
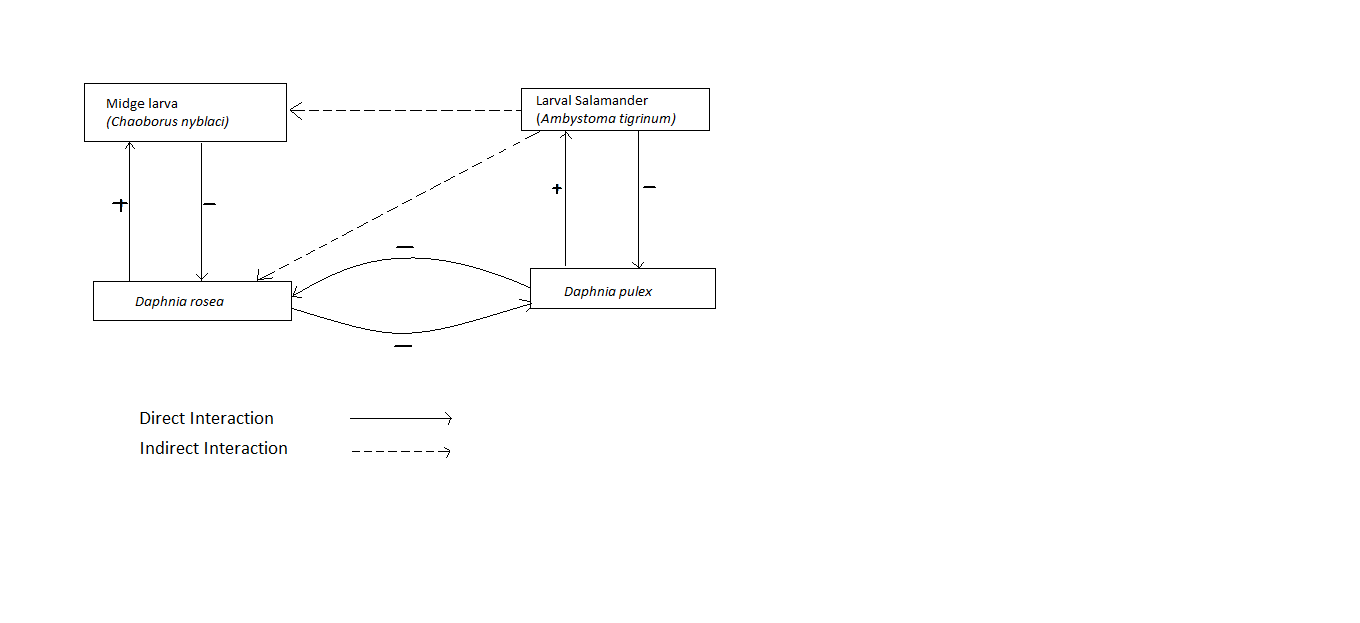
The diagram shows the relationships among the midge larva(Chaoborus nyblaci), larval salamander(Ambystoma tigrinum), and two species of the crustacean Daphnia(D. rosea and the larger D. pulex) that inhabit certain pond communities. Study the relationships and deduce which of the following is/are correct.
This question has multiple correct options.
A.Presence of high numbers of larval Salamander has an indirect effect on D. rosea and it is a positive effect.
B.When larval salamanders are present, predation reduces the population growth rate of the larger Daphnia, facilitating the coexistence of the two species of Daphnia.
C.The two species of Daphnia compete for the same resources and hence increase in resource availability will reduce the number of midge larvae and larval salamander
D.Increase in the number of D. pulex would lead to a decrease in the number of midge larvae.

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint:The animal world depicts different types of relationships in the form of interactions. Ecological interdependence is reflected in their interactions, mainly for food, space, reproduction, and protection. These can have direct effects or indirect effects that means they can have positive and negative effects.
Complete step by step answer:The above question is based on the concept of ecological interdependence.
The effects of interactions are broadly categorized as direct (directly from one individual to another) and indirect effects (mediated through a transmitter).
Interactions have direct effects between populations of species in a community and are broadly categorized into positive, negative, or neutral interactions, depending upon the nature of the effect of the interacting organism.
In neutral interaction, interacting species have no effect on each other.
The interaction in which both participating species are benefitted is called positive interaction.
The interacting species in which one or both participating species get harmed is called a negative interaction.
As indicated by the picture, the presence of high quantities of larval lizards will restrain the Daphnia pulex creation or formation. This will show constructive outcomes on D. rosea on the grounds that D. pulex has a negative impact on it. At the point when larval lizards are available, predation lessens the populace development pace of the bigger Daphnia, D. pulex. This will encourage the concurrence of the Daphnia rosea. The two types of Daphnia for similar assets and henceforth increment in asset accessibility will build the number of midge hatchlings and larval lizards as the two types of Daphnia have beneficial outcomes. Expansion in the quantity of D. pulex would prompt a lessening in the quantity of D. rosea. This ultimately will diminish the number of midge hatchlings.
Consequently, the choices (A) Presence of high numbers of larval Salamander have an indirect effect on D. rosea and it is a positive effect.
(B) When larval salamanders are present, predation reduces the population growth rate of the larger Daphnia, facilitating the coexistence of the two species of Daphnia.
and (D) Increase in the number of D. pulex would lead to a decrease in the number of midge larvae is right.
So, (A), (B), and (D) are correct choices.
Note:The effects of interaction between a community can be direct effects or indirect effects. The receiver and donor are both affected differently according to the extent of effects. The transmitter is an important second species that plays a major role in indirect transmission. Direct interactions further lead to positive interactions (facilitation), negative interaction, and neutral interaction (neutralism).
Complete step by step answer:The above question is based on the concept of ecological interdependence.
The effects of interactions are broadly categorized as direct (directly from one individual to another) and indirect effects (mediated through a transmitter).
Interactions have direct effects between populations of species in a community and are broadly categorized into positive, negative, or neutral interactions, depending upon the nature of the effect of the interacting organism.
In neutral interaction, interacting species have no effect on each other.
The interaction in which both participating species are benefitted is called positive interaction.
The interacting species in which one or both participating species get harmed is called a negative interaction.
As indicated by the picture, the presence of high quantities of larval lizards will restrain the Daphnia pulex creation or formation. This will show constructive outcomes on D. rosea on the grounds that D. pulex has a negative impact on it. At the point when larval lizards are available, predation lessens the populace development pace of the bigger Daphnia, D. pulex. This will encourage the concurrence of the Daphnia rosea. The two types of Daphnia for similar assets and henceforth increment in asset accessibility will build the number of midge hatchlings and larval lizards as the two types of Daphnia have beneficial outcomes. Expansion in the quantity of D. pulex would prompt a lessening in the quantity of D. rosea. This ultimately will diminish the number of midge hatchlings.
Consequently, the choices (A) Presence of high numbers of larval Salamander have an indirect effect on D. rosea and it is a positive effect.
(B) When larval salamanders are present, predation reduces the population growth rate of the larger Daphnia, facilitating the coexistence of the two species of Daphnia.
and (D) Increase in the number of D. pulex would lead to a decrease in the number of midge larvae is right.
So, (A), (B), and (D) are correct choices.
Note:The effects of interaction between a community can be direct effects or indirect effects. The receiver and donor are both affected differently according to the extent of effects. The transmitter is an important second species that plays a major role in indirect transmission. Direct interactions further lead to positive interactions (facilitation), negative interaction, and neutral interaction (neutralism).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




