
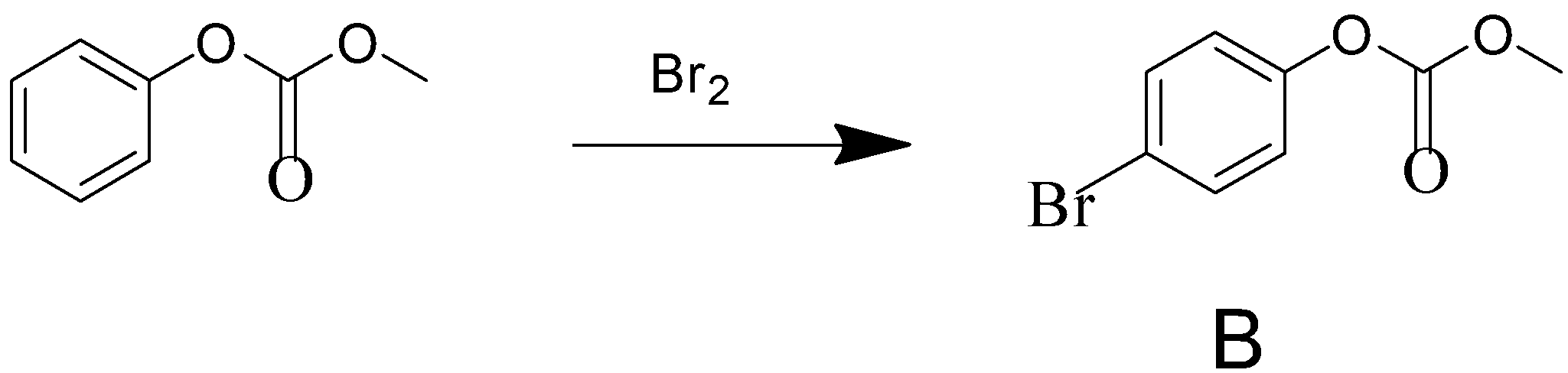
Phenol reacts with methyl chloroformate in the presence of $NaOH$ to form product A. A reacts with $B{r_2}$ to form product B. A and B are respectively:
A.
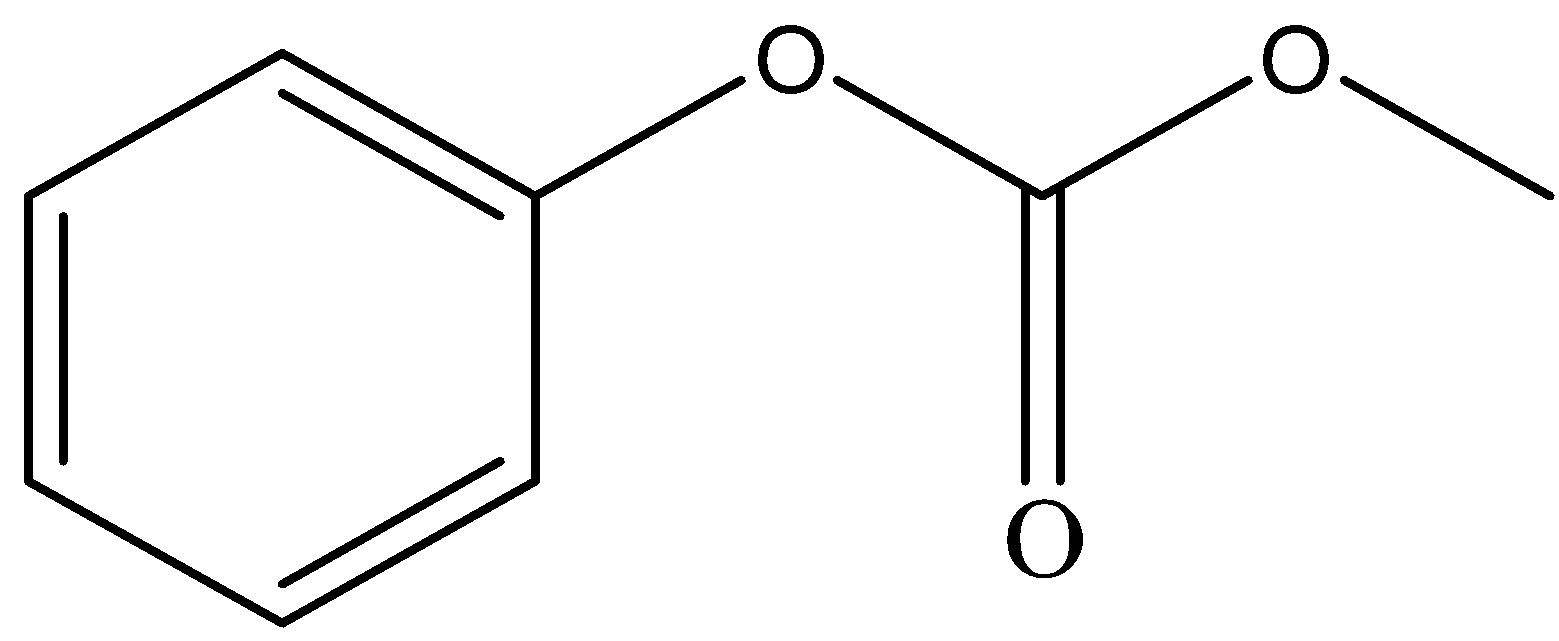 and
and
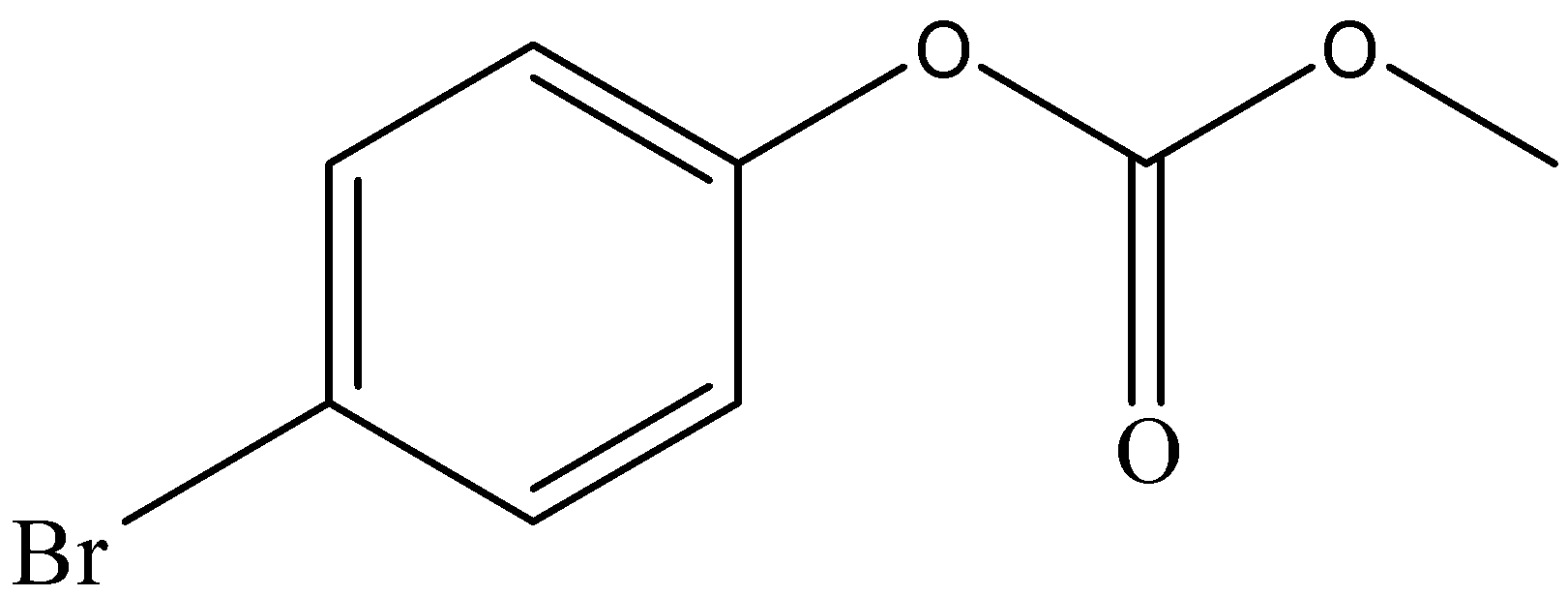
B.
