
The increasing order of the reactivity of the following with $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ is:
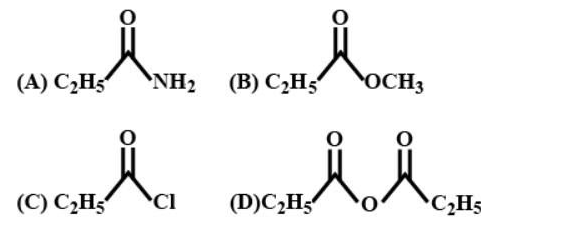
A. (A) < (B) < (D) < ©
B. (A) < (B) <(C) < (D)
C. (B) < (A) < (D) <(C)
D. (B) < (A) < (C) < (D)

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The given compounds are amide, acid halide, acid anhydride and ester. The answer will depend on the reactivity of carbonyl groups along with the stability of the base and leaving group tendency. Higher will be the reactivity of the compound when the leaving tendency of the leaving group is higher.
Complete answer:
- As we know $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ or lithium aluminium hydride is a reducing agent. These reagents will serve as a source of hydride ion due to the presence of a polar metal-hydrogen bond and as a result $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ acts as a stronger reducing agent. It can react violently with alcohols, water, and other acidic groups along with the evolution of hydrogen gas.
- Since the hydride ion reduces the reactant, the product of every reaction will be an alcohol${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$. The hydride ion will attack on the carbonyl group. To each carbonyl group different bases are attached.
- As we mentioned the given compounds are amide, acid halide, acid anhydride and ester. The reactivity will depend on the leaving group tendency. The weaker the base attached to the carbonyl group the better the leaving group.
- Among the given compounds the $C{{l}^{-}}$ is the weaker base and the leaving group tendency can be represented as follows
\[C{{l}^{-}}{{>}^{-}}OCO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}{{>}^{-}}OC{{H}_{3}}{{>}^{-}}N{{H}_{2}}\]
Since weaker the base, the better the leaving group, Cl will have the high leaving group tendency and as a result it has the high reactivity towards the$LiAl{{H}_{4}}$. Thus the order of reactivity toward $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ is (A) < (B) < (D) < (C).
Therefore the answer is option (A).
Note: Keep in mind that the $NaB{{H}_{4}}$ is less reactive than $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$but is otherwise similar. It is also appropriate that, although $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$is strong enough to reduce the carbon− carbon double bond of a conjugated carbonyl compound, $NaB{{H}_{4}}$is not and as a result the carbonyl group can be reduced without the alkene.
Complete answer:
- As we know $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ or lithium aluminium hydride is a reducing agent. These reagents will serve as a source of hydride ion due to the presence of a polar metal-hydrogen bond and as a result $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ acts as a stronger reducing agent. It can react violently with alcohols, water, and other acidic groups along with the evolution of hydrogen gas.
- Since the hydride ion reduces the reactant, the product of every reaction will be an alcohol${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{2}}OH$. The hydride ion will attack on the carbonyl group. To each carbonyl group different bases are attached.
- As we mentioned the given compounds are amide, acid halide, acid anhydride and ester. The reactivity will depend on the leaving group tendency. The weaker the base attached to the carbonyl group the better the leaving group.
- Among the given compounds the $C{{l}^{-}}$ is the weaker base and the leaving group tendency can be represented as follows
\[C{{l}^{-}}{{>}^{-}}OCO{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}{{>}^{-}}OC{{H}_{3}}{{>}^{-}}N{{H}_{2}}\]
Since weaker the base, the better the leaving group, Cl will have the high leaving group tendency and as a result it has the high reactivity towards the$LiAl{{H}_{4}}$. Thus the order of reactivity toward $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ is (A) < (B) < (D) < (C).
Therefore the answer is option (A).
Note: Keep in mind that the $NaB{{H}_{4}}$ is less reactive than $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$but is otherwise similar. It is also appropriate that, although $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$is strong enough to reduce the carbon− carbon double bond of a conjugated carbonyl compound, $NaB{{H}_{4}}$is not and as a result the carbonyl group can be reduced without the alkene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




