
The local maximum of \[{\text{y = }}{{\text{x}}^3} - 3{{\text{x}}^2} + 5\] is attained at
(a) ${\text{x = 0}}$ (C) ${\text{x = 1}}$
(b) ${\text{x = 2}}$ (D) ${\text{x = - 1}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:Local maxima can be found by differentiating the given expression with respect to variable x. The Points where 1st order differential becomes zero are known as critical points. And the value of the function at that point will be either maxima or minima.
Here, given cubic curve
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{y = }}{{\text{x}}^3} - 3{{\text{x}}^2} + 5\]
On differentiating above equation
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^3} - 3{x^2} + 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^3}} \right) - 3\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^2}} \right) + \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( 5 \right)$
Differentiation of constant term is zero
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \left( {3{x^2}} \right) - \left( {6x} \right) + \left( 0 \right)$
Now making 1st order differential equal to zero
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \left( {3{x^2}} \right) - \left( {6x} \right) + \left( 0 \right) \Rightarrow 0$
$ \Rightarrow 3{x^2} - 6x = 0 \Rightarrow 3x\left( {x - 2} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x = 0,2$
There are two critical points 0 and 2. So to decide which one will be maxima or minima, find 2nd order differential of y
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {3{x^2} - 6x} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = 6x - 6 \Rightarrow 6(x - 1){\text{ (1)}}\]
We know that, by putting the values of critical points in the 2nd order differential.
\[{\text{if }}\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\] is negative at $x = {x_1}$ then. ${x_1}$ Will be maxima
\[{\text{if }}\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\] is positive at $x = {x_2}$ then. ${x_2}$ Will be minima
So using above result, on putting x = 0, in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = 6x - 6 \Rightarrow 6(0 - 1){\text{ }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = {\text{ - }}6 < 0{\text{ }}\]
So, here 2nd order differential comes negative which means at x= 0 will be local maxima
And on putting x=2,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = 6x - 6 \Rightarrow 6(2 - 1){\text{ }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = {\text{ }}6 > 0{\text{ }}\]
So, here 2nd order differential comes positive which means at x= 2 will be local minima
In question it was asked about maxima so option (a) is correct.
Note:-
In these types of questions, find the critical points and check the sign of the 2nd order derivative whether it is positive or negative.
Note : Alternative Method
We know that, where $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ equals zero at a certain point, it means the slope of the tangent at that point is zero. So by finding the sign of $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$in the neighbourhood of that point, then we can comment on maxima or minima. If the sign of $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$changes from positive to negative, then at that point it will be maxima otherwise Minima.
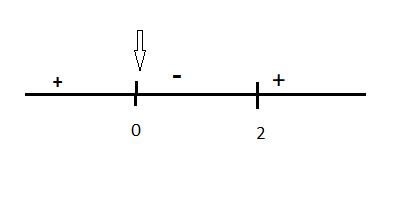
So here at 0 it will be maxima.
Here, given cubic curve
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{y = }}{{\text{x}}^3} - 3{{\text{x}}^2} + 5\]
On differentiating above equation
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^3} - 3{x^2} + 5} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^3}} \right) - 3\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {{x^2}} \right) + \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( 5 \right)$
Differentiation of constant term is zero
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \left( {3{x^2}} \right) - \left( {6x} \right) + \left( 0 \right)$
Now making 1st order differential equal to zero
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}} = \left( {3{x^2}} \right) - \left( {6x} \right) + \left( 0 \right) \Rightarrow 0$
$ \Rightarrow 3{x^2} - 6x = 0 \Rightarrow 3x\left( {x - 2} \right) = 0$
$ \Rightarrow x = 0,2$
There are two critical points 0 and 2. So to decide which one will be maxima or minima, find 2nd order differential of y
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = \dfrac{d}{{dx}}\left( {3{x^2} - 6x} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = 6x - 6 \Rightarrow 6(x - 1){\text{ (1)}}\]
We know that, by putting the values of critical points in the 2nd order differential.
\[{\text{if }}\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\] is negative at $x = {x_1}$ then. ${x_1}$ Will be maxima
\[{\text{if }}\dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}}\] is positive at $x = {x_2}$ then. ${x_2}$ Will be minima
So using above result, on putting x = 0, in equation (1)
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = 6x - 6 \Rightarrow 6(0 - 1){\text{ }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = {\text{ - }}6 < 0{\text{ }}\]
So, here 2nd order differential comes negative which means at x= 0 will be local maxima
And on putting x=2,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = 6x - 6 \Rightarrow 6(2 - 1){\text{ }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d^2}y}}{{d{x^2}}} = {\text{ }}6 > 0{\text{ }}\]
So, here 2nd order differential comes positive which means at x= 2 will be local minima
In question it was asked about maxima so option (a) is correct.
Note:-
In these types of questions, find the critical points and check the sign of the 2nd order derivative whether it is positive or negative.
Note : Alternative Method
We know that, where $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$ equals zero at a certain point, it means the slope of the tangent at that point is zero. So by finding the sign of $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$in the neighbourhood of that point, then we can comment on maxima or minima. If the sign of $\dfrac{{dy}}{{dx}}$changes from positive to negative, then at that point it will be maxima otherwise Minima.

So here at 0 it will be maxima.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits