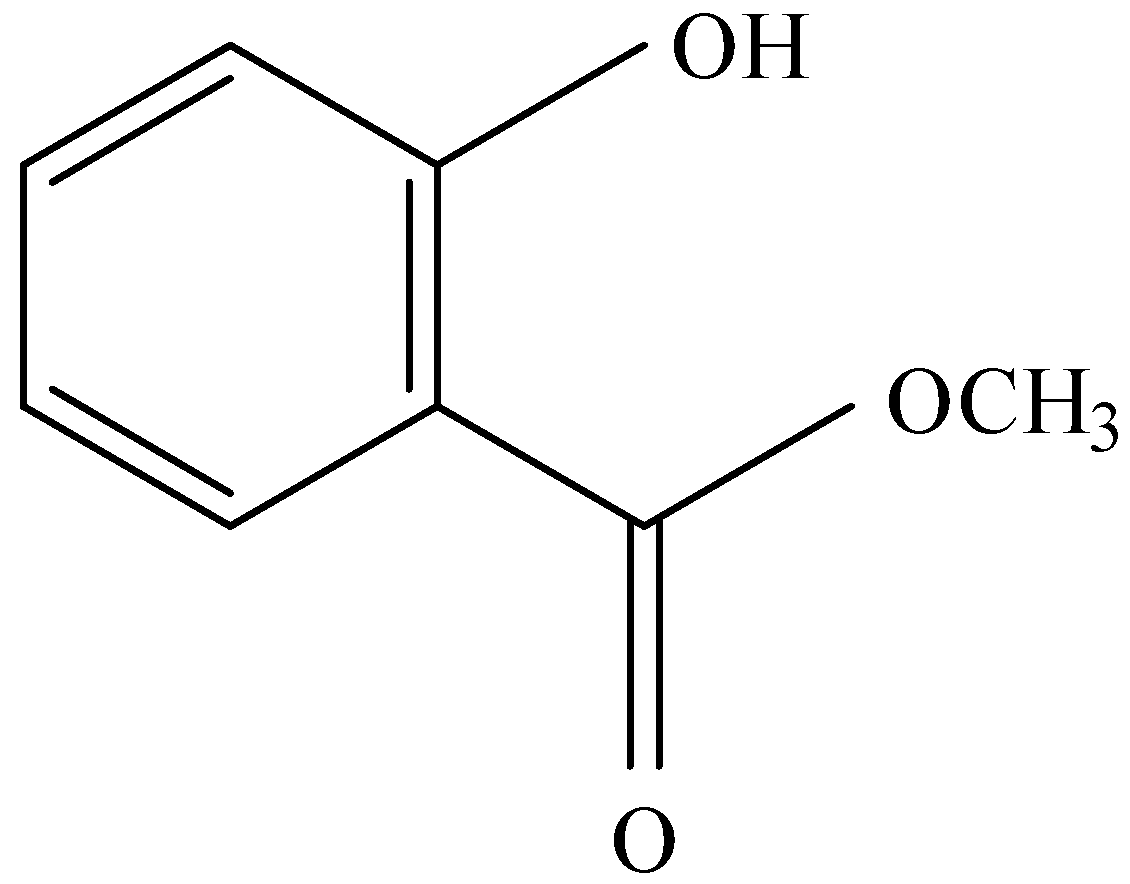 and
and
