
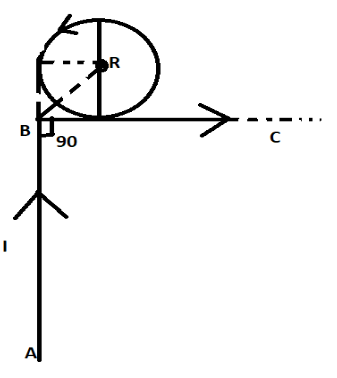
The magnetic field at the center of the circular loop as shown in the figure, when the single wire is bent to form a circular loop and also extends to form a straight section is:
A. $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}} \odot $
B. $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\pi \sqrt 2 }}} \right) \odot $
C. $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{{\pi \sqrt 2 }}} \right) \otimes $
D. $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{R}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{{\pi \sqrt 2 }}} \right) \otimes $

Answer
562.5k+ views
Hint:In the above question, we have to find the total magnetic field. Then firstly, finding the magnetic field along the straight wire and then extending the circular loop and then again, the magnetic field of the straight wire. After adding all the magnetic fields, we got the final answer.
Complete step by step answer:
The total magnetic field will be given by adding the magnetic field of straight line and the magnetic field of the circular loop and again the magnetic field of straight line.Magnetic field can be calculated by the Biot savart’s law whose expression be given by,
$dB = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{Idr \times r}}{{{r^3}}}$
Magnetic field of straight wire be given by the formula,
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}}\left( {sin{\theta _1} + \sin {\theta _2}} \right)$
where ${\theta _{1,}}{\theta _2}$ are the angles corresponding to the two ends of the wire.
Now, the magnetic field along AB,
$
{B_1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi R}}\left( {sin\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) \otimes \\
\Rightarrow{B_1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi R}}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \otimes \\
$ $ \ldots \ldots \left( 1 \right)$
Now, the magnetic field along the circular loop
${B_2} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}} \odot $ $ \ldots \ldots \left( 2 \right)$
Magnetic field along the wire BC,
$
{B_3} = \dfrac{{\mu {}_0I}}{{4\pi R}}\left( {\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) \odot \\
\Rightarrow{B_3} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi R}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \odot \\
$ $ \ldots \ldots \left( 3 \right)$
Now adding all the above marked equations:
$\overrightarrow B = {B_1} + {B_2} + {B_3}$
$
\Rightarrow\overrightarrow B = \left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}} + \dfrac{{2{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi R}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \odot \\
\therefore\overrightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\pi \sqrt 2 }}} \right) \odot \\ $
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:The value of proportionality is $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} = {10^{ - 7}}N{A^{ - 2}}$.Biot savart law is a vector quantity which contains both magnitude and direction.$ \otimes $ is the inward direction of the field and $ \odot $ is the outward direction of the field.
Complete step by step answer:
The total magnetic field will be given by adding the magnetic field of straight line and the magnetic field of the circular loop and again the magnetic field of straight line.Magnetic field can be calculated by the Biot savart’s law whose expression be given by,
$dB = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{Idr \times r}}{{{r^3}}}$
Magnetic field of straight wire be given by the formula,
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi r}}\left( {sin{\theta _1} + \sin {\theta _2}} \right)$
where ${\theta _{1,}}{\theta _2}$ are the angles corresponding to the two ends of the wire.
Now, the magnetic field along AB,
$
{B_1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi R}}\left( {sin\dfrac{\pi }{2} - \sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) \otimes \\
\Rightarrow{B_1} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi R}}\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \otimes \\
$ $ \ldots \ldots \left( 1 \right)$
Now, the magnetic field along the circular loop
${B_2} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}} \odot $ $ \ldots \ldots \left( 2 \right)$
Magnetic field along the wire BC,
$
{B_3} = \dfrac{{\mu {}_0I}}{{4\pi R}}\left( {\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2} + \sin \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) \odot \\
\Rightarrow{B_3} = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi R}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \odot \\
$ $ \ldots \ldots \left( 3 \right)$
Now adding all the above marked equations:
$\overrightarrow B = {B_1} + {B_2} + {B_3}$
$
\Rightarrow\overrightarrow B = \left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}} + \dfrac{{2{\mu _0}I}}{{4\pi R}}\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}} \right) \odot \\
\therefore\overrightarrow B = \dfrac{{{\mu _0}I}}{{2R}}\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{{\pi \sqrt 2 }}} \right) \odot \\ $
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:The value of proportionality is $\dfrac{{{\mu _0}}}{{4\pi }} = {10^{ - 7}}N{A^{ - 2}}$.Biot savart law is a vector quantity which contains both magnitude and direction.$ \otimes $ is the inward direction of the field and $ \odot $ is the outward direction of the field.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




