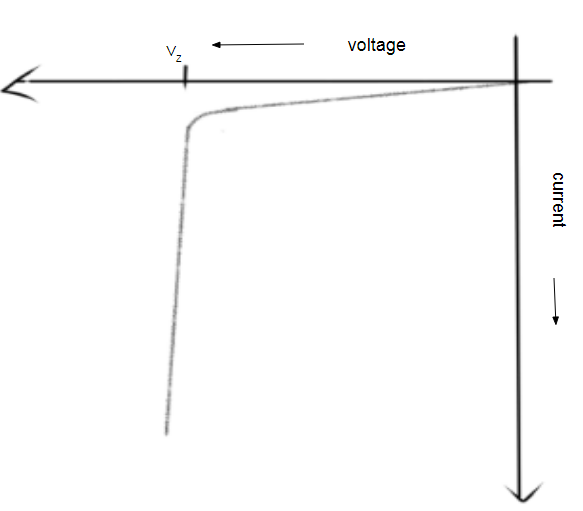
In reverse bias of a p-n junction diode, the current only exists due to the presence of minority carriers generated due to thermal excitation. For heavily doped junctions, when reverse voltage is increased, the electric field at junction increases (as more carriers are present now to create such a pull) which causes covalent bonds to break. The process is analogous to what happens when we apply accurate potential difference across a gas (spoiler: It ionizes). So, in our zener diode, upon breakdown, large numbers of minority carriers are generated and current flows through the junction.
The correct option, therefore, is (D) high doping.
Additional Information:
The breakdown voltage is controlled with the help of doping concentrations in a zener diode. A zener diode is an application of the zener breakdown phenomenon. In it, the voltage remains fixed upon breakdown. Hence, zener diodes are called voltage regulators.
Note:
An easier way to remember this is to consider the fact that heavy doping means more carriers and more carriers facilitate breakdown, which is a condition when a massive amount of current flows.
Complete step by step answer:
The main cause of zener breakdown is high doping concentrations. The breakdown is a condition when upon increasing the voltage in small amounts; we experience a massive current flow in the device. Zener breakdown occurs when we apply reverse bias to a heavily doped diode. In a reverse bias situation, ideally no current flows for a p-n junction diode, the diode acts as an open switch. But, when we increase the amount of doping the junction seems to narrow down.

In reverse bias of a p-n junction diode, the current only exists due to the presence of minority carriers generated due to thermal excitation. For heavily doped junctions, when reverse voltage is increased, the electric field at junction increases (as more carriers are present now to create such a pull) which causes covalent bonds to break. The process is analogous to what happens when we apply accurate potential difference across a gas (spoiler: It ionizes). So, in our zener diode, upon breakdown, large numbers of minority carriers are generated and current flows through the junction.
The correct option, therefore, is (D) high doping.
Additional Information:
The breakdown voltage is controlled with the help of doping concentrations in a zener diode. A zener diode is an application of the zener breakdown phenomenon. In it, the voltage remains fixed upon breakdown. Hence, zener diodes are called voltage regulators.
Note:
An easier way to remember this is to consider the fact that heavy doping means more carriers and more carriers facilitate breakdown, which is a condition when a massive amount of current flows.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




