
The compound of molecular formula ${ C }_{ 5 }{ H }_{ 10 }{ O }$(A) reacts with Tollen’s reagent to give a silver mirror but does not undergo aldol condensation. The compound A is :
A.)3-pentanone
B.)2,2-dimethyl propanal
C.)2-hydroxy-2-pentene
D.)3-methyl butanal
E.)3-methyl-2-butanone
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: A compound giving positive Tollens test implies that it's an aldehyde and if that compound does noy undergo aldol condensation means that the aldehyde is not having hydrogen at its $\alpha $ -position.
Complete answer:
As we mentioned in the hint, the compound giving positive Tollens test is an aldehyde. The aldehyde when introduced with Tollen’s reagent is getting oxidised into carboxylic acid.
Being a mild oxidising agent, Tollen’s reagent can’t oxidise ketone groups, so it can be used for distinguishing between aldehydes and ketones.
We can have a look at the structures of molecules in the given options.
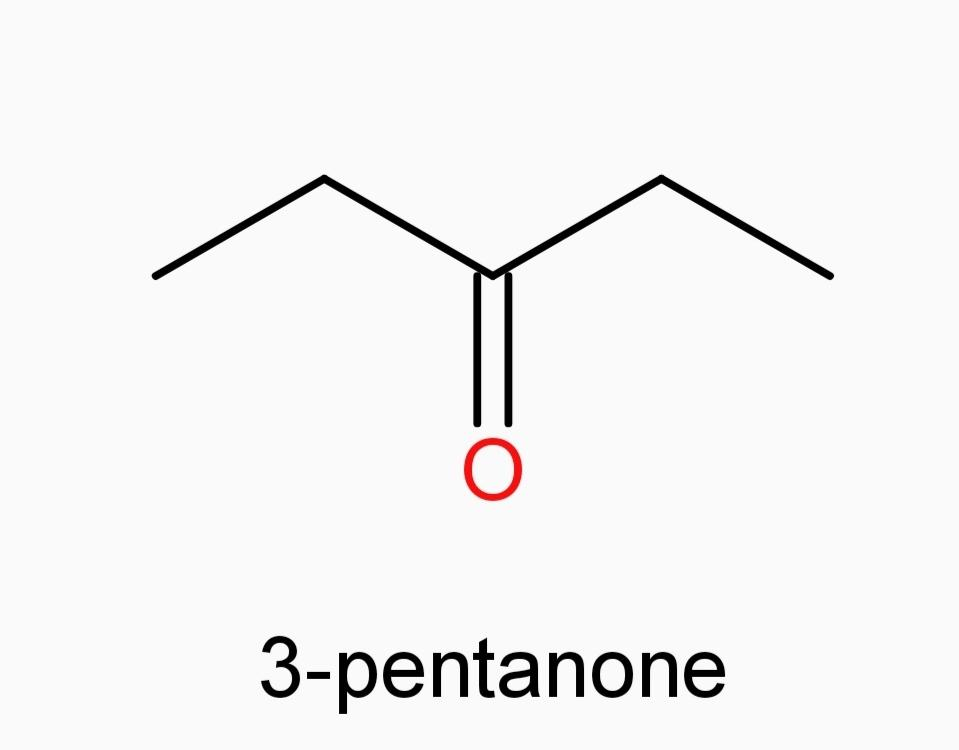
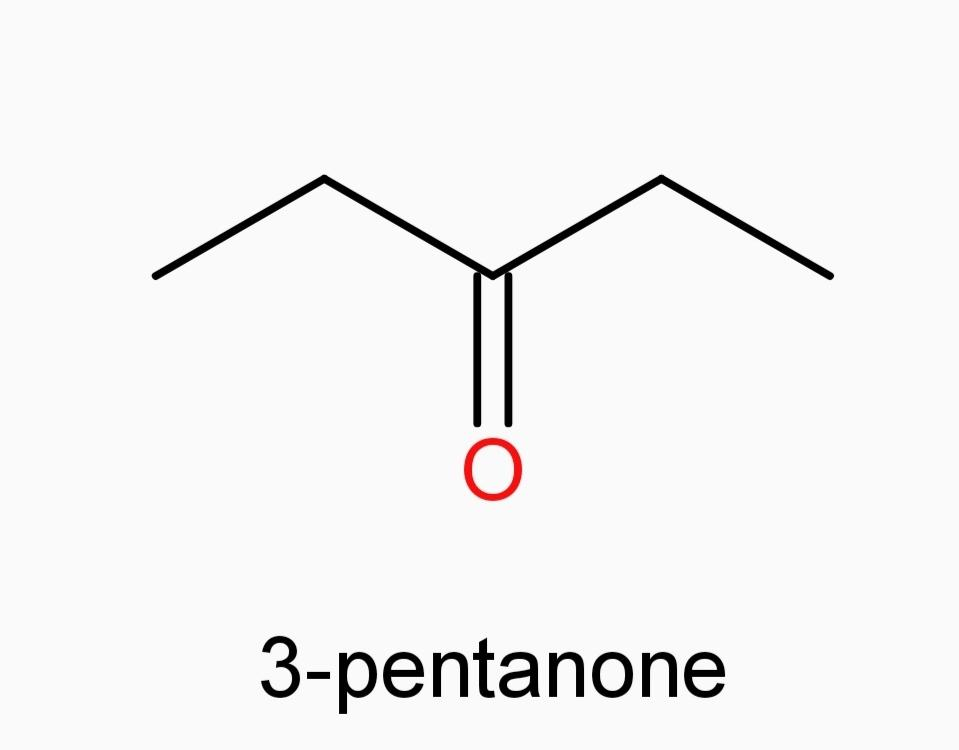
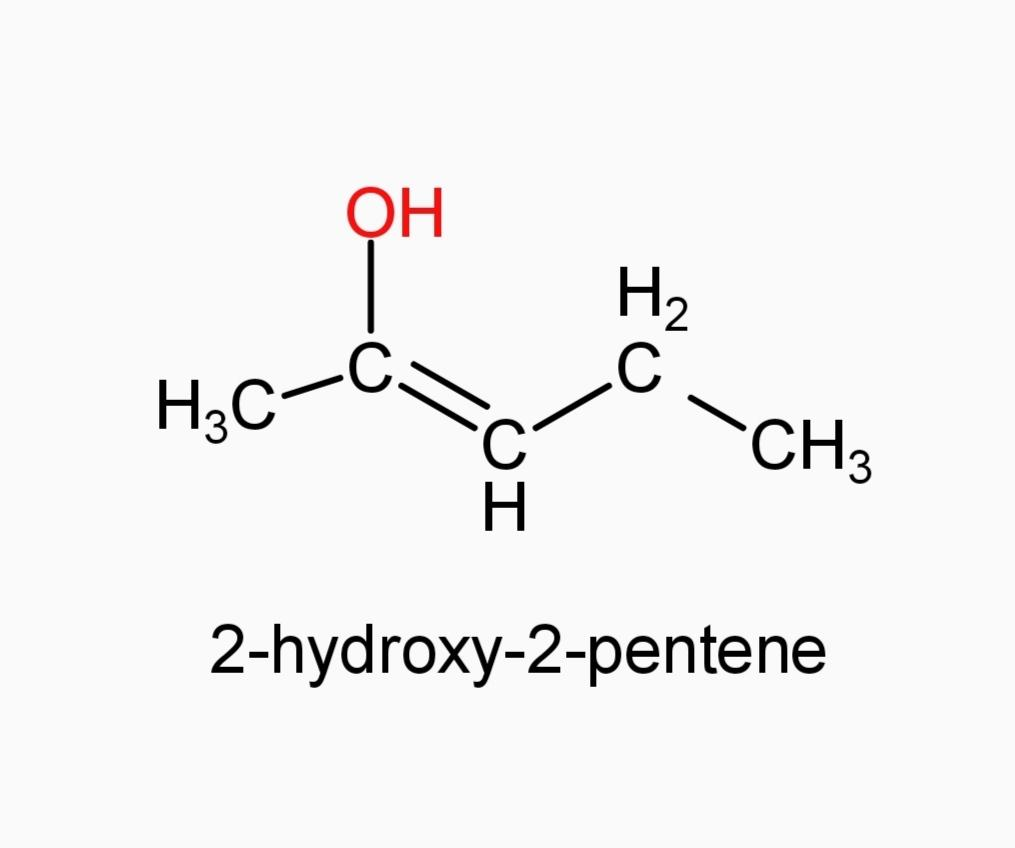
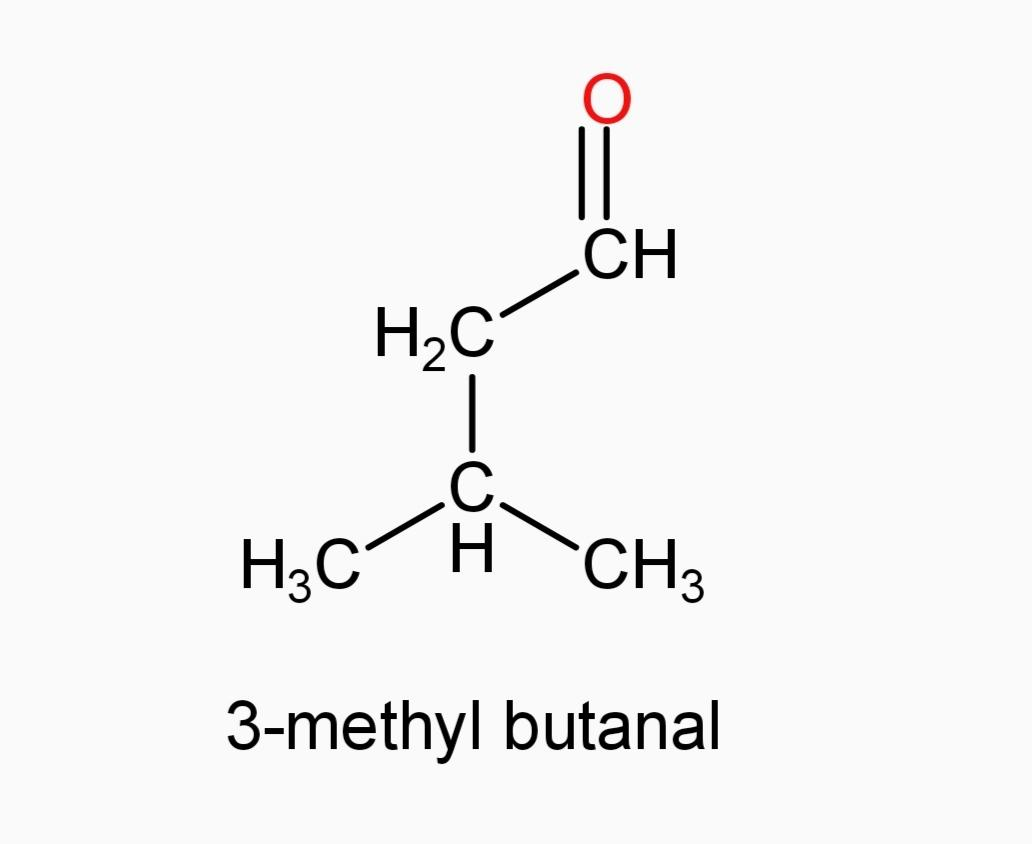
