
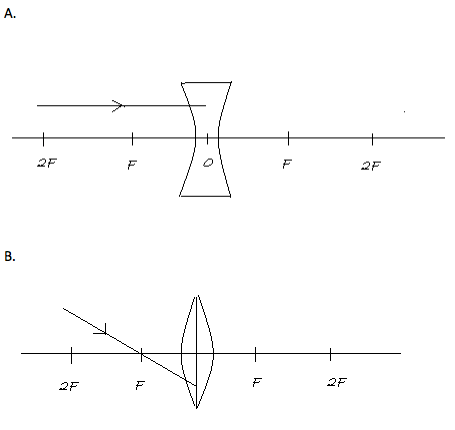
Redraw the diagram given below and complete the path or ray.

Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint:When the parallel rays of light pass through a concave lens to the principal axis, it deviates from its focal length. Also, when a ray passes through a focal point through a convex lens it goes parallel to the principal axis.
Step by step solution:
For part A: The given lens in figure A is concave. A concave lens is a diverging lens meaning that it spreads out light rays that have been refracted through it. A concave lens is thinner at its center than at its edges.
In the given figure A, the incident ray is coming from the infinity, that is the object is at infinity. The rays diverge from the focal center and an imaginary line is passed through the focal center as shown below:
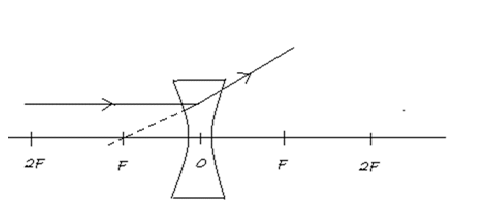
When an object is placed at infinity, a virtual image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
For part B: The given lens in figure B is convex. The convex lens is a lens that converges rays of light that convey to its principal axis which is relatively thick across the middle and thin at the lower and upper edges.
In figure B the incident ray is passing through the first focus (F). Whenever a ray is passing through the focus it will go parallel to the principal axis as shown below:
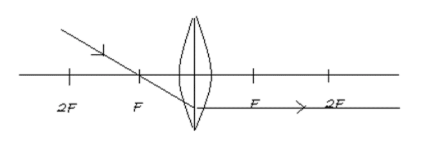
The image of the object will be formed at infinity in this condition.
Note:The action of the convex lens is to collect the light rays at one point. On the other hand, rays falling on the concave lens, after refraction at both surfaces of the lens, become more separated. Thus a concave lens produces spreading in the light rays.
Step by step solution:
For part A: The given lens in figure A is concave. A concave lens is a diverging lens meaning that it spreads out light rays that have been refracted through it. A concave lens is thinner at its center than at its edges.
In the given figure A, the incident ray is coming from the infinity, that is the object is at infinity. The rays diverge from the focal center and an imaginary line is passed through the focal center as shown below:

When an object is placed at infinity, a virtual image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object.
For part B: The given lens in figure B is convex. The convex lens is a lens that converges rays of light that convey to its principal axis which is relatively thick across the middle and thin at the lower and upper edges.
In figure B the incident ray is passing through the first focus (F). Whenever a ray is passing through the focus it will go parallel to the principal axis as shown below:

The image of the object will be formed at infinity in this condition.
Note:The action of the convex lens is to collect the light rays at one point. On the other hand, rays falling on the concave lens, after refraction at both surfaces of the lens, become more separated. Thus a concave lens produces spreading in the light rays.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