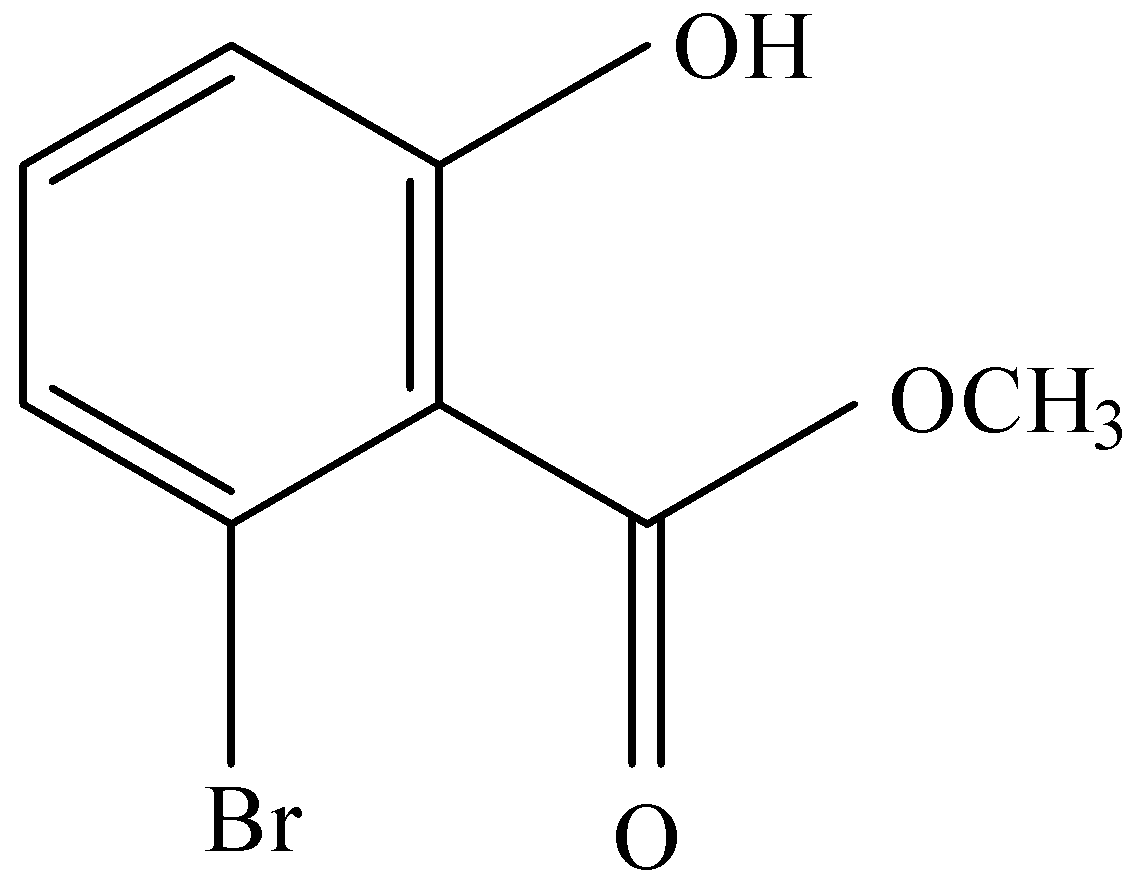
C.
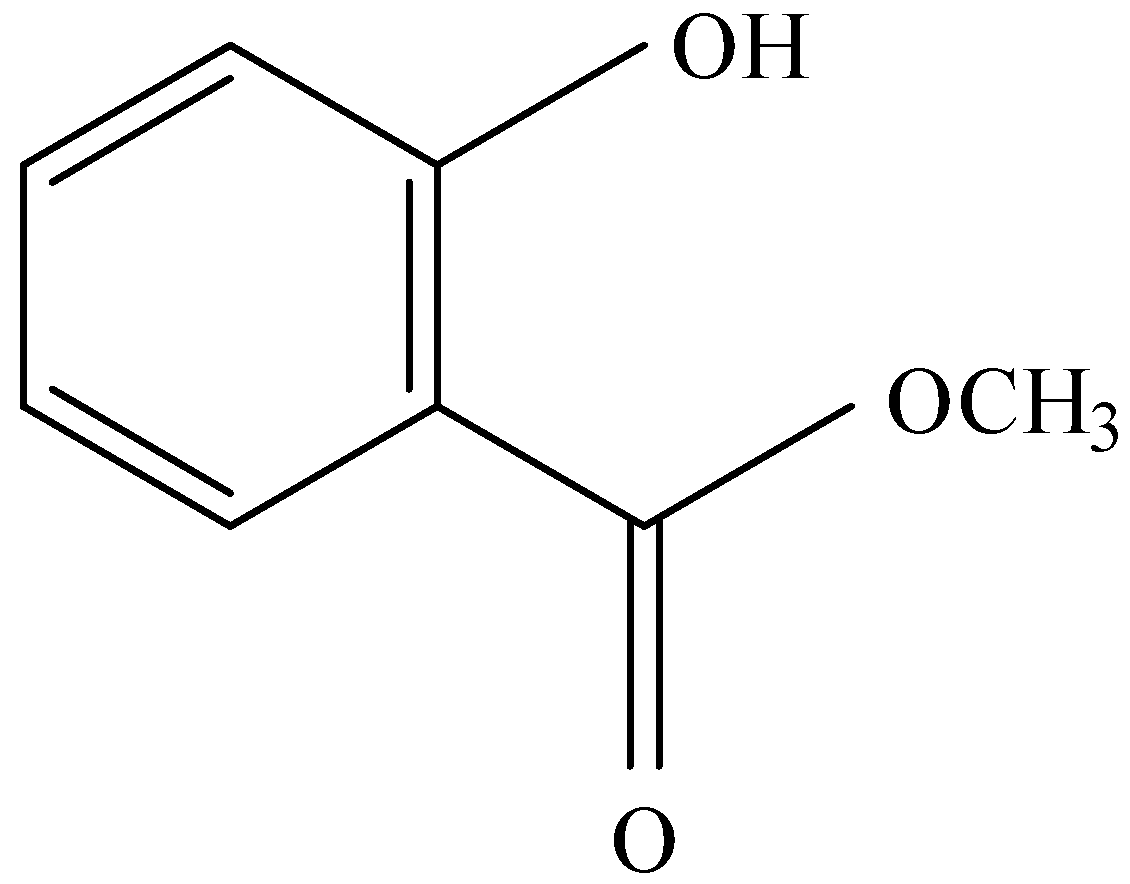