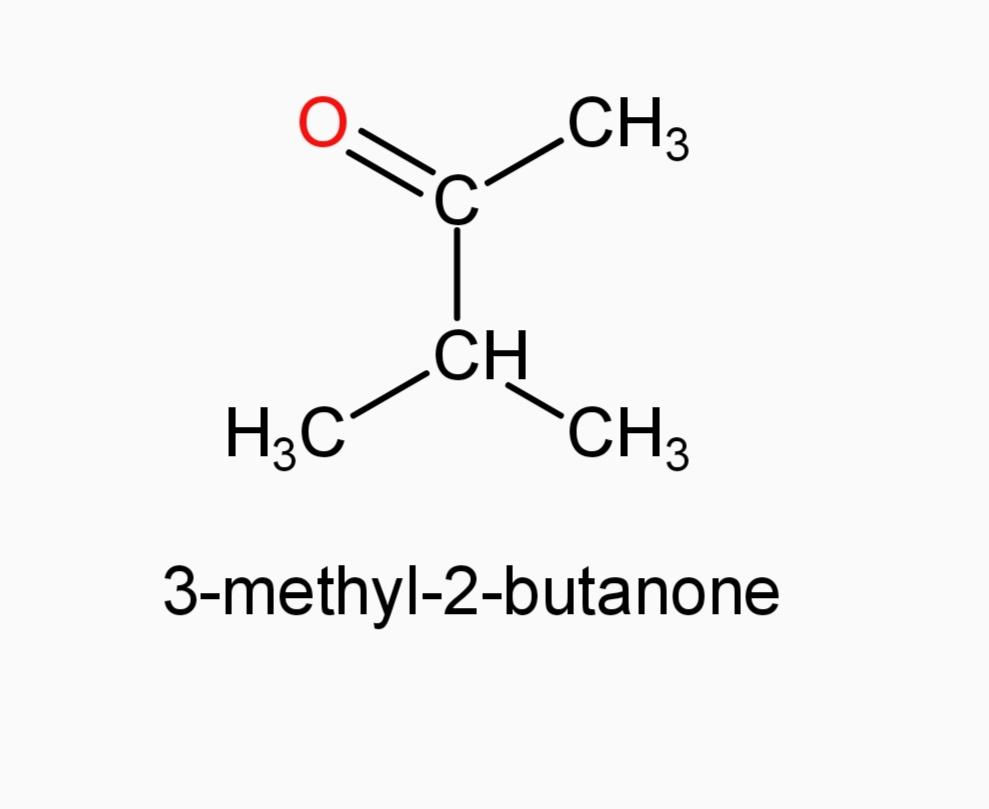
And now Option (A) 3-pentanone and Option (E) 3-methyl-2-butanone, since they are ketones, they can’t be our answer.
Along with these, Option (C) is also not the answer, since 2-hydroxy-2-pentene is an alkene and not an alcohol.
Coming to the next part of the question, i.e, the aldol condensation.
Aldol condensation occurs in aldehydes having $\alpha $-hydrogen with a dilute base to give $\beta $-hydroxy aldehydes called aldols.
If this reaction occurs between two different carbonyl compounds it is called crossed aldol condensation.
So, if a compound is giving aldol condensation, then it should have an $\alpha $-hydrogen.
Considering the rest options, i.e, Option (B)2,2-dimethyl propanal
and Option (D)3-methyl butanal
By looking at the structure of both the compounds, we can find that in the case of 3-methyl butanal, $\alpha $-hydrogen is present and so it can undergo aldol condensation.
The compound 2,2-dimethyl propanal has no $\alpha $-hydrogen present in it and therefore, it cannot undergo aldol condensation, which is in agreement with our question.