
The arrangement of the ovules on the placenta developed from the central axis of the ovary is called
A. Parietal placentation
B. Axile placentation
C. Basal placentation
D. Marginal placentation
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: In plants, placenta refers to the surface of the carpel to which the ovules remain attached. Arrangement of ovules on the placenta developed from the central axis of the ovary gives rise to axial placenta.
Complete answer:
In Botany, placentation means the arrangement of placenta in the ovary of a flower. Now let us discuss different types of placentation mentioned above:
Parietal placentation: In this, the ovules are developed on the wall or as some outgrowths of the wall. Example- Mustard.
Axile placentation: Here, the ovules develop on the central axis of the ovary. The ovules develop at the angles where septa join the central placenta.
Example- Tomato.
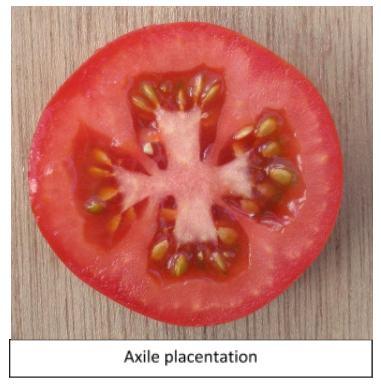
Basal placentation: In this type of placentation, a single or a few ovules are developed at the base of an ovary. Example- Sunflower.
Marginal placentation: Here the ovules develop on the wall and along the ventral suture of a simple ovary.
Example- Pea
So, the correct answer is B. Axile placentation.
Note: When ovules arise on the central axis and the septa are absent, it is called free central aestivation. Example- Dianthus.
In Zoology, placentation is the formation of the placenta which is a structure in a woman’s uterus that transfers nutrients, water and respiratory gases from the maternal tissue to growing embryos.
Complete answer:
In Botany, placentation means the arrangement of placenta in the ovary of a flower. Now let us discuss different types of placentation mentioned above:
Parietal placentation: In this, the ovules are developed on the wall or as some outgrowths of the wall. Example- Mustard.
Axile placentation: Here, the ovules develop on the central axis of the ovary. The ovules develop at the angles where septa join the central placenta.
Example- Tomato.

Basal placentation: In this type of placentation, a single or a few ovules are developed at the base of an ovary. Example- Sunflower.
Marginal placentation: Here the ovules develop on the wall and along the ventral suture of a simple ovary.
Example- Pea
So, the correct answer is B. Axile placentation.
Note: When ovules arise on the central axis and the septa are absent, it is called free central aestivation. Example- Dianthus.
In Zoology, placentation is the formation of the placenta which is a structure in a woman’s uterus that transfers nutrients, water and respiratory gases from the maternal tissue to growing embryos.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




