
The angular momentum of an electron is $J$. Its magnetic moment will be
A. $\dfrac{{mJ}}{{2e}}$
B. $\dfrac{{eJ}}{{2m}}$
C. $\dfrac{{2m}}{{ej}}$
D. $\dfrac{{emJ}}{2}$
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint:We know that according to the Bohr model of hydrogen like atom, electron (negative charge) revolves around the nucleus (positive charge). The uniform circular motion of the electron around the nucleus is equivalent to the current loop which has a magnetic dipole moment $\left( {\mu = IA} \right)$ and angular momentum is the product of linear momentum and perpendicular distance.
Complete step by step answer:
From the question, we know that the angular momentum is $J$ and we have developed the expression of the magnetic moment in terms of $J$. Now let us consider an electron revolving counter clockwise a nucleus in an orbit of radius $r$ with speed $v$ and time period $T$.
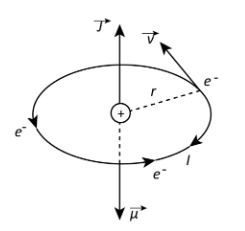
The above figure represents the orbital magnetic moment of a revolving electron.
The expression of the current in the loop,
$
I = \dfrac{q}{T}\\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{e}{T}\\
$
The area of the loop in which current is revolving is,
$A = \pi {r^2}$
The time period of the electron can be expressed as,
$
T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }\\
\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{v}\\
$
Here, $\omega $ is the angular velocity of the electron.
We know that the orbital magnetic moment or the magnetic moment due to orbital motion of the electron motion of the electron is expressed as,
$\mu = IA$
Substitute the expression in the above equation.
$\mu = \dfrac{e}{{\left( {\dfrac{{2\pi r}}{v}} \right)}} \times \pi {r^2}$
$\Rightarrow\mu = \dfrac{{evr}}{2}$ ... (I)
Also, the angular momentum of the electron due to its orbital motion,
$J = mvr$ ... (II)
Here, $m$ is the mass of the electron.
From equation (I) and (2), we get,
$
\dfrac{\mu }{J} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{evr}}{2}} \right)}}{{mvr}}\\
\therefore \mu = \dfrac{{eJ}}{{2m}}\\
$
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note:As the electron (negative charge) is revolving counter clockwise, the direction of the current associated to it is clockwise. From the right hand thumb rule, the direction of the magnetic moment of the electron will be perpendicular to the plane of its orbit.
Complete step by step answer:
From the question, we know that the angular momentum is $J$ and we have developed the expression of the magnetic moment in terms of $J$. Now let us consider an electron revolving counter clockwise a nucleus in an orbit of radius $r$ with speed $v$ and time period $T$.

The above figure represents the orbital magnetic moment of a revolving electron.
The expression of the current in the loop,
$
I = \dfrac{q}{T}\\
\Rightarrow I = \dfrac{e}{T}\\
$
The area of the loop in which current is revolving is,
$A = \pi {r^2}$
The time period of the electron can be expressed as,
$
T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }\\
\Rightarrow T = \dfrac{{2\pi r}}{v}\\
$
Here, $\omega $ is the angular velocity of the electron.
We know that the orbital magnetic moment or the magnetic moment due to orbital motion of the electron motion of the electron is expressed as,
$\mu = IA$
Substitute the expression in the above equation.
$\mu = \dfrac{e}{{\left( {\dfrac{{2\pi r}}{v}} \right)}} \times \pi {r^2}$
$\Rightarrow\mu = \dfrac{{evr}}{2}$ ... (I)
Also, the angular momentum of the electron due to its orbital motion,
$J = mvr$ ... (II)
Here, $m$ is the mass of the electron.
From equation (I) and (2), we get,
$
\dfrac{\mu }{J} = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{evr}}{2}} \right)}}{{mvr}}\\
\therefore \mu = \dfrac{{eJ}}{{2m}}\\
$
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note:As the electron (negative charge) is revolving counter clockwise, the direction of the current associated to it is clockwise. From the right hand thumb rule, the direction of the magnetic moment of the electron will be perpendicular to the plane of its orbit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