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Tollen’s as well as Fehling's reagent are mild oxidising agents and can be used for distinguishing between aldehydes and ketones. Tollen’s test shows some exceptions in a way that it gives positive test for formic acid, chloroform, alpha hydroxy ketones and alkyl hydroxy amines and even acetylene.
Complete answer:
As we mentioned in the hint, the compound giving positive Tollens test is an aldehyde. The aldehyde when introduced with Tollen’s reagent is getting oxidised into carboxylic acid.
Being a mild oxidising agent, Tollen’s reagent can’t oxidise ketone groups, so it can be used for distinguishing between aldehydes and ketones.
We can have a look at the structures of molecules in the given options.





And now Option (A) 3-pentanone and Option (E) 3-methyl-2-butanone, since they are ketones, they can’t be our answer.
Along with these, Option (C) is also not the answer, since 2-hydroxy-2-pentene is an alkene and not an alcohol.
Coming to the next part of the question, i.e, the aldol condensation.
Aldol condensation occurs in aldehydes having $\alpha $-hydrogen with a dilute base to give $\beta $-hydroxy aldehydes called aldols.
If this reaction occurs between two different carbonyl compounds it is called crossed aldol condensation.
So, if a compound is giving aldol condensation, then it should have an $\alpha $-hydrogen.
Considering the rest options, i.e, Option (B)2,2-dimethyl propanal
and Option (D)3-methyl butanal
By looking at the structure of both the compounds, we can find that in the case of 3-methyl butanal, $\alpha $-hydrogen is present and so it can undergo aldol condensation.
The compound 2,2-dimethyl propanal has no $\alpha $-hydrogen present in it and therefore, it cannot undergo aldol condensation, which is in agreement with our question.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Tollen’s as well as Fehling's reagent are mild oxidising agents and can be used for distinguishing between aldehydes and ketones. Tollen’s test shows some exceptions in a way that it gives positive test for formic acid, chloroform, alpha hydroxy ketones and alkyl hydroxy amines and even acetylene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