 and
and
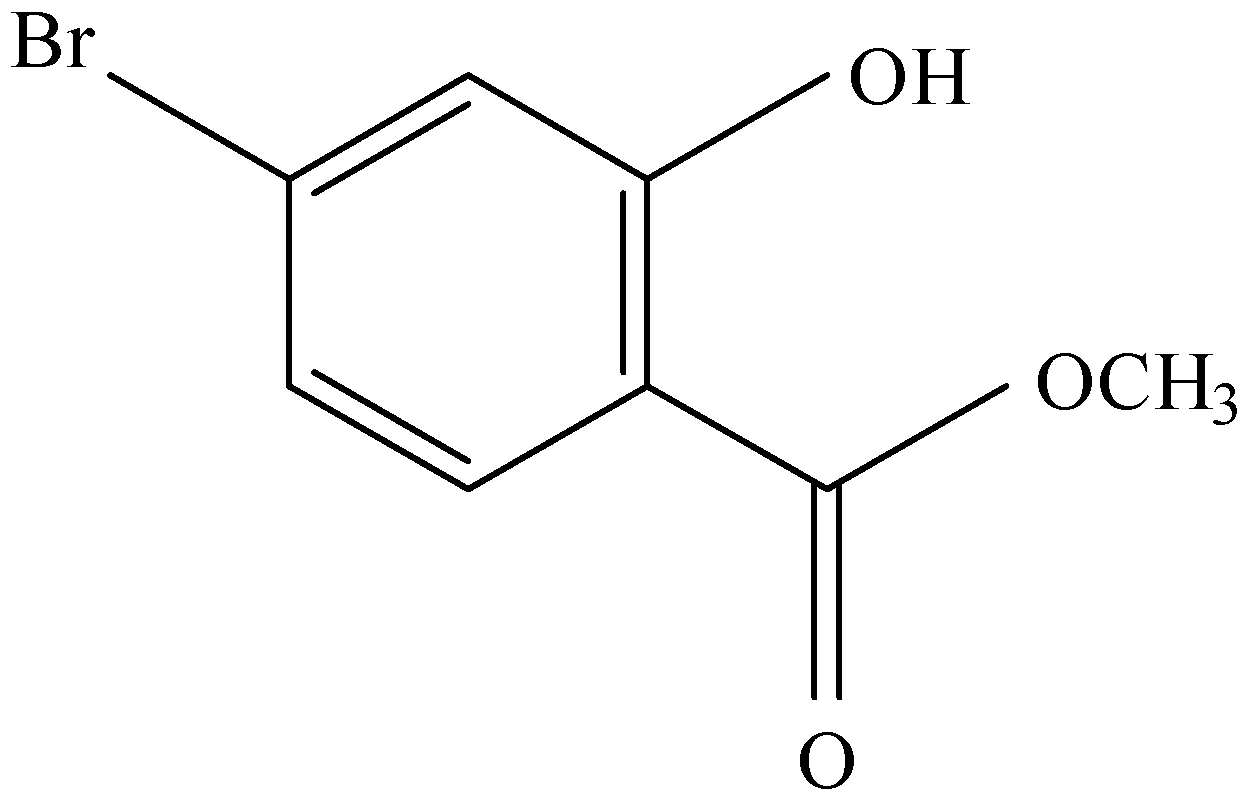
D.
