
What is the shape of the wavefront originating from
A. A point source
B. A line source?
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: You can start by briefly explaining the wavefront. Then describe the spherical waveform formed by a point source and the cylindrical waveform formed by a line source along with the diagrams of the waveforms.
Complete answer:
Before discussing the shapes of wavefront originating from a point source and a line source, it will be beneficial to discuss what a wavefront is
Wavefront – If we consider a time-varying field we have a set (locus) of points in which all the particles have the same phase. When we join all these points we get what we call a waveform. This waveform moves with time and its dimension changes.
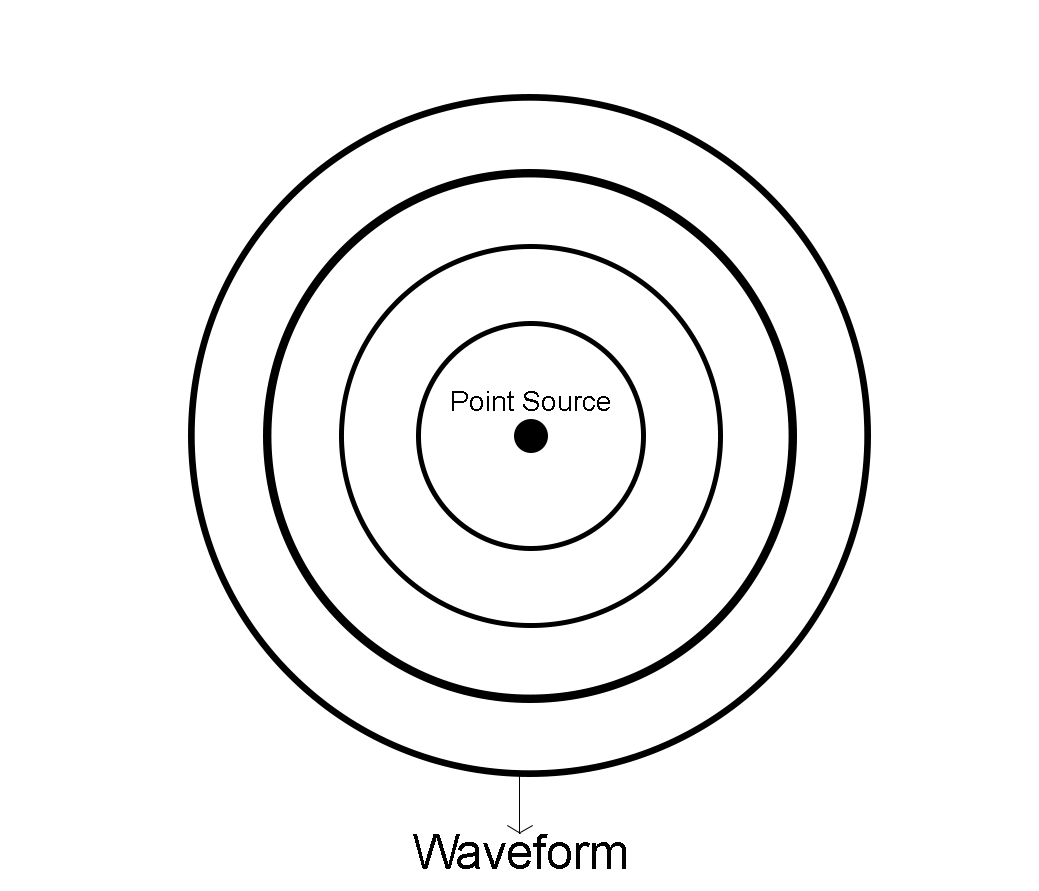
For a point source – For a point source, the waveform spreads in the form of a sphere, every point on the waveform is equidistant from the point source. Every point on this spherical waveform will have the same phase.
The wavefront of a point source is shown below
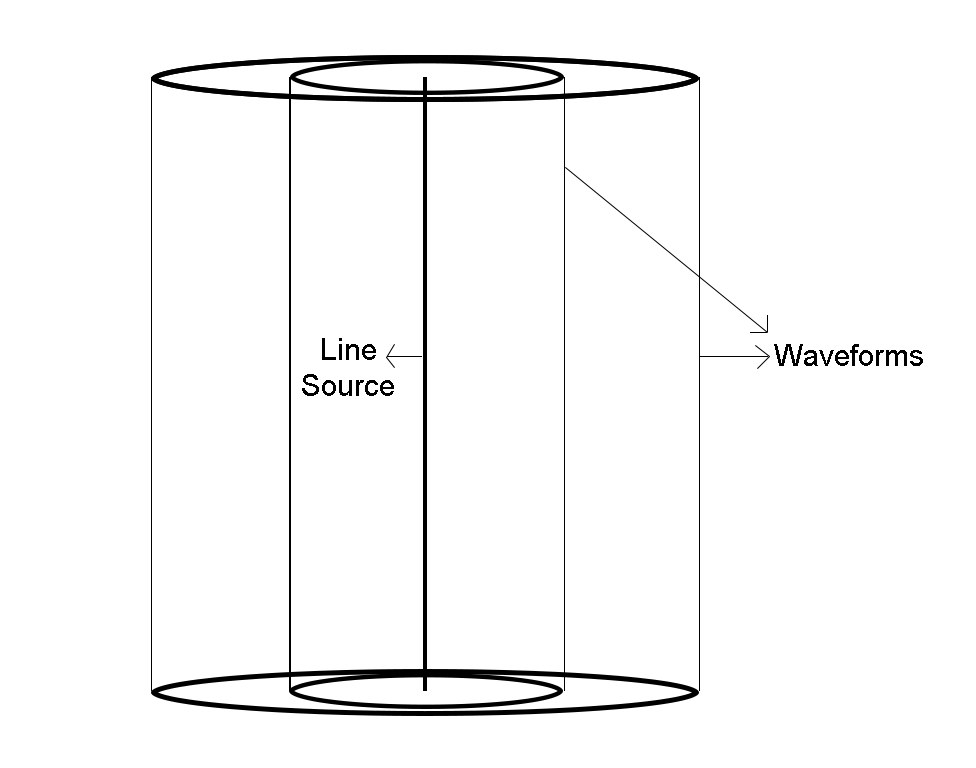
For a line source – For a line source, the waveform spreads in the form of a cylinder, every point on the waveform is equidistant from the nearest point on the line. Every point on this cylindrical waveform will have the same phase.
The wavefront of a line source is shown below
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
In the solution above, we discussed how the wavefront propagates with time. A quick method to predict the propagation of a waveform is to use the Huygens-Fresnel principle, i.e. every point where a waveform disturbance reaches in itself becomes a source of spherical wavelets and emits secondary wavelets.
Complete answer:
Before discussing the shapes of wavefront originating from a point source and a line source, it will be beneficial to discuss what a wavefront is
Wavefront – If we consider a time-varying field we have a set (locus) of points in which all the particles have the same phase. When we join all these points we get what we call a waveform. This waveform moves with time and its dimension changes.
For a point source – For a point source, the waveform spreads in the form of a sphere, every point on the waveform is equidistant from the point source. Every point on this spherical waveform will have the same phase.
The wavefront of a point source is shown below

For a line source – For a line source, the waveform spreads in the form of a cylinder, every point on the waveform is equidistant from the nearest point on the line. Every point on this cylindrical waveform will have the same phase.
The wavefront of a line source is shown below

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
In the solution above, we discussed how the wavefront propagates with time. A quick method to predict the propagation of a waveform is to use the Huygens-Fresnel principle, i.e. every point where a waveform disturbance reaches in itself becomes a source of spherical wavelets and emits secondary wavelets.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




