
Switch $S$ is closed at time $t=0$. Which of the following statements is correct?
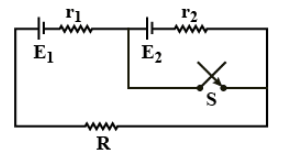
A. Current in the resistance R increases if \[{E_1}{r_2} < {E_2}(R + {r_1})\]
B. Current in the resistance R increases if \[{E_1}{r_2} > {E_2}(R + {r_1})\]
C. Current in the resistance R decreases if \[{E_1}{r_2} = {E_2}(R + {r_1})\]
D. Current in the resistance R increases if \[{E_1}{r_2} = {E_2}(R + {r_1})\]

Answer
517.5k+ views
Hint: An electric switch is a system that can either make or break an electrical circuit. When a switch makes or completes a circuit and allows current to flow through, it is assumed to be in the 'ON' state. A switch is in the 'OFF' state as it splits the circuit and prevents current from flowing into it.
Complete step by step answer:
To measure an unknown electrical resistance, a Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit that balances two legs of a bridge circuit, one of which contains the unknown component. The ability to make extremely accurate calculations is the circuit's greatest benefit (in contrast with something like a simple voltage divider). It functions in the same manner as the first potentiometer.
The initial current, also known as initialization current, is the current drawn by the battery when it is connected to a charger for the first time. In most cases, the original charge current is significantly lower than the constant charge current. In most cases, the original charge current is significantly lower than the constant charge current. Switch $S$ is closed at time $t=0$.
Before closing the switch the initial current is given as = \[{i_1} = \dfrac{{{E_1} + {E_2}}}{{R + {r_1} + {r_2}}}\]
When the second battery is short-circuited, then the final current is,
\[{i_2} = \dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{R + {r_1}}}\]
By comparing the above 2 equations we get
\[{i_2} > {i_1}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{R + {r_1}}} > \dfrac{{{E_1} + {E_2}}}{{R + {r_1} + {r_2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {E_1}R + {E_1}{r_1} + {E_1}{r_2} > {E_1}R + {E_1}{r_1} + {E_2}R + {E_2}{r_1}\]
\[\therefore {E_1}{r_2} > {E_2}\left( {R + {r_1}} \right)\]
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: Resistance is a measurement of the resistance to current flow in an electrical circuit. Resistance in ohms is expressed by the Greek letter omega ($\Omega $). Ohms was named after Georg Simon Ohm (1784-1854), a German physicist who studied the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
Complete step by step answer:
To measure an unknown electrical resistance, a Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit that balances two legs of a bridge circuit, one of which contains the unknown component. The ability to make extremely accurate calculations is the circuit's greatest benefit (in contrast with something like a simple voltage divider). It functions in the same manner as the first potentiometer.
The initial current, also known as initialization current, is the current drawn by the battery when it is connected to a charger for the first time. In most cases, the original charge current is significantly lower than the constant charge current. In most cases, the original charge current is significantly lower than the constant charge current. Switch $S$ is closed at time $t=0$.
Before closing the switch the initial current is given as = \[{i_1} = \dfrac{{{E_1} + {E_2}}}{{R + {r_1} + {r_2}}}\]
When the second battery is short-circuited, then the final current is,
\[{i_2} = \dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{R + {r_1}}}\]
By comparing the above 2 equations we get
\[{i_2} > {i_1}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{E_1}}}{{R + {r_1}}} > \dfrac{{{E_1} + {E_2}}}{{R + {r_1} + {r_2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {E_1}R + {E_1}{r_1} + {E_1}{r_2} > {E_1}R + {E_1}{r_1} + {E_2}R + {E_2}{r_1}\]
\[\therefore {E_1}{r_2} > {E_2}\left( {R + {r_1}} \right)\]
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: Resistance is a measurement of the resistance to current flow in an electrical circuit. Resistance in ohms is expressed by the Greek letter omega ($\Omega $). Ohms was named after Georg Simon Ohm (1784-1854), a German physicist who studied the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




