
The histones facilitate the coiling of the DNA molecule to form
A. Polynucleotide
B. Chromatin fibre
C. Polypeptide
D. Polysaccharide
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: Histones are the special sort of low relative molecular mass, charged proteins that are rich in basic amino acids like lysine and arginine. They provide the basic support to the coiled-up chromosomes with the nucleus of a cell.
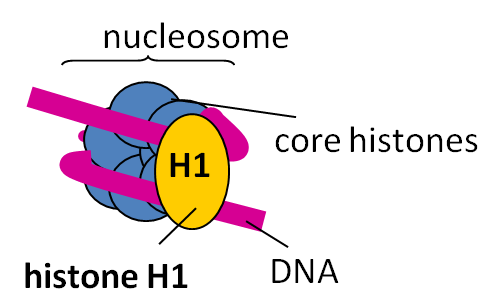
Complete answer: There are five sorts of histone proteins, HI, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Four of them (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) occur during a pair to supply a histone octamer called the core of the nucleosome. The ends of the histone proteins are positively charged face outwards.
This particularly aids to draw in and hold the strands of DNA as DNA is negatively charged (there is an attractive force between the two). The nucleosome body is wrapped over by almost 166 base pairs of the DNA. The DNA strands that join the two adjacent nucleosomes together is commonly known as the linker DNA.
It typically bears the H1 histone protein out of the others, which connects one core particle with the opposite. This entire structure of the charged DNA wound around the charged histone protein octamer is what we know as the nucleosome which is essentially the basic unit of chromatin threads.
The nucleosome and linker DNA is jointly also referred to as the chromatosome. In this way, the histones pack DNA molecules to form the chromatin fibre.
So, the correct answer is option B. Chromatin fibre.
Note: The nucleosomal arrangement has a thickness of about 10 nm which further gets super-condensed and coiled thus forming a composite structure known as the solenoid (this has approximately a diameter of 30 nm). The coiling undergoes further coiling to supply a chromatin fibre of 30-80 nm, then a chromatid of 700 nm.
Complete answer: There are five sorts of histone proteins, HI, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Four of them (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) occur during a pair to supply a histone octamer called the core of the nucleosome. The ends of the histone proteins are positively charged face outwards.
This particularly aids to draw in and hold the strands of DNA as DNA is negatively charged (there is an attractive force between the two). The nucleosome body is wrapped over by almost 166 base pairs of the DNA. The DNA strands that join the two adjacent nucleosomes together is commonly known as the linker DNA.
It typically bears the H1 histone protein out of the others, which connects one core particle with the opposite. This entire structure of the charged DNA wound around the charged histone protein octamer is what we know as the nucleosome which is essentially the basic unit of chromatin threads.
The nucleosome and linker DNA is jointly also referred to as the chromatosome. In this way, the histones pack DNA molecules to form the chromatin fibre.

So, the correct answer is option B. Chromatin fibre.
Note: The nucleosomal arrangement has a thickness of about 10 nm which further gets super-condensed and coiled thus forming a composite structure known as the solenoid (this has approximately a diameter of 30 nm). The coiling undergoes further coiling to supply a chromatin fibre of 30-80 nm, then a chromatid of 700 nm.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