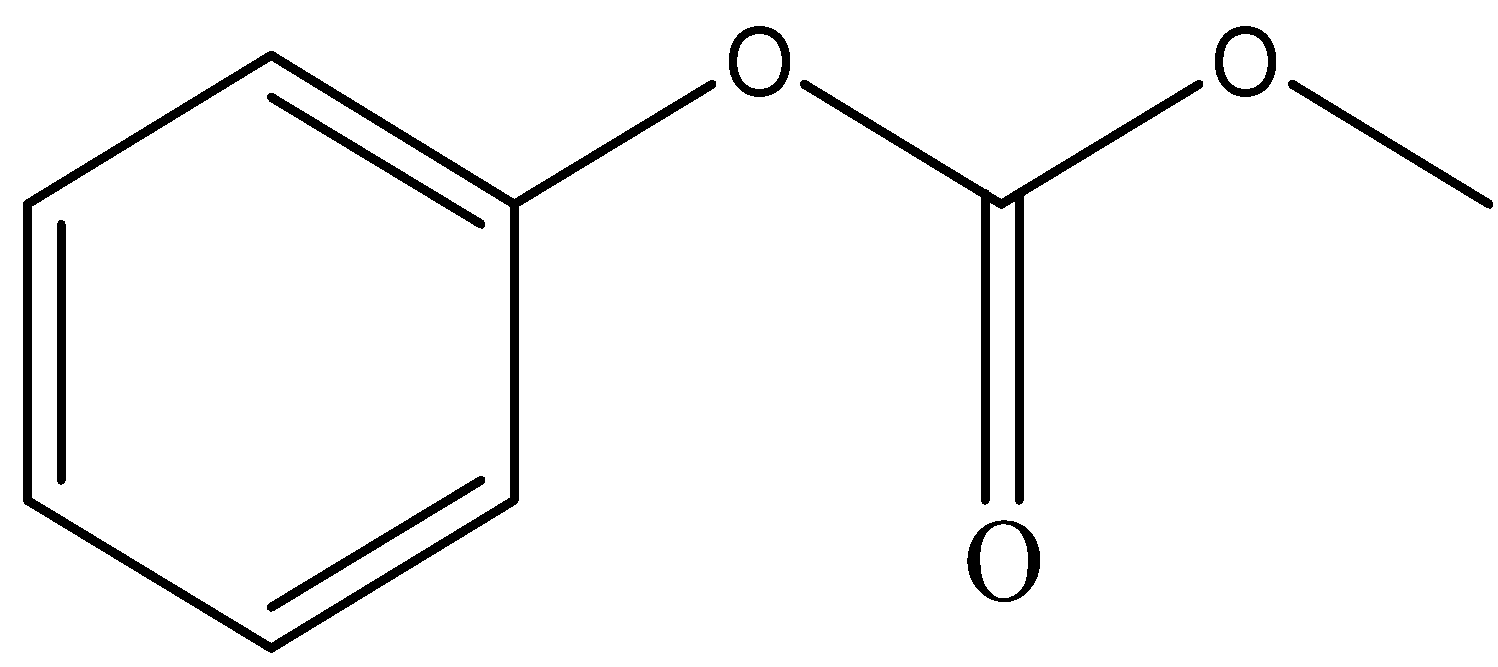 and
and
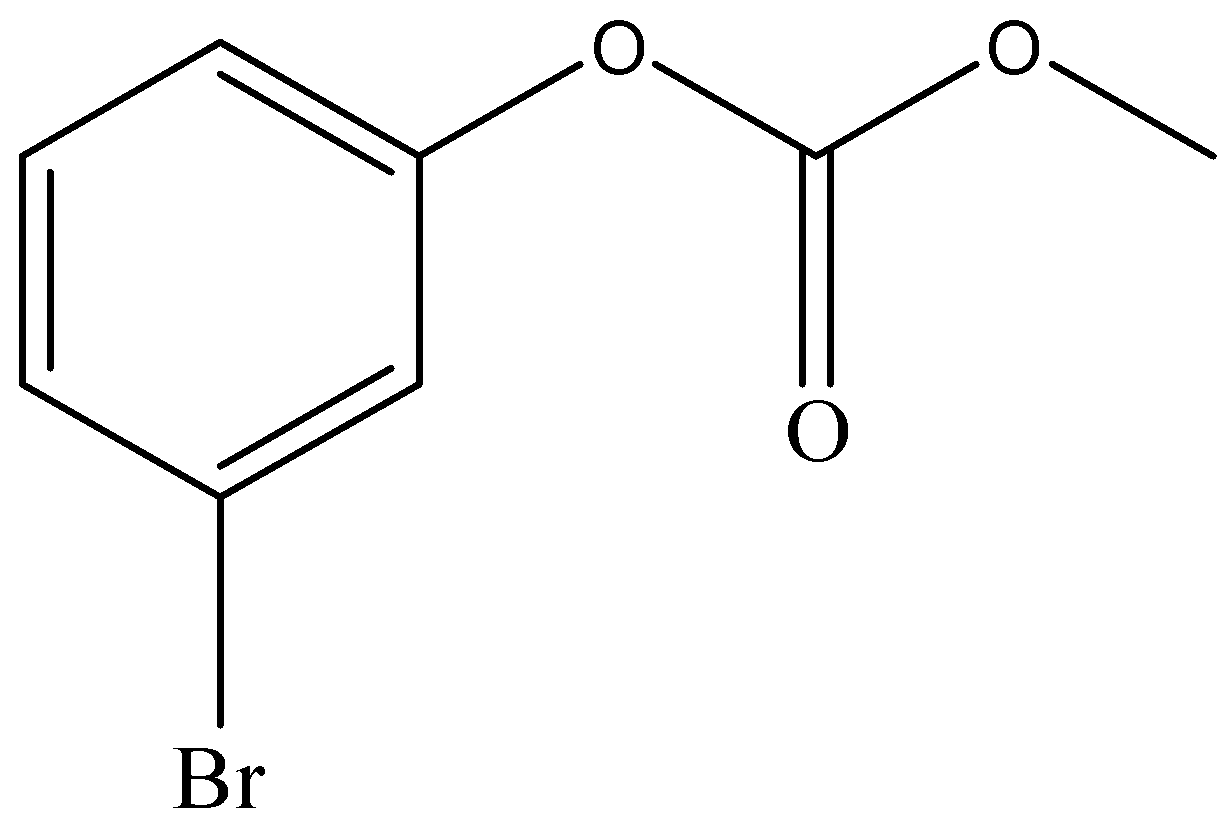








Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: Here, in this reaction it is given that phenol reacts with methyl chloroformate which is a methyl ester of chloroformic acid in the presence of a strong base $NaOH$ and it produces a product named A. The product A then reacts with $B{r_2}$ to produce product B.
