
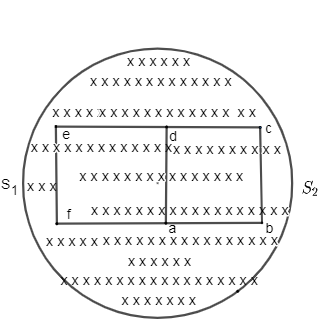
The magnetic field in the cylinder region shown in the figure increases at a constant rate of 20.0mT/s. each side of the square loop abcd and defa has a length of 1.00cm and a resistance of 4.00$\Omega $. Find the current (magnitude and sense) in the wire and if
A. The switch ${{S}_{1}}$is closed but ${{S}_{2}}$ is open,
B.${{S}_{1}}$ is open but ${{S}_{2}}$ is closed,
C. both ${{S}_{1}}$and ${{S}_{2}}$ are open
D. both ${{S}_{1}}$and ${{S}_{2}}$are closed

Answer
562.2k+ views
Hint: In order to find current we have to find the emf and the resistance of the circuit in (a) current will flow in edaf in (b) current will flow in abcd in (c) no current will flow in (d) circuit will act as a balanced Wheatstone bridge hence no current will flow along ad.
Formula used:
$\phi =B.A$
$\begin{align}
& e=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& e=emf \\
\end{align}$
Complete answer:
A) ${{S}_{1}}$ Closed and ${{S}_{2}}$ is open
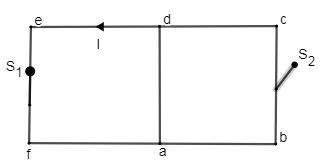
Formula for the flux = $\phi =B.A\cos \theta $
Here the θ will be zero because magnetic field is perpendicular
$\phi =B.A$
Where,
$\phi =$ Flux
B = magnetic field
A = area
Now emf,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow e=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow e=A\dfrac{dB}{dt} \\
& \therefore e={{l}^{2}}\times \dfrac{dB}{dt}....(1) \\
\end{align}$
It is given that
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow l=1cm \\
& \Rightarrow l=1\times {{10}^{-2}}m \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{db}{dt}=20mT/s \\
& \therefore \dfrac{db}{dt}=20\times {{10}^{-3}}T/s \\
\end{align}$
Substituting value in equation (1)
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow e={{\left( 1\times {{10}^{-2}} \right)}^{2}}\times 20\times {{10}^{-3}} \\
& \Rightarrow e={{10}^{-4}}\times 2\times {{10}^{-2}} \\
& \therefore e=2\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now we know that current
$I=\dfrac{e}{R}....\left( 2 \right)$
Here it is given that resistance is $4\Omega $ on every side hence
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow R=4+4+4+4 \\
& \therefore R=16\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Hence the current
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow I=\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{-6}}}{16} \\
& \therefore I=1.25\times {{10}^{-7}}A \\
\end{align}$
Along ad
B.${{S}_{1}}$ is open but ${{S}_{2}}$ is closed,
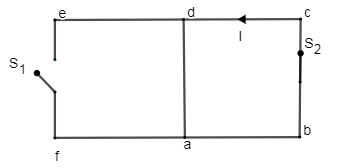
Current will form a circuit abcd since all values are the same; the magnitude of the current will also be the same. Hence
$I=1.25\times {{10}^{-7}}A$
C. both ${{S}_{1}}$and ${{S}_{2}}$ are open
If both ${{S}_{1}}$and ${{S}_{2}}$ are open then the circuit will not complete hence current along and is zero.
D. both ${{S}_{1}}$and ${{S}_{2}}$are closed
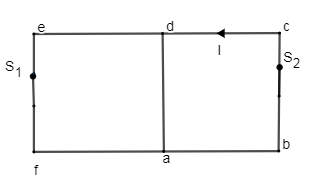
Since all sides have equal resistance, the circuit can act as a balanced Wheatstone bridge.
Formula for checking balanced Wheatstone bridge.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{R}_{3}}}{{{R}_{4}}}=1 \\
& \therefore \dfrac{4}{4}=\dfrac{4}{4}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the circuit will act as a balanced Wheatstone bridge hence current flow along ad is zero.
Note:
We have to remember two points first it is given that resistance is all four sides so don’t forget to consider resistance and in (d) we have to check for Wheatstone bridge otherwise it will lead us to the wrong answer.
Formula used:
$\phi =B.A$
$\begin{align}
& e=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& e=emf \\
\end{align}$
Complete answer:
A) ${{S}_{1}}$ Closed and ${{S}_{2}}$ is open

Formula for the flux = $\phi =B.A\cos \theta $
Here the θ will be zero because magnetic field is perpendicular
$\phi =B.A$
Where,
$\phi =$ Flux
B = magnetic field
A = area
Now emf,
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow e=\dfrac{d\phi }{dt} \\
& \Rightarrow e=A\dfrac{dB}{dt} \\
& \therefore e={{l}^{2}}\times \dfrac{dB}{dt}....(1) \\
\end{align}$
It is given that
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow l=1cm \\
& \Rightarrow l=1\times {{10}^{-2}}m \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{db}{dt}=20mT/s \\
& \therefore \dfrac{db}{dt}=20\times {{10}^{-3}}T/s \\
\end{align}$
Substituting value in equation (1)
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow e={{\left( 1\times {{10}^{-2}} \right)}^{2}}\times 20\times {{10}^{-3}} \\
& \Rightarrow e={{10}^{-4}}\times 2\times {{10}^{-2}} \\
& \therefore e=2\times {{10}^{-6}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now we know that current
$I=\dfrac{e}{R}....\left( 2 \right)$
Here it is given that resistance is $4\Omega $ on every side hence
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow R=4+4+4+4 \\
& \therefore R=16\Omega \\
\end{align}$
Hence the current
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow I=\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{-6}}}{16} \\
& \therefore I=1.25\times {{10}^{-7}}A \\
\end{align}$
Along ad
B.${{S}_{1}}$ is open but ${{S}_{2}}$ is closed,

Current will form a circuit abcd since all values are the same; the magnitude of the current will also be the same. Hence
$I=1.25\times {{10}^{-7}}A$
C. both ${{S}_{1}}$and ${{S}_{2}}$ are open
If both ${{S}_{1}}$and ${{S}_{2}}$ are open then the circuit will not complete hence current along and is zero.
D. both ${{S}_{1}}$and ${{S}_{2}}$are closed

Since all sides have equal resistance, the circuit can act as a balanced Wheatstone bridge.
Formula for checking balanced Wheatstone bridge.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{R}_{1}}}{{{R}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{R}_{3}}}{{{R}_{4}}}=1 \\
& \therefore \dfrac{4}{4}=\dfrac{4}{4}=1 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the circuit will act as a balanced Wheatstone bridge hence current flow along ad is zero.
Note:
We have to remember two points first it is given that resistance is all four sides so don’t forget to consider resistance and in (d) we have to check for Wheatstone bridge otherwise it will lead us to the wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




