
Spherical aberration in a thin lens can be reduced by.
Answer
528.6k+ views
Hint: Spherical aberration is a form of aberration that occurs in optical structures with elements that have spherical surfaces. Since this form is simpler to produce, lenses and curved mirrors are prime examples.
Complete answer:
After travelling across a spherical surface, all incoming light rays end up focused at various locations, which is known as spherical aberration. Light rays travelling through a lens on the horizontal axis are refracted less than rays passing through the lens closest to the side or "periphery," resulting in varying locations around the optical axis. In other words, after going through the prism, the parallel light rays of incoming light do not intersect at the same place. Spherical Aberration can impair resolution and visibility as a result, making it difficult to obtain sharp images.
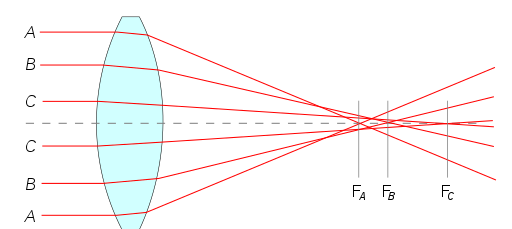
The tendency of a lens to cover marginal rays of the same wavelength to the focus as it converges the paraxial rays causes spherical aberration; this flaw can be corrected by blocking marginal rays. A circular annular mask may be placed over the lens to do this.
The spherical aspect of the lens causes spherical aberration.
The lens's paraxial and marginal rays are centred at various points along its axis. As a result, the picture is distorted. This aberration may be minimised by either stopping paraxial or marginal rays with a circular annular label placed over the lens.
Note: As a result, the highest focus point with the smallest circle of doubt is right on this focal point. Since a standard spherical lens design does not enable the above to happen, manufacturers have created advanced, accurate methods to reduce the impact of spherical aberration over time.
Complete answer:
After travelling across a spherical surface, all incoming light rays end up focused at various locations, which is known as spherical aberration. Light rays travelling through a lens on the horizontal axis are refracted less than rays passing through the lens closest to the side or "periphery," resulting in varying locations around the optical axis. In other words, after going through the prism, the parallel light rays of incoming light do not intersect at the same place. Spherical Aberration can impair resolution and visibility as a result, making it difficult to obtain sharp images.

The tendency of a lens to cover marginal rays of the same wavelength to the focus as it converges the paraxial rays causes spherical aberration; this flaw can be corrected by blocking marginal rays. A circular annular mask may be placed over the lens to do this.
The spherical aspect of the lens causes spherical aberration.
The lens's paraxial and marginal rays are centred at various points along its axis. As a result, the picture is distorted. This aberration may be minimised by either stopping paraxial or marginal rays with a circular annular label placed over the lens.
Note: As a result, the highest focus point with the smallest circle of doubt is right on this focal point. Since a standard spherical lens design does not enable the above to happen, manufacturers have created advanced, accurate methods to reduce the impact of spherical aberration over time.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




