
State true or false.
If the angles subtended by the chords of a circle at the center are equal , then the chords are equal.
Answer
600.6k+ views
Hint: It is no surprise that equal chords and equal arcs both subtend equal angles at the centre of a fixed circle. The result for chords can be proven using congruent triangles, but congruent triangles cannot be used for arcs because they are not straight lines, so we need to identify the transformation involved.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let’s try to figure our relation between length of chord & angle subtended and the center.
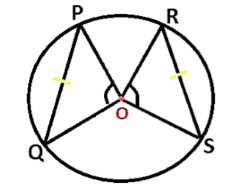
Given: \[\angle SOR{\text{ }} and \angle POQ\] are two equal angles subtended by chords SR and PQ of a circle at its centre O.
Here in the circle, the two chords are given
To Prove : RS = PQ
Proof : In \[\vartriangle SOR{\text{ }} and {\text{ }}\vartriangle POQ\],
OR = OP [Radii of a circle]
OS = OQ [Radii of a circle]
So OP = OS = OQ = OR (all are radii of the circle)
\[\angle SOR{\text{ }} and \angle POQ\] [Given]
Therefore, \[\vartriangle SOR \cong \vartriangle POQ\][By SAS]
Hence, RS = PQ [By cpctc, corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent. It means that once two triangles are proven to be congruent, then the three pairs of sides that correspond must be congruent and the three pairs of angles that correspond must be congruent.]
Thus, we conclude that if the angles made by the chords of a circle at the centre are equal, then the chords must be equal.
Note: The converse is also true.
The converse theorem : Equal chords of a circle subtend equal angles at the centre
For convenience, you can use the abbreviation CPCT in place of ‘Corresponding parts of congruent triangles’, and the abbreviation SAS will be used in place of ‘Side-Angle-Side’, because we use this very frequently for proving geometrical problems.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let’s try to figure our relation between length of chord & angle subtended and the center.

Given: \[\angle SOR{\text{ }} and \angle POQ\] are two equal angles subtended by chords SR and PQ of a circle at its centre O.
Here in the circle, the two chords are given
To Prove : RS = PQ
Proof : In \[\vartriangle SOR{\text{ }} and {\text{ }}\vartriangle POQ\],
OR = OP [Radii of a circle]
OS = OQ [Radii of a circle]
So OP = OS = OQ = OR (all are radii of the circle)
\[\angle SOR{\text{ }} and \angle POQ\] [Given]
Therefore, \[\vartriangle SOR \cong \vartriangle POQ\][By SAS]
Hence, RS = PQ [By cpctc, corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent. It means that once two triangles are proven to be congruent, then the three pairs of sides that correspond must be congruent and the three pairs of angles that correspond must be congruent.]
Thus, we conclude that if the angles made by the chords of a circle at the centre are equal, then the chords must be equal.
Note: The converse is also true.
The converse theorem : Equal chords of a circle subtend equal angles at the centre
For convenience, you can use the abbreviation CPCT in place of ‘Corresponding parts of congruent triangles’, and the abbreviation SAS will be used in place of ‘Side-Angle-Side’, because we use this very frequently for proving geometrical problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