Complete step by step solution:
Sodium hydroxide, being a strong base, abstracts the proton from phenol to form phenoxide ion. Phenoxide ion, which is an electron rich species attacks the carbonyl carbon of methyl chloroformate which is an electron deficient carbon. This led to the removal of $C{l^ - }$ ion from methyl chloroformate. This leads to the formation of compound A.
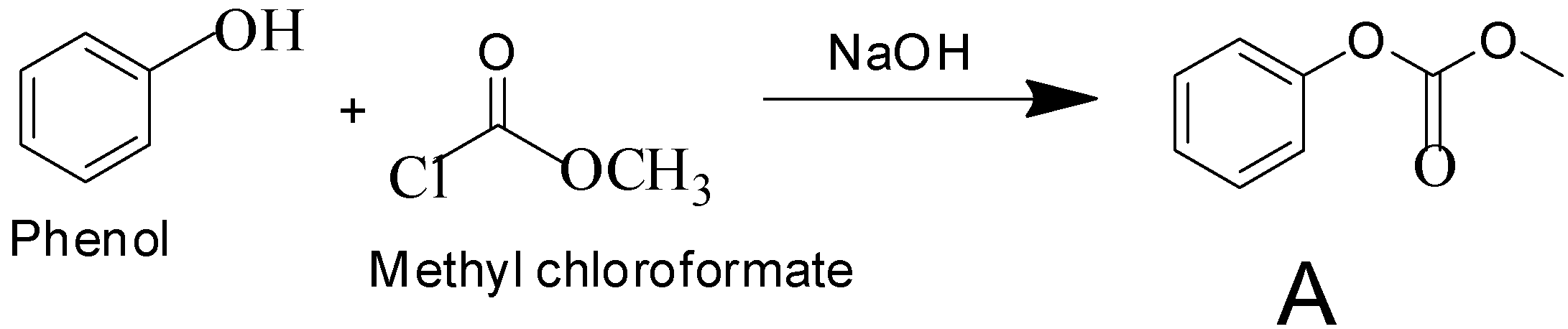
After the formation of compound A, it reacts with $B{r_2}$ to form compound B. The functional group of compound A, which is a para-directing group, pushes the electron density to para position. This leads the compound to attack $B{r_2}$ through its para position to form compound B.
Hence, the option (a) is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
Methyl chloroformate is a common reagent used in organic synthesis whenever there is a need to introduce a methoxycarbonyl functional group to attack a nucleophile in a chemical reaction (called carboxymethylation). Methyl chloroformate is also generally used for the derivatization of functional groups such as carboxylic acids, , phenols and amines.
Methyl chloroformate is synthesised using methanol and phosgene.
$COC{l_2} + MeOH \to ClCOOC{H_3} + HCl$
Note:
It is very important to note the nature of each of the compounds involved in the reaction. One should keep in mind that, in a chemical reaction, whenever there is possibility of an acid-base reaction to take place, we must make sure that it happens at first.
Complete step by step solution:
Sodium hydroxide, being a strong base, abstracts the proton from phenol to form phenoxide ion. Phenoxide ion, which is an electron rich species attacks the carbonyl carbon of methyl chloroformate which is an electron deficient carbon. This led to the removal of $C{l^ - }$ ion from methyl chloroformate. This leads to the formation of compound A.

After the formation of compound A, it reacts with $B{r_2}$ to form compound B. The functional group of compound A, which is a para-directing group, pushes the electron density to para position. This leads the compound to attack $B{r_2}$ through its para position to form compound B.

Hence, the option (a) is the correct answer.
Additional Information:
Methyl chloroformate is a common reagent used in organic synthesis whenever there is a need to introduce a methoxycarbonyl functional group to attack a nucleophile in a chemical reaction (called carboxymethylation). Methyl chloroformate is also generally used for the derivatization of functional groups such as carboxylic acids, , phenols and amines.
Methyl chloroformate is synthesised using methanol and phosgene.
$COC{l_2} + MeOH \to ClCOOC{H_3} + HCl$
Note:
It is very important to note the nature of each of the compounds involved in the reaction. One should keep in mind that, in a chemical reaction, whenever there is possibility of an acid-base reaction to take place, we must make sure that it happens at first.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